Floresp - OX Nasal Spray
1.0 Generic name
Fluticasone Furoate & Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Spray
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each spray delivers :
Fluticasone Furoate 27.5 mcg
Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride IP 50 mcg
Composition :
Fluticasone Furoate 0.028% w/w
Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride IP 0.050% w/w
Benzalkonium Chloride Solution IP 0.030% w/w
3.0 Dosage form & strength
Nasal Spray, Fluticasone Furoate 27.5 mcg & Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride 50 mcg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of symptoms of allergic rhinitis with nasal congestion.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The recommended dose is two spray actuations (27.5 micrograms of. Fluticasone Furoate and 50 mcg of Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride per spray actuation) in each nostril once daily (total daily dose, 110 micrograms of Fluticasone Furoate and 200 mcg of Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride). Once adequate control of symptoms is achieved, dose reduction to one spray actuation in each nostril (total daily dose 55 micrograms of Fluticasone Furoate and 100 mcg of Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride) may be effective for maintenance.
Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Spray is for administration by the intranasal route only.
The intranasal device should be shaken before use. The device is primed by pressing the mist release button for at least six spray actuations (until a fine mist is seen), whilst holding the device upright. Re-priming (approximately 6 sprays until a fine mist is seen) is only necessary if the cap is left off for 5 days or the intranasal device has not been used for 30 days or more.
Children < 12 years of age
Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Spray should not be used in children less than 12 years of age.
Elderly (≥ 65 years old)
No dose adjustment is required in this population.
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is required in this population.
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is required in this population.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to Fluticasone Furoate, Oxymetazoline or any other ingredients of this medicine.
- Age less than 12 years.
- In patients who have undergone recent trans-nasal surgery.
- In patients with chronic nasal inammation with very dry nasal passages (rhinitis sicca or atrophic rhinitis).
- In patients with cardiovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, angle closure glaucoma or prostatic enlargement.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Keep the spray away from the eyes.
Systemic corticosteroid effects
Systemic effects of nasal corticosteroid may occur, particularly at high doses prescribed for prolonged periods. These effects are much less likely tooccur than with oral corticosteroids and may vary in individual patients and between different corticosteroid preparations. Potential systemic effects may include Cushing's syndrome, Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, cataract, glaucoma and more rarely, a range of psychological or behavioural effects including psychomotor hyperactivity, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression or aggression (particularly in children). Treatment with higher than recommended doses of nasal corticosteroids may result in clinically significant adrenal suppression. If there is evidence for higher than recommended doses being used, then additional systemic corticosteroid cover should be considered during periods of stress or elective surgery. Fluticasone furoate 110 micrograms once daily has not been associated with hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression in adult or adolescent subjects. However, the dose of intranasal fluticasone furoate should be reduced to the lowest dose at which effective control of the symptoms of rhinitis is maintained. As with all intranasal corticosteroids, the total systemic burden of corticosteroids should be considered whenever other forms of corticosteroid treatment are prescribed concurrently. If there is any reason to believe that adrenal function is impaired, care must be taken when transferring patients from systemic steroid treatment to fluticasone furoate.
Visual disturbance
Visual disturbance may be reported with systemic and topical corticosteroid use. If a patient present with symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, the patient should be considered for referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation of possible causes which may include cataract, glaucoma or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR) which have been reported after use of systemic and topical corticosteroids.
Growth retardation
Growth retardation has been reported in children receiving nasal corticosteroids at licensed doses. A reduction in growth velocity has been observed in children treated with fluticasone furoate 110 micrograms daily for one year. Therefore, children should be maintained on the lowest possible efficacious dose which delivers adequate symptom control. It is recommended that the growth of children receiving prolonged treatment with nasal corticosteroids is regularly monitored. If growth is slowed, therapy should be reviewed with the aim of reducing the dose of nasal corticosteroid if possible, to the lowest dose at which effective control of symptoms is maintained.
Patients on ritonavir
Concomitant administration with ritonavir is not recommended because of the risk of increased systemic exposure of fluticasone Furoate.
4.5 Drug interactions
Interaction with CYP3A inhibitors
Fluticasone furoate is rapidly cleared by extensive first-pass metabolism mediated by the cytochrome P450 3A4.
Based on data with another glucocorticoid (fluticasone propionate), that is metabolised by CYP3A4, coadministration with ritonavir is not recommended because of the risk of increased systemic exposure of fluticasone furoate. Caution is recommended when co-administering fluticasone furoate with potent CYP3A inhibitors including cobicistat containing products as an increase in the risk of systemic side effects is expected. Co-administration should be avoided unless the benefit outweighs the increased risk of systemic corticosteroid side effects, in which case patients should be monitored for systemic corticosteroid side effects. In a drug interaction study of intranasal fluticasone furoate with the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole there were more subjects with measurable fluticasone furoate concentrations in the ketoconazole group (6 of the 20 subjects) compared to placebo (1 out of 20 subjects). This small increase in exposure did not result in a statistically significant difference in 24-hour serum cortisol levels between the two groups.
The enzyme induction and inhibition data suggest that there is no theoretical basis for anticipating metabolic interactions between fluticasone furoate and the cytochrome P450 mediated metabolism of other compounds at clinically relevant intranasal doses. Therefore, no clinical studies have been conducted to investigate interactions of fluticasone furoate on other drugs Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), nonselective beta adrenergic antagonists, or tricyclic antidepressants.
Use of Oxymetazoline containing nasal spray in combination with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), nonselective beta adrenergic antagonists, or tricyclic antidepressants may cause hypertension and is not recommended.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate data from the use of fluticasone furoate and Oxymetazoline containing nasal sprays in pregnant women. In animal studies glucocorticoids have been shown to induce malformations including cleft palate and intra-uterine growth retardation. This is not likely to be relevant for humans given recommended nasal doses which results in minimal systemic exposure.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether nasal administered fluticasone furoate or Oxymetazoline is excreted in human breast milk. Administration of Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Spray to women who are breast-feeding should only be considered if the expected benet to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the child.
Fertility
There are no fertility data in humans.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Spray has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The most common AEs reported with the use of Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline containing Nasal Spray are epistaxis, nasal ulceration, nasal dryness & discomfort, sneezing and headache. The other AEs include : rhinalgia, transient ocular changes, vision blurred, nasal septum perforation, dry mouth, stomatitis, dry throat, local irritation, insomnia, sedation, anxiety, irritability, nausea, hypertension, irregular heart rate, increased heart rate, restlessness, somnolence, fatigue, hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria. Prolonged use may cause rebound congestion and rhinitis medicamentosa.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com Website : https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Overdosage may give rise to local irritation and rebound congestion. Treatment need only be symptomatic
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Fluticasone furoate is a synthetic tri-fluorinated corticosteroid that possesses a very high affinity for the glucocorticoid receptor and has a potent anti-inflammatory action.
Oxymetazoline is a direct-acting sympathomimetic amine. It acts on alpha-adrenergic receptors in the vessels of the nasal mucosa producing vasoconstriction and decongestion.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Fluticasone Furoate
Absorption: Fluticasone furoate undergoes incomplete absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver and gut resulting in negligible systemic exposure. The intranasal dosing of 110 micrograms once daily does not typically result in measurable plasma concentrations (<10 pgl ml). The absolute bioavailability for intranasal uticasone furoate is 0.50 %, such that less than 1 microgram of fluticasone furoate would be systemically available after administration of 110 micrograms
Distribution: The plasma protein binding of fluticasone furoate is greater than 99%. Fluticasone furoate is widely distributed with volume of distribution at steady-state of, on average, 608 L.
Biotransformation: Fluticasone furoate is rapidly cleared (total plasma clearance of 58.7 I/h) from systemic circulation principally by hepatic metabolism to an inactive 17p-carboxylic metabolite (GW694301X), by the cytOchrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. The principal route of metabolism was hydrolysis of the S-fluoromethyl carbothioate function to form the 1713- carboxylic acid metabolite. In vivo studies have revealed no evidence of cleavage of the furoate moiety to form fluticasone.
Elimination: Elimination is primarily via the faecal route following oral and intravenous administration indicative of excretion of fluticasone furoate and its metabolites via the bile. Following intravenous administration, the elimination phase half-life averaged 15.1 hours. Urinary excretion accounted for approximately 1 % and 2 % of the orally and intravenously administered dose, respectively.
Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride
Oxymetazoline enters tissues rapidly and local vasoconstriction is normally achieved within 5-10 minutes of intranasal administration. The full effect lasts for 5-6 hours and then gradually subsides over the next 6 hours. Plasma half-life is 5-8 days with 30% of any absorbed drug being excreted in the urine unchanged and 10% being excreted in the faeces
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or pharmacology
Fluticasone Furoate
Findings in general toxicology studies were similar to those observed with other glucocorticoids and are associated with exaggerated pharmacological activity. These findings are not likely to be relevant for humans given recommended nasal doses which results in minimal systemic exposure. No genotoxic effects of fluticasone furoate have been observed in conventional genotoxicity tests. Further, there were no treatment-related increases in the incidence of tumours in two-year inhalation studies in rats and mice.
Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride
There are no preclinical data of relevance
7.0 Description
Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Spray is white to off white suspension in a pre-filled intranasal sprayer. The pH of suspension is 5.0 ± 1.0 The product contains two active ingredients : Fluticasone Furoate and Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride.
The chemical name of fluticasone Furoate is (6a,1113,16a,17a)-6,9- diuoro-17-{[(uoro-methypthioicarbony1}-11-hydroxy-16-methyl-3- oxoandrosta-1,4-dien-17-y1 2-furancarboxylate. The molecular weight is 538.6.
The chemical formula of Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride is 3-[(4,5- dihydro1H-imidazol-2-yOmethyl]-6-(1,1 ,-dimethylethyl)-2,4- dimethylphenol mono-hydrochloride. Its molecular weight is 296.8 for the hydrochloride salt and 260.4 for the free base.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
FLORESP-OX sales pack contains 7 gm (70 metered doses).
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store in a dry & dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Keep the spray away from the eyes.
- Prolonged use of spray may lead to systemic corticosteroid effects. Consult your physician for duration of use of the product.
- Do not use the product in children less than 12 years of age
- Do not use the product if you have cardiovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, angle closure glaucoma or prostatic enlargement Do not use the product if you have undergone recent trans-nasal surgery, or in case of chronic nasal inflammation with very dry nasal passages (rhinitis sicca or atrophic rhinitis).
12.0 Date of issue
30 September 2024
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
What is in this leaflet
- What FLORESP OX is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use FLORESP OX
- How to use FLORESP OX
- Possible side effects
- How to store FLORESP OX
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What FLORESP OX is and what it is used for
FLORESP OX is a nasal spray that contains two active substances: Fluticasone Furoate: a corticosteroid that reduces inflammation. Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride: a decongestant that relieves nasal congestion.
It is used to treat symptoms of allergic rhinitis, such as
- Nasal congestion
- Sneezing
- Runny or itchy nose
2. What you need to know before you use FLORESP OX
Do not use FLORESP OX if you:
- Are allergic to Fluticasone Furoate, Oxymetazoline, or any other ingredients.
- Are under 12 years of age.
- Have had recent nasal surgery.
- Have very dry nasal passages (rhinitis sicca or atrophic rhinitis).
- Have heart disease, high blood pressure, thyroid problems, glaucoma, or prostate issues.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before using this spray if you:
- Are taking other corticosteroids.
- Have eye problems like blurred vision or glaucoma.
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Are taking ritonavir or other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Children
Do not use in children under 12 years. Long-term use may affect growth.
3. How to take Floresp OX Nasal Spray
For Adults and Teenagers (12 years and older):
- Start with 2 sprays in each nostril once a day (total of 110 micrograms).
- Once your symptoms are under control, you can reduce to 1 spray in each nostril once a day (total of 55 micrograms).
- Always use the lowest dose that works for you.
For Children (2 to 11 years old):
- Start with 1 spray in each nostril once a day (total of 55 micrograms).
- If symptoms don’t improve, your doctor may recommend 2 sprays in each nostril once a day (total of 110 micrograms).
- Once symptoms are better, go back to 1 spray in each nostril once a day.
For Elderly People:
- No special dose changes are needed.
For People with Kidney or Liver Problems:
- No dose changes are needed.
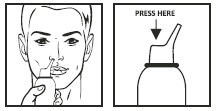
Method of administration:
- Remove the protective cap.
- Insert the nozzle into the nostril and press to spray.
- Allow excess solution to trickle down and clear your nose after 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Repeat if necessary.
- Wash the nozzle with soapy water, wipe dry, and replace the cap. • For infants and children, use under adult supervision.
Other Precautions
- Shake the bottle before using the medicine.
- Clean your nose thoroughly before using the medicine.
- Insert the bottle tip into one nostril and close the other nostril.
- Direct the spray towards the sides of your nostril, away from the cartilage dividing the two sides of your nose.
- Breathe out gently through your mouth and repeat the same process for the other nostril.
- Avoid deep breathing as it will cause medication to go back to the throat and make it less effective.
- Avoid deep breathing as it will cause the medication to go back to the throat and make it less effective.
- Do not share the bottle with anyone else so that you do not spread germs.
If you use more Floresp OX Nasal Spray than you should
Tell your doctor if you accidentally use more than you were told.
If you forget to use Floresp OX Nasal Spray
If you forget to take at the right time, use it as soon as you remember, then carry on as before. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using Floresp OX Nasal Spray
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor. If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Common side effects:
- Nosebleeds
- Nasal dryness or discomfort
- Sneezing
- Headache
Uncommon or rare side effects:
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth or throat
- Sleep problems, anxiety, or irritability
- Allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
- Rebound congestion with prolonged use
If you experience serious side effects, stop using the spray and seek medical help immediately.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page. Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Floresp OX Nasal Spray
- Store in a dry & dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
- Keep out of reach of children.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What FLORESP OX contains:
Fluticasone Furoate 27.5 mcg
Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride 50 mcg
Other ingredients: Benzalkonium Chloride, water, etc.
Pack size: 7 g (70 metered doses)
Revised on 06/25