Zustpen Injection
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
Biapenem for Injection 300 mg
2.0 Quantitative and qualitative composition
Each vial contains :
Biapenem IP 300 mg
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Injection (Powder for solution) 300 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections (cUTI)
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The recommended dose for adults is 0.6 g/day, administered in two separate intravenous injections at interval of 12 hours each time over approximately 30 - 60 minutes. Dosage can be adjusted according to the age and symptom of individual patient, but should not exceed 1.2 g/day.
Instructions for intravenous administration
Reconstitute the appropriate number of Biapenem for Injection vials to achieve the desired dose. Reconstitute each vial with 20 mL sterile water for injection. Vigorously shake or roll the vial until all solids are dissolved. The resulting solution will contain Biapenem 15 mg/mL. The solution should be clear. Parenteral drug product should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, discard if the reconstituted solution contains any foreign visible particles.
Withdraw the required amount of Biapenem for Injection solution to deliver the desired dose and inject immediately into 100 mL infusion bag of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection
Solution stability
Biapenem for Injection reconstituted for Intravenous administration may be stored for up to 24 hours at 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F) 6 hours at room temperature in infusion bag.
4.3 Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to the active substance (Biapenem).
• Patients who are concurrently taking sodium valproate.
4.4 Warning & precautions
• Use with caution for patients who are allergic to carbopenems, penicillins and cephalosporins.
• Used with caution for patients who or whose direct relatives are susceptible to induced hypersensitivities including bronchial asthma, rash, urticaria etc.
• Not recommended for patients with severe renal inadequacy;
• Use with caution for senile patients (see Use in the elderly section)
• When this product is used by the patients with eating difficulty and body deteriorating, symptoms of Vitamin k Deficiency may occur;
• Use with caution for patients with history of epilepsy and illness of central nervous system;
• False positive findings may occur during clinical Urine Glucose Test, Benedict's test and Fehling's test;
• Positive findings may occur in Kveim test. Effects on Laboratory Tests: Caution is required in the following: False-positive results may occur in urine glucose tests with Benedict's solution, Fehling's solution and Clinitest, but not with Tes-Tape. Positive results may occur in the direct Coombs' test.
4.5 Drug interactions
A clinically significant reduction in serum valproic acid concentration has been reported in patients receiving carbapenem antibiotics and may result in loss of seizure control. Patients concurrently taking valproic acid concentrations should be monitored frequently after initiating carbapenem therapy. Alternative antibacterial or anticonvulsant therapy should be considered if serum valproic acid concentrations drop below the therapeutic range or a seizure occurs.
4.6 Special populations (such as pregnant women, lactating women, paediatric patients, geriatric patients etc.)
Use in pregnancy and lactation
Biapenem injection should be used in pregnant women or women who may possibly be pregnant only if the expected therapeutic benefits outweigh the possible risks associated with treatment. The safety of Biapenem injection in pregnant women has not been established. It is advisable to avoid using Biapenem injection in lactating mothers. If use of Biapenem injection is judged to be essential, breastfeeding must be discontinued during treatment. It has been reported that Biapenem injection is excreted in breast milk in animal studies (rats).
Use in children
The safety of Biapenem injection in low birth weight infants, newborns, suckling infants, infants and children has not been established.
Use in the elderly
Special attention should be paid to the following points when Biapenem injection is used in elderly patients. Biapenem injection should be used with care and the dose and dosing interval must be adjusted based on careful clinical observation of the patient's condition. Adverse reactions are likely to occur in elderly patients since they often have reduced physiological function. In elderly patients, use of Biapenem injection may be associated with the development of a bleeding tendency due to vitamin K deficiency.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Biapenem injection has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
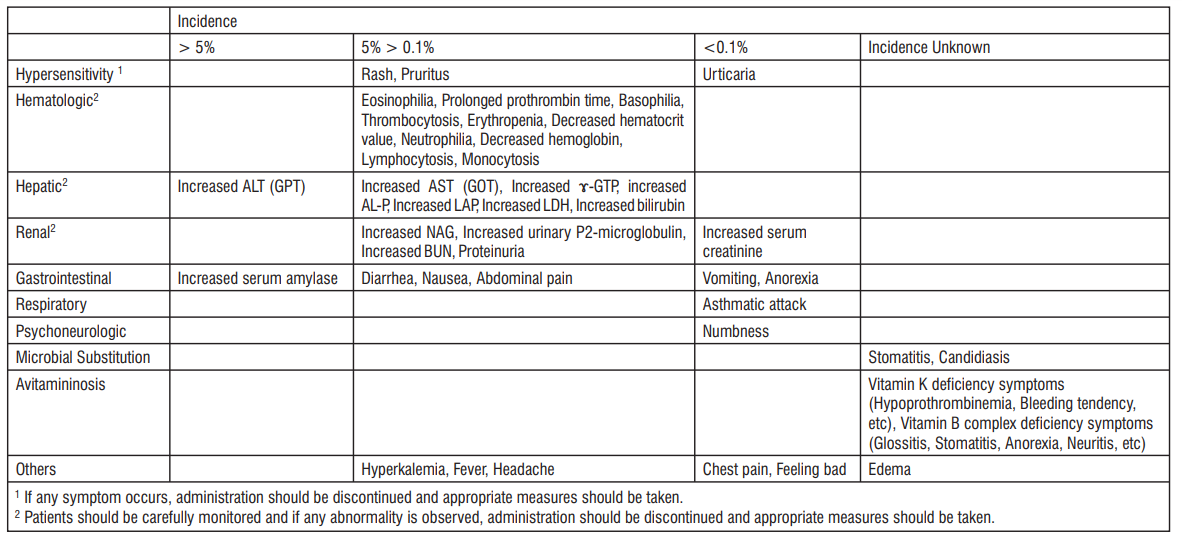
4.8 Undesirable effects
Adverse reactions were observed in 64 (2.7%) of 2348 cases evaluated in the clinical study. The main adverse reactions were rash (1%) and diarrhea (including loose stool) (0.7%). In a total of 2287 cases, 522 events of abnormal changes in laboratory test values were observed in 304 cases (13.3%), including increased ALT (GPT) in 144 cases, increased AST (GOT) in 93 cases and eosinophilia in 77 cases (based on the number of patients summed up at the time of the latest approval of indications). Clinically significant adverse reactions : Shock (<1%) or anaphylactoid reactions (incidence unknown) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored and if any abnormalities eg, feeling unwell, oral cavity discomfort, stridor, vertigo, defecation desire, tinnitus or diaphoresis are observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Interstitial pneumonia (0.1 to <5%) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored and if any abnormalities eg, fever, cough, exertional breathlessness and dyspnea are observed, a chest X-ray should be obtained immediately. When interstitial pneumonia is suspected, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures eg, administration of adrenocortical hormones should be taken.
Serious colitis with diarrhoea or bloody stool e.g., pseudomembranous colitis (incidence unknown) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored and if any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued immediately and appropriate measures should be taken. Central nervous system disorder eg, convulsion or disturbed consciousness (incidence unknown) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored and if such symptoms occur, administration should be discontinued immediately and appropriate measures should be taken. Since convulsion or disturbed consciousness is more likely to occur in patients with renal disorder or central nervous system disorder, special attention should be given when Biapenem injection is administered to such patients. Hepatic function disorder with markedly increased AST (GOT), ALT (GPT), γ-GTP or AL-P or jaundice (incidence unknown) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored, and periodic laboratory tests should be performed. If any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Serious renal disorder eg, acute renal failure (incidence unknown) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored, and periodic laboratory tests should be performed. If any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, leucopenia or thrombocytopenia (incidence unknown) may occur. Patients should be carefully monitored, and periodic blood tests should be performed. If any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Clinically significant adverse reactions (similar drugs) : Muco-cutaneo-ocular syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome) may occur when other carbapenem antibiotics are used. Patients should be carefully monitored, and if any abnormalities e.g., fever, erythema, itching, ocular hyperemia or stomatitis are observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken.
Hemolytic anemia may occur when other carbapenem antibiotics are used. Patients should be carefully monitored, and periodic blood tests should be performed. If any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Thrombophlebitis may occur when other carbapenem antibiotics are used. Patients should be carefully monitored, and if any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia (PIE) syndrome may occur when other carbapenem antibiotics are used. Patients should be carefully monitored, and if any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Fulminant hepatitis may occur when other carbapenem antibiotics are used. Patients should be carefully monitored, and if any abnormality is observed, administration should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken. Other adverse reactions : When the following adverse reactions occur, appropriate measures should be taken to treat the symptoms.
Geno-toxicity
No relevant data are found regarding geno-toxicity.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptom of an overdose is not known. If an overdose happens, seek routine monitoring symptomatic treatment
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Biapenem inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis (by blocking the murein crosslink formation). In particular, Biapenem exhibits high affinity for penicillin-binding protein (PBP) 1 and 4 in MSSA and PBP 2 and 4 in E. coli and P. aeruginosa.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Antibacterial Activity (In vitro) : Biapenem has a broad antibacterial spectrum against aerobic gram-positive/gram-negative bacteria and anaerobic bacteria, and shows strong antibacterial activity. It also shows strong antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa resistant to Imepenem, meropenem, ceftazidime, ofloxacin and gentamicin. Biapenem exerts bactericidal activity and its bactericidal activity against P. aeruginosa and B. fragilis is equivalent to or better than that of imipenem in particular. In addition, biapenem is more stable than meropenem against human renal dehydropeptidase-I (DHP-I). Therapeutic Effect on Experimental Infection in Mice : The therapeutic efficacy of biapenem against intraperitoneal infection caused by various bacteria, mixed intraperitoneal infection caused by E. coli and P. aeruginosa, P. aeruginosa infection in leucopenic mice, respiratory infections caused by K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa and penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae and urinary tract infections (UTI) caused by E. coli and P. aeruginosa in mice was equivalent to or better than that of Imepenem.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
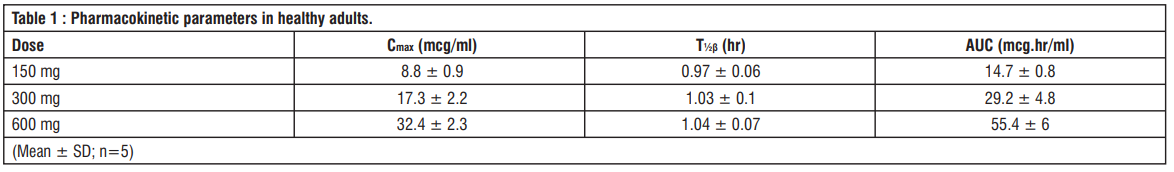
Plasma concentration
The plasma concentrations in healthy adults (n=5) after a single administration of 150 mg, 300 mg and 600 mg of Biapenem by IV drip infusion over 60 min and a dose dependency was observed. When Biapenem was administered by repeated IV drip infusion, the pharmacokinetics were almost similar to those obtained after a single IV drip infusion and no accumulation of Biapenem was observed.
Body fluid and tissue distribution
When Biapenem 300 mg was administered once by IV drip infusion over 30 or 60 min, the maximum concentration in the dead space fluid in the pelvis was 9.6 mcg/mL. The concentrations in the sputum within 6 hrs after administration ranged from 0.1 - 2.5 mcg/mL.
Metabolism
No metabolites were detected in the plasma following a single IV drip infusion of Biapenem 150, 300 and 600 mg or repeated IV drip infusion of 300 and 600 mg in healthy adults (n=5). When Biapenem was administered once by IV drip infusion or administered by repeated IV drip infusion, 9.7 - 23.4% of its total metabolites were excreted in the urine. These metabolites showed no antibacterial activity.
Excretion
When Biapenem 150, 300 and 600 mg were administered once by IV drip infusion over 60 min to healthy adults (n=5), the average urinary concentrations of Biapenem were, 325.5, 584.8 and 1105.1 mcg/mL, respectively at 0 - 2 hrs after administration, and 2.4, 4.7 and 21.4 mcg/mL, respectively at 8 - 12 hrs after administration. The cumulative urinary excretion rates were 62.1%, 63.4% and 64%, respectively at 0 - 12 hrs after administration
Plasma Concentrations in Patients with Renal Function Impairment
When Biapenem 300 mg was administered once by IV drip infusion over 60 min to patients with renal function impairment (n=3), Biapenem disappearance from the plasma was confirmed to be delayed as renal function decreased. When Biapenem was administered twice daily for 7 days, (14 times in total) by repeated IV drip infusion over 30 min to patients with moderate renal function impairment with a creatinine clearance (CrCl) of about 50 mL/min, no accumulation of Biapenem was observed in the plasma or urine. Biapenem disappearance from the plasma was confirmed to be delayed when hemodialysis was not performed, following administration of Biapenem 300 mg by IV drip infusion over 60 min to patients with renal function impairment requiring hemodialysis (n=5).
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Pharmacology
As a carbapenem antibiotics, the bactericidal activity of Biapenem results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Biapenem has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, and display inhibiton against gram-positive gram-negative and aerobic bacteria. Biapenem is stable to DHP-I, which can be administrated without co-administration of DHP-Iinhibitor.
Toxicity
Multiple-dose toxicology
After intravenous injection of Biapenem in rats and canine for continuous 3 months, major toxic reaction is abnormal feces, watery stool, mucous stool, etc. After intraveneously administered with Biapenem 600 mg/kg/d in rat, mild cloudy swelling was observed on the renal tubular epithelial cell; the spleen and the cecum swell, and no pathological alteration occurs
Genotoxicity
Biapenem was not mutagenic in bacterial reverse mutation assay, mammalian mutation assays in mouse lymphoma, chromosomal aberration assays in hamster ovary cell, and the Mouse micronuclear test.
Reproductive toxicity
Reproductive studies have been performed with Biapenem in rats at doses of up to 300 mg/kg/day pre-pregnancy and early pregnancy i.v, toxic reaction like reduction of food intake and body weight loss occurs while fertility is not affected. Intraveneous injection of 300 mg/kg/d Biapenem at pregnant rat organ formation stage result in weight loss of F1 generation fetal rats, but shows no lethal effect and teratogenic effect on fetal rats. In perinatal toxicity test, delayed vagina open was observed in F1 generation female rats of 100mg/kg/d and over dose group at 6 weeks age testing; but abnormal change of reproductive function was not observed at 10 weeks age. Biapenem has no obvious influence on F2 generation fetal and newborn rats.
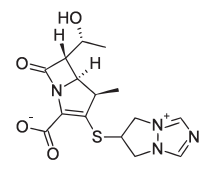
7.0 Description
Biapenem is white to yellowish crystalline powder. Biapenem is a carbapenem β-lactam antibiotic. Like other carbapenems, Biapenem binds penicillin-binding proteins to inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Biapenem exhibits broad spectrum antibacterial activity and is clinically used to treat respiratory and urinary tract infections. Biapenem displays activity against several species of bacteria, including Bacteriodes, Prevotella, Clostridium, and Pseudomonas. In animal models of pneumonia, Biapenem decreases bacteria numbers and increases survival rates.
Chemical formula : C15H18N4O4S
Molecular weight : 350.393 g/mol
ATC code : J01DH05
IUPAC name : (4R,5S,6S)-3-(6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrazolo[1,2-a][1,2,4]triazol-4-ium-6-ylsulfanyl)-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylate. Biapenem has the following structural formula :
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
8.2 Shelf life
Please see manufacturing date and expiry date printed on pack. Do not use the product after the expiry date which is stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
8.3 Packaging information
Supplied in a 30 ml USP Type-I transparent glass vial packed in a carton along with pack insert.
8.4 Storage and handing Instructions Store below 30°C. Protect from direct light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Caution should be exercised when Biapenem for Injection is administered to
• Patients allergic to carbapenems, penicillins and cephalosporin antibiotics
• Patients himself or herself and their relatives with allergic constitution to bronchial asthma, erythra, urticarial
• Patients with serious renal insufficiency
• Elderly patients (refer to elderly medication)
• Patients with eating difficulties or systemic deterioration, and may be with Vitamin K deficiency symptoms, which should be monitored closely.
• Patients with a history of seizure or central nervous system disease.
• Test paper reaction and GLU test by Benedict's reagent or Fehling's solution may produce false positive results; Kevin test may produce positive results.