ZU-C 500
1.0 Generic name
Vitamin C Chewable Tablets 500
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each uncoated chewable tablets contains:
Ascorbic Acid IP 50 mg
Sodium Ascorbate IP equivalent to Ascorbic Acid 400 mg '
Ascorbyl Palmitate IP 120 mg '
L- Lysine Hydrochloride USP 7.49 mg
'equivalent to L- Lysine 6 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset of Yellow FCF
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral, Chewable Tablets, 500 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the prevention and treatment of Vitamin C deficiency
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Method of administration
Vitamin C Chewable Tablets are to be chewed before swallowing.
Posology
- Adults and Children > 12 years: 1-2 tablets per day (equivalent to 500 or 1000 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Children 6-12 years: 1 tablet per day (equivalent to 500 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Vitamin C Chewable Tablets are not recommended for children under 6 years.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
- Ascorbic acid should not be given to patients with hyperoxaluria.
- Oxalate urolithiasis and iron storage diseases (thalassaemia, haemochromatosis, sideroblastic anaemia) or other medical conditions that predispose individuals to iron overload.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
a. Increased intake of ascorbic acid over a prolonged period may result in an increased renal clearance of ascorbic acid, and deficiency may result if the intake is reduced or withdrawn rapidly.
b. Exceeding the recommended dose should be avoided as there have been isolated reports of severe haemolysis in patients with erythrocytic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency when taking high doses (> 4000 mg/day) of ascorbic acid. Do not exceed the recommended dose.
c. Caution is required and use the minimum recommended dose in patients with renal impairment.
d. Patients with rare hereditary fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucraseisomaltase deficiency should not take ascorbic acid.
e. Interference with serological testing
- Ascorbic acid may interfere with tests and assays for urinary glucose, giving false-negative results with methods utilising glucose oxidase with indicator and false-positive results with neocuproine methods.
- Estimation of uric acid by phosphotungstate or uricase with copper reduction and measurement of creatinine in non-deproteinised serum may also be affected.
- High doses of ascorbic acid may give false-negative readings in faecal occult blood tests.
- Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
4.5 Drugs interactions
- Ascorbic acid increases the renal excretion of amphetamine.
- The plasma concentration of ascorbate is decreased by smoking and oral contraceptives.
- Ascorbic acid increases the absorption of iron. This should be borne in mind in the case of iron replacement.
- Concomitant administration of aspirin and ascorbic acid may interfere with absorption of ascorbic acid. Renal excretion of salicylate is not affected and does not lead to reduced anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin.
- Concomitant administration of aluminium-containing antacids may increase urinary aluminium elimination. Concurrent administration of antacids and ascorbic acid is not recommended, especially in patients with renal insufficiency.
- Co-administration with amygdalin (a complementary medicine) can cause cyanide toxicity.
- Concurrent administration of ascorbic acid with desferrioxamine enhances urinary iron excretion. Cases of cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure have been reported in patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis and thalassaemias receiving desferrioxamine who were subsequently given ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid should be used with caution in these patients and cardiac function monitored.
- Ascorbic acid may interfere with biochemical determinations of creatinine, uric acid and glucose in samples of blood and urine.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
For ascorbic acid no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available. Animal studies do not indicate direct or harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition or postnatal development. Pregnant women should exercise caution.
Breast-feeding
Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk. Though again caution should be exercised, no evidence exists suggesting such excretion is hazardous to the infant.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
On the basis of the product's pharmacodynamic profile and reported adverse events, ascorbic acid has no known effect on an individual's ability to drive or operate machinery.
4.8 Undesirable effects
- Nervous system disorders: headache.
- Vascular disorders: flushing.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting and stomach cramps. Large doses of ascorbic acid may cause diarrhoea.
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: redness of skin.
- Renal and urinary disorders: Patients known to be at risk of hyperoxaluria should not ingest ascorbic acid doses exceeding 1g daily as there may be increased urinary oxalate excretion. However, such risk has not been demonstrated in normal, non-hyper oxaluric individuals. Ascorbic acid has been implicated in precipitating haemolytic anaemia in certain individuals deficient of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Increased intake of ascorbic acid over a prolonged period may result in increased renal clearance of ascorbic acid, and deficiency may result if the intake is reduced or withdrawn rapidly. Doses of more than 600mg daily have a diuretic effect.
- Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms: At doses of over 3g per day unabsorbed ascorbic acid is mainly excreted unmetabolised in the faeces. Absorbed ascorbic acid additional to the body's needs is rapidly eliminated. Large doses of ascorbic acid may cause diarrhoea and the formation of renal oxalate calculi. Symptomatic treatment may be required. Ascorbic acid may cause acidosis or haemolytic anaemia in certain individuals with a deficiency of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Renal failure can occur with massive ascorbic acid overdosage.
Management: Gastric lavage may be given if ingestion is recent otherwise general supportive measure should be employed as required.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Vitamins – Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) ATC code: A11GA01
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Ascorbic acid, coupled with dehydroascorbic acid to which it is reversibly oxidised, has a variety of functions in cellular oxidation processes.
5.2 Pharmacodynamicproperties
5.3 Pharmacodynamic properties
Ascorbic acid is required in several important hydroxylations, including the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline (and thus collagen formation e.g. for intercellular substances and during wound healing); the formation of the neurotransmitters 5-hydroxytryptamine from tryptophan and noradrenaline from dopamine, and the biosynthesis of carnitine from lysine and methionine. Ascorbic acid appears to have an important role in metal ion metabolism, including the gastrointestinal absorption of iron and its transport between plasma and storage organs. There is evidence that ascorbic acid is required for normal leucocyte functions and that it participates in the detoxification of numerous foreign substances by the hepatic microsomal system. Deficiency of ascorbic acid leads to scurvy, which may be manifested by weakness, fatigue, dyspnoea, aching bones, perifollicular hyperkeratosis, petechia and ecchymosis, swelling and bleeding of the gums, hypochromic anaemia and other haematopoietic disorders, together with reduced resistance to infections and impaired wound healing. In addition, an ascorbic acid deficiency impairs the immune defence reactions, especially chemotaxis, complement activation and interferon production. Ascorbic acid improves the absorption of iron salts by reducing ferric ions and forming iron chelates. It blocks the chain reactions triggered by oxygen radicals in aqueous compartments of the body. The anti-oxidative functions form a close biochemical interaction with those of vitamin E, vitamin A and carotenoids.
5.4 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Ascorbic acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. As the unit dose increases the bioavailability falls to 60-75% after 1 g, to approximately 40% after 3 g and down to 16% after 12 g. The unabsorbed proportion is broken down by the flora in the large intestine, predominantly to CO2 and organic acids.
Distribution
Ascorbic acid is widely distributed to all tissues. Body stores of ascorbic acid normally are about 1.5g. The concentration is higher in leucocytes and platelets than in erythrocytes and plasma.
Metabolism
In healthy adults the maximum metabolic turnover of 40 to 50 mg/day is achieved at plasma concentrations of 0.8 to 1.0 mg/dl. The total daily turnover is about 1 mg/kg. At extremely high oral doses plasma concentrations of up to 4.2 mg/dl are achieved for a short time after about 3 hours
Elimination
Ascorbic acid additional to the body's needs, generally amounts above 200mg daily, is rapidly eliminated; unmetabolised ascorbic acid and its inactive metabolic products are chiefly excreted in the urine. The amount of ascorbic acid excreted unchanged in the urine is dose-dependent and may be accompanied by mild diuresis.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
There are no other preclinical data of relevance to the prescriber which are additional to that already included in other sections of the prescribing information.
7.0 Description
Vitamin C Chewable Tablets 500 is a blend of water soluble ascorbic acid (450mg) along with 120 mg Ascorbyl palmitate, a fat-soluble derivative of ascorbic acid. Ascorbyl palmitate is approximately 42.5% of Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Considering this 120 mg Ascorbyl palmitate will provide approximately 50 mg of ascorbic acid. Therefore, each Vitamin C Chewable 500 Tablets provide tablet provides total 500 mg of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C).
Ascorbyl Palmitate (120 mg):
- Ascorbyl palmitate is also known as "vitamin C ester" because it is an ester formed from ascorbic acid and palmitic acid. It is used either as a fat-soluble form of vitamin C, or as an antioxidant food additive.
- Ascorbyl palmitate possesses all the benefits of vitamin C. Ascorbyl palmitate is highly bioavailable, fat-soluble derivative of ascorbic acid and is able to be stored in the lipid cell membrane until the body is ready to put it to use.
- Ascorbyl palmitate is an amphipathic molecule (fat as well as water soluble form of vitamin C) which is better absorbed than ascorbic acid (water-soluble form). This dual solubility allows it to be incorporated into cell membranes.
- The fat-soluble aspect of ascorbyl palmitate extends vitamin C free radical protection (free radical protection) into the fat parts of the body.
- When incorporated into the cell membranes of human red blood cells, ascorbyl palmitate has been found to protect them from oxidative damage and to protect alpha-tocopherol (a fat-soluble antioxidant) from oxidation by free radicals.
L-Lysine:
L-Lysine is an essential amino acid, necessary building block for all proteins in the body. Amino acids such as L-lysine and vitamin C are crucial for the body’s production of collagen and the protection of the endothelium of the artery walls.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None.
8.2 Shelf-life
18 months
8.3 Packaging information
20 strips of 15 tablets in each strip
1 strip of 15 chewable tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Protect from Light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Chew the tablets carefully before swallowing. Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Do not take Ascorbic Acid Tablets if:
- You are allergic to Ascorbic Acid or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- You suffer from hyperoxaluria (excretion of urine containing large amounts of calcium oxalate crystals).
Talk to your doctor before taking Ascorbic Acid Tablets:
- If you are to undergo any blood or urine tests as ascorbic acid can interfere with some blood and urine tests.
- If you are a regular smoker.
- If you have kidney failure as ascorbic acid enhances aluminium absorption (present in antacids) which may reach toxic levels.
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. This is particularly important if you are taking any of the following:
- Amphetamines.
- Contraceptives.
- Aspirin.
- Iron-containing medicines.
- Amygdalin (Vitamin B17) - can cause cyanide toxicity
Ascorbic Acid Tablets should not be taken for the first month after starting desferrioxamine treatment
If you stop taking Ascorbic Acid Tablets:
Keep taking this medicine until your doctor tells you to stop. You may need to stop taking the tablets slowly as they may alter your kidney function.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours
- If you get any side-effects talk to your doctor, this includes any possible side effects not included in this leaflet.
In this leaflet:
- What ZU-C 500 is and what they are used for?
- What you need to know before you are given ZU-C 500
- How to take ZU-C 500
- Possible side effects
- How to store ZU-C 500
- Content of pack and other information.
1. What ZU-C 500 is and what they are used for?
ZU-C 500 contains ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid is a nutritional supplement commonly called Vitamin C. It is used to prevent and treat Vitamin C deficiency (e.g. scurvy) or other conditions requiring extra vitamin C.
2. What you need to know before you are given ZU-C 500?
Do not use ZU-C 500 if:
- If you are allergic to ascorbic acid or any of the other ingredient of this medicine.
- You have a condition called hyperoxaluria, where you have too much calcium oxalate crystals in your urine. This can lead to kidney stones.
If this applies to you talk to your doctor or nurse.
Warnings and Precautions
Check with your doctor before taking ZU-C 500 if:
- You have kidney problems
- You smoke
- You have an enzyme deficiency called G6PD deficiency. Large doses of ascorbic acid can cause your blood cells to break up.
- If you have undergone any blood or urine test as Vitamin-c interfere with the results.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Aspirin
- Desferrioxamine used to treat iron overload
- Medicines used to treat epilepsy (e.g. phenytoin)
- Appetite suppressants (e.g. fenfluramine)
- Oral contraceptives which contains oestrogen (e.g. “the pill”)
- antibiotics (e.g. tetracycline)
- iron supplement
- oral anticoagulants (e.g. Warfarin)
- fluphenazine for mental disorders
- Any other medicine, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
If any of the above applies to you talk to your doctor or nurse. Ascorbic acid tablets should not be taken for the first month after starting Desferrioxamine treatment.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, trying to become pregnant or breastfeeding. Large doses of ascorbic acid, i.e. greater than 1g daily, should not be taken during pregnancy since the effect of large doses on the foetus is unknown. Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk but there is no evidence of any hazard to the baby.
Driving and using machines.
This medicine doesn’t affect the ability to drive or operate the machinery. If you think it you are affected, you should not drive or operate machinery until you feel better.
3. How to take ZU-C 500 tablets
Always take ZU-C 500 exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Tablet should be chewed before swallowing.
Unless otherwise prescribed by your doctor, the usual dose is as follows:
- Adults and Children > 12 years: 1-2 tablets per day (equivalent to 500 or 1000 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Children 6-12 years: 1 tablet per day (equivalent to 500 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Vitamin C Chewable Tablets are not recommended for children under 6 years.
If you take more ZU-C 500 tablets than you should
If you have taken a lot of tablet at the same time or you think your child may have swallowed any, contact nearest hospital casualty department and tell the doctor immediately.
Large doses of ascorbic acid may cause diarrhoea and kidney stones may form if your urine is acidic. Doses of 600 mg or more may lead to more frequent passing water.
If you forget to take ZU-C 500 tablets
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose, as you would not substitute the missing amount but you risk overdosing. Continue the treatment according to the instructions.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines ZU-C 500 can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
- Diarrhoea, stomach cramps, nausea (feeling sick), vomiting, headache etc.
- Flushing, redness of skin
- Haemolytic anemia (body’s own immune system breaks the Red blood cells), signs may include fatigue and paleness.
- Increased urination (passing water) due to diuretic effect
- Formation of kidney stones if your urine is acidic.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or nurse. Reporting of side effects If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store ZU-C 500 tablets
Keep out of the reach and sight of children. Do not use ZU-C 500 tablets after the expiry date which is stated on the outer carton/container. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. Do not store above 25°C.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Content of the pack and other information
What ZU-C 500 tablets contain:
Each uncoated chewable tablets contains: Ascorbic Acid IP 50 mg
Sodium Ascorbate IP equivalent to Ascorbic Acid 400 mg
Ascorbyl Palmitate IP 120 mg
L- Lysine Hydrochloride USP equivalent to L- Lysine 6 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset of Yellow FCF
Packaging information: 20 strips of 15 tablets each.
For More Information About This Product
Zinconia Syrup
1.0 Generic name
Zinc Acetate Oral Solution USP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each 5ml contains:
Zinc acetate USP (as dihydrate) equivalent to Elemental Zinc 20 mg
Colour: Sunset Yellow FCF.
In a mentholated flavoured syrup base.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Dosage form - Syrup
Dosage Strength –Elemental Zinc 20 mg/5 ml
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of acute diarrhoea in children as an adjunct to oral rehydration.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
As per WHO/UNICEF recommendations zinc supplementation can be used orally, as an adjunct to Oral Rehydration Therapy in acute diarrhea in following dose regimen:
In infants (under six months): 2.5ml (10 mg of elemental Zinc) daily for 10–14 days after meals
In children (children older than six months): 5 ml (20 mg of elemental Zinc) daily for 10 –14 days after meals
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to zinc salts or any component of a zinc-containing supplement.
- Copper deficiency
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Renal impairment: Accumulation of zinc may occur in cases of renal failure. Hence caution should be exercised in patients with renal impairment with careful patient monitoring
4.5 Drugs interactions
Copper: Zinc may inhibit the absorption of copper.
Tetracyclines: Zinc may reduce the absorption of concurrently administered tetracyclines, also the absorption of zinc may be reduced by tetracyclines; when both are being given an interval of at least three hours should be allowed.
Quinolone Antibacterials: Zinc may reduce the absorption of quinolones; ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin.
Calcium Salts: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by calcium salts.
Iron: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by oral iron, also the absorption of oral iron may be reduced by zinc.
Penicillamine: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by penicillamine, also the absorption of penicillamine may be reduced by zinc. Trientine: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by trientine, also the absorption of trientine may be reduced by zinc.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
The safety of this product in human pregnancy has not been established. Zinc crosses the placenta and is present in breast milk.
Lactation
Zinc is excreted in human breast milk and zinc-induced copper deficiency in the breast-fed baby may occur. Therefore, breast-feeding should be avoided during zinc therapy.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Zinconia® Syrup has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Zinc salts may cause abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, gastric irritation and gastritis. There have also been cases of irritability, headache and lethargy observed. Zinc may interfere with the absorption of copper, leading to reduced copper levels, and potentially copper deficiency. The risk of copper deficiency may be greater with long-term treatment (e.g. if zinc deficiency is no longer present) and/or with higher doses of zinc.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
- Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com '
- Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.8 Overdose
Zinc acetate is corrosive in overdosage. Symptoms are corrosion and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth and stomach; ulceration of the stomach followed by perforation may occur. Gastric lavage and emesis should be avoided. Demulcents such as milk should be given. Chelating agents such as sodium calcium edetate may be useful.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Zinc supplementation improves immunity. Various studies have quoted different mechanisms of action of zinc in persistent and infective diarrhea patients: Preclinical studies have shown that zinc inhibits cAMP induced, chloride dependent fluid secretion by inhibiting basolateral potassium (K) channels of ileal mucosa. Zinc also improves the absorption of water and electrolytes, improves regeneration of the intestinal epithelium, increases the levels of brush border enzymes, and enhances the immune response, allowing for a better clearance of the pathogens. Recent evidence demonstrate that zinc inhibits toxin induced cholera. Thus by different mechanisms zinc supplementation could be beneficial in diarrhea.
It is demonstrated that zinc supplementation could improve symptoms of acute respiratory illness. It may prevent premature cell destruction and promotes activity of enzymes that affect production of prostaglandin from essential fatty acids, and as a result, leads to decrement of inflammation in airways. It also can activate natural killer cells, macrophages and lymphocytes. Zinc administration has also been demonstrated to improve tachypnea during acute phase of Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in hospitalized children.
Zinc has critical effect in homeostasis, in immune function, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and aging, and significant disorders of great public health interest are associated with zinc deficiency. In many chronic diseases, including atherosclerosis, several malignancies, neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, aging, age-related degenerative diseases, and Wilson's disease, the concurrent zinc deficiency may complicate the clinical features, affect adversely immunological status, increase oxidative stress, and lead to the generation of inflammatory cytokines. In these diseases, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation may play important causative roles.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Zinc is an essential trace element involved in many enzyme systems. Severe deficiency causes skin lesion, alopecia, diarrhoea, increased susceptibility to infections and failure to thrive in children. Symptoms of less severe deficiency include distorted or absent perceptions of taste and smell and poor wound healing.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Zinc is absorbed (20% to 30%) from the gastrointestinal tract and distributed throughout the body. The highest concentrations occur in hair, eyes, male reproductive organs and bone. Lower levels are present in liver, kidney and muscle. In blood 80% is found in erythrocytes. Plasma zinc levels range from 70 to 110μg/dL and about 50% of this is loosely bound to albumin. About 7% is amino-acid bound and the rest is tightly bound to alpha 2-macroglobulins and other proteins. The liver is the main storage for zinc and hepatic zinc levels are increased during maintenance therapy with zinc.
The plasma elimination half-life of zinc in healthy subjects is around 1 hour. The elimination of zinc results primarily from faecal excretion with relatively little from urine and sweat. The faecal excretion is in the greatest part due to the passage of unabsorbed zinc but it is also due to endogenous intestinal secretion.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
None stated.
7.0 Description
Zinc acetate as the dihydrate is a salt of zinc used for the treatment of acute diarrhoea in children as an adjunct to oral rehydration.
Zinc is an integral component of many metallo enzymes in the body; it is involved in the synthesis and stabilization of proteins, DNA and RNA, and plays a structural role in ribosomes and membranes. Zinc is involved in oxygen transport and protection against free radical damage. Zinc facilitates wound healing and helps maintain normal growth rates, normal skin hydration and senses of taste and smell. Zinc acts as an integral part of several enzymes important to protein and carbohydrate metabolism.
Its structural formula is
Zinc acetate dihydrate structure
Molecular Formula: C4H6O4Zn.2H2O
Molecular Weight: 219.5 g/mol
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer to pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Amber-coloured bottle of 100 mL.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store in a cool, dry place protected from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Do not take Zinconia® Syrup
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to zinc acetate or any of the other ingredients.
- if you have copper deficiency
Talk to your doctor, before taking Zinconia® Syrup if you suffer from kidney disease. If this applies to you it is important that you tell your doctor or pharmacist before taking Zinconia® Syrup and they will decide what to do.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. This is especially important if you are taking or have recently taken any of the following:
- Copper supplements
- Tetracycline antibiotics (such as oxytetracycline or doxycycline) used to treat certain bacterial infections
- Quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin) used to treat certain bacterial infections
- Calcium Salt Preparations
- Penicillamine (used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, Wilson's disease, autoimmune hepatitis and cystinuria)
- Trientine (used in the treatment of Wilson's disease)
Zinconia® Syrup should be taken after meals. Patients should take Zinconia® Syrup two to three hours after meals. In the rare event of gastric intolerance of zinc, generally occurring with the morning dose, this dose may be taken between breakfast and lunch.
12.0 Date of revision
16th Oct. 2023
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, please ask your child’s doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as your child’s.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your child’s doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4
What is in this leaflet
- What ZINCONIA® Syrup is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use ZINCONIA® Syrup
- How to use ZINCONIA® Syrup
- Possible side effects
- How to store ZINCONIA® Syrup
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What ZINCONIA® Syrup is and what it is used for
ZINCONIA® Syrup is a mineral supplement used for the treatment of acute diarrhoea in children as an adjunct to oral rehydration. It contains zinc acetate (as dihydrate). Zinc acetate dihydrate is a source of zinc, which is an essential trace element and involved in a number of body enzyme functions.
Zinc is an essential trace element involved in many enzyme systems. Severe deficiency causes skin lesion, alopecia, diarrhoea, increased susceptibility to infections and failure to thrive in children. Symptoms of less severe deficiency include distorted or absent perceptions of taste and smell and poor wound healing.
You must talk to a doctor if you do not feel better or if you feel worse.
2. Before you take ZINCONIA® Syrup
Do not take ZINCONIA® Syrup if you
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to zinc or to any of the components of the formulation.
- if you have copper deficiency
Talk to your doctor if this applies to you.
Warnings and precautions
- Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking ZINCONIA® syrup if you suffer from kidney disease.
- If this applies to you it is important that you tell your doctor or pharmacist before taking ZINCONIA® syrup and they will decide what to do. It may still be safe for you to take syrup.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
This is especially important if you are taking or have recently taken any of the following:
-copper supplements (see section 2 “Do not take ZINCONIA® ….’)
-tetracycline antibiotics (such as oxytetracycline or doxycycline) used to treat certain bacterial infections
-quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin) used to treat certain bacterial infections
-calcium salt preparations
-iron preparations
-penicillamine (used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, Wilson’s disease, autoimmune hepatitis and cystinuria)
-trientine (used in the treatment of Wilson’s disease)
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Taking ZINCONIA® Syrup with food and drink
You should take ZINCONIA® Syrup after meals.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
The safety of ZINCONIA® Syrup in human pregnancy is not known. Zinc has been shown to cross the placenta and is present in breast milk in females taking zinc supplements. Only take this product during pregnancy or while breast-feeding if your doctor has advised you to do so.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine during pregnancy or while breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines
ZINCONIA® Syrup is not expected to affect the ability to drive or use machine.
3. How to take ZINCONIA® Syrup
Always take ZINCONIA® Syrup exactly as your doctor has told you. It should be taken orally.
Dose
Acute Diarrhoea:
- For children below 6 months: 2.5 ml daily for 10-14 days
- For children above 6 months: 5 ml daily for 10-14 days
If you take more ZINCONIA® Syrup than you should
If you take too large dosage, contact your nearest hospital casualty department or doctor immediately.
If you forget to take ZINCONIA® Syrup
If you forget to take your dose, take it as soon as you remember and then continue with the next dose as instructed. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you stop taking ZINCONIA® Syrup
To get the most benefit from ZINCONIA® Syrup, always finish the course of treatment recommended by your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, ZINCONIA® Syrup can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects with ZINCONIA® Syrup may include:
- reduced copper levels, potentially leading to copper deficiency
- abdominal pain -indigestion
- nausea (feeling sick)
- vomiting (being sick)
- diarrhoea
- stomach discomfort
- irritability
- headache
- lethargy (a feeling of weariness)
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store ZINCONIA® Syrup
Store in a cool, dry place protected from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and tablet container.
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in the original packaging to protect the tablets from moisture.
Do not take ZINCONIA® Syrup if you notice that the bottle is damaged.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What ZINCONIA® Syrup contains
Each 5 ml contains:
Zinc acetate USP (as dihydrate) equivalent to Elemental Zinc 20 mg
Colour: Sunset Yellow FCF.
In a mentholated flavoured syrup base
What ZINCONIA® Syrup looks like and contents of pack
Amber-coloured bottle of 100 mL with measuring cap
For More Information About This Product
Vitanova®-D3 800 IU Drops
1.0 Generic Name
Vitamin-D3 (Cholecalciferol) Drops
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each ml contains:
Cholecalciferol IP 800 IU.
In a Flavoured base q.s.
Colour: Tartrazine Supra
Appropriate overages of vitamin added to compensate loss on storage.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Dosage Form: Oral Drops.
Dosage Strength: 800 IU per ml
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of vitamin D3 deficiency
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Treatment vitamin D deficiency should be for up to 12 weeks dependent upon the severity of the disease and the patient's response to treatment, followed by the appropriate long term maintenance therapy.
Pediatric Posology
Infants aged 0 to 2 years
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency: 0.5 ml to 1.25 ml (400 – 1,000 IU) daily.
Long term maintenance therapy following treatment of Deficiency and Prevention of vitamin D deficiency: 0.25ml to 1.25 ml (200 – 1,000 IU) daily.
Children aged 2 years to 11 years
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency: 0.5 ml to 2.5ml (400 – 2,000 IU) daily. Long term maintenance therapy following treatment of deficiency AND Prevention of vitamin D deficiency: 0.5ml to 1.25 ml (400 – 1,000 IU) daily.
Adolescents aged 12 years to 18 years
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency: 0.5 ml – 5ml (400 – 4,000 IU) daily.
Long term maintenance therapy following treatment of deficiency AND Prevention of vitamin D deficiency: 0.5 ml to 2 ml (400 – 1,600 IU) daily.
Adults and the elderly
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency: 1 ml – 5 ml (800 – 4,000 IU) daily. Long term maintenance therapy following treatment of deficiency AND Prevention of vitamin D deficiency: 1 ml – 2 ml (800 – 1,600 IU) daily. As an adjunct to specific therapy for osteoporosis: 1ml (800 IU) daily.
During Pregnancy and Breast-feeding
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency: 1ml – 5ml (800 – 4000 IU) daily.
Long term maintenance therapy following treatment of deficiency: 1ml – 2 ml (800 – 1600 IU) daily.
Table summarising the Posologies of different indications against patient population
| Paediatric posology | Adult posology | ||||
| Infant (0 – 2 years) | Children (2 – 11 years | Adolescents (12 – 18 years) | Adults and elderly | Pregnancy / breast feeding | |
| Treatment | 400 – 1,000 IU/day | 400 – 2,000 IU/day | 400 – 4,000 IU/day | 800 – 4,000 IU/day | 400 – 4,000 IU/day |
| Prevention ( long-term maintenance) | 200 – 1,000 IU/day | 400 – 1,000 IU/day | 400 – 1,600 IU/day | 800 – 1,600 IU/day | 400 IU/day (but up to 2,000) IU/day |
| adjunct to specific therapy for osteoporosis | - | - | - | 800 IU/day | - |
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to vitamin D or any of the excipients in the product
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Nephrolithiasis
- Diseases or conditions resulting in hypercalcaemia and/or hypercalciuria
- Severe renal impairment
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Vitamin D should be used with caution in patients with impairment of renal function and the effect on calcium and phosphate levels should be monitored. The risk of soft tissue calcification should be taken into account. In patients with severe renal insufficiency, vitamin D in the form of cholecalciferol is not metabolised normally and other forms of vitamin D should be used.
- Caution is required in patients receiving treatment for cardiovascular disease.
- Vitanova- D3 should be prescribed with caution to patients suffering from sarcoidosis because of the risk of increased metabolism of vitamin D to its active form. These patients should be monitored with regard to the calcium content in serum and urine.
- Allowances should be made for vitamin D supplements from other sources.
- The need for additional calcium supplementation should be considered for individual patients. Calcium supplements should be given under close medical supervision.
- Medical supervision is required whilst on treatment to prevent hypercalcaemia.
4.5 Drugs interactions
- Concomitant treatment with phenytoin or barbiturates can decrease the effect of vitamin D because of metabolic activation. Concomitant use of glucocorticoids can decrease the effect of vitamin D.
- The effects of digitalis and other cardiac glycosides may be accentuated with the oral administration of calcium combined with Vitamin D. Strict medical supervision is needed and, if necessary monitoring of ECG and calcium.
- Simultaneous treatment with ion exchange resins such as cholestyramine or laxatives such as paraffin oil may reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of vitamin D.
- The cytotoxic agent actinomycin and imidazole antifungal agents interfere with vitamin D activity by inhibiting the conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D by the kidney enzyme, 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1-hydroxylase.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of cholecalciferol in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity. The recommended daily intake for pregnant women is 400 IU, however, in women who are considered to be vitamin D deficient a higher dose may be required. During pregnancy women should follow the advice of their medical practitioner as their requirements may vary depending on the severity of their disease and their response to treatment.
Nursing Mothers
Vitamin D and its metabolites are excreted in breast milk. Overdose in infants induced by nursing mothers has not been observed, however, when prescribing additional vitamin D to a breast-fed child the practitioner should consider the dose of any additional vitamin D given to the mother.
Infants
Vitamin D3 should be used with caution in infants, who may have increased sensitivity to its effects.
Geriatric Patients
Elderly patients may be given the same dose as recommended for adults. However, studies have shown that the elderly people may have greater requirement for vitamin D due to a possible decrease in the capacity of skin to produce pro-vitamin D3, or a decrease in exposure to the sun, or impaired renal function, or impaired vitamin D absorption.
Renal impairment
Cholecalciferol should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment and the effect on calcium and phosphate levels should be monitored. The risk of soft tissue calcification should be taken into account. In patients with severe renal impairment cholecalciferol is not metabolized normally thus, another form of vitamin D should be used. Use of cholecalciferol is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
Liver disease may impair the absorption of cholecalciferol. Thus, cholecalciferol should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Vitanova-D3 has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Adverse reactions are listed below, by system organ class and frequency. Frequencies are defined as: uncommon (>1/1,000, <1/100) or rare (>1/10,000, <1/1,000).
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Uncommon: Hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria. Skin and subcutaneous disorders
Rare: Pruritus, rash and urticaria.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
- Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
- Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.8 Overdose
The most serious consequence of acute or chronic overdose is hypercalcaemia due to vitamin D toxicity. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, polyuria, anorexia, weakness, apathy, thirst and constipation. Chronic overdoses can lead to vascular and organ calcification as a result of hypercalcaemia.
Symptoms:
Acute or chronic overdose of vitamin D can cause hypercalcaemia. Symptoms of hypercalcemia are tiredness, psychiatric symptoms (e.g., euphoria, dazedness, disturbed consciousness), nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, weight loss, thirst, polyuria, formation of renal calculi, nephrocalcinosis, extraosseous calcification and kidney failure, changes in ECG, arrhythmias, and pancreatitis. In isolated cases their course has been described as fatal.
Treatment:
If a massive dose has been ingested ventricular emptying may be considered, together with the administration of carbon. Sunlight and further administration of vitamin D or calcium should be avoided. Rehydration and treatment with diuretics, e.g. furosemide to ensure adequate diuresis. In hypercalcemia biphosphonates or calcitonin and corticosteroids may be given. The treatment is directed to symptoms.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of 1,25(OH)2D(calcitriol) is mediated by the interaction of calcitriol with the vitamin D receptor (VDR). Calcitriol binds to cytosolic VDRs within target cells, and the receptor-hormone complex translocates to the nucleus and interacts with DNA to modify gene transcription. The VDR belongs to the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor supergene family. Calcitriol also exerts nongenomic effects that may require the presence of a functional VDR.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Vitamin D3 is converted to 25hydroxyvitamin D3 in the liver. Conversion to the active calcium-mobilizing hormone 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) in the kidney is stimulated by both parathyroid hormone and hypophosphatemia. The principal action of 1,25dihydroxyvitamin D3 is to increase intestinal absorption of both calcium and phosphate as well as regulate serum calcium, renal calcium and phosphate excretion, bone formation and bone resorption.
Vitamin D is required for normal bone formation. Vitamin D insufficiency develops when both sunlight exposure and dietary intake are inadequate. Insufficiency is associated with negative calcium balance, increased parathyroid hormone levels, bone loss, and increased risk of skeletal fracture. In severe cases, deficiency results in more severe hyperparathyroidism, hypophosphatemia, proximal muscle weakness, bone pain and osteomalacia.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Vitamin D substances are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The presence of bile is essential for adequate intestinal absorption; absorption may be decreased in patients with decreased fat absorption.
Distribution
Vitamin D and its metabolites circulate in the blood, bound to a specific alpha-globulin. Vitamin D can be stored in adipose and muscle tissue for long periods of time. It is slowly released from such storage sites and from the skin where it is formed in the presence of sunlight or ultraviolet light. Cholecalciferol has a slow onset and a long duration of action.
Metabolism
Cholecalciferol is converted in the liver by hydroxylation to the active form 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. It is then further converted in the kidneys to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol is the metabolite responsible for increasing calcium absorption. Vitamin D that is not metabolized is stored in adipose and muscle tissues.
Excretion
Vitamin D compounds and their metabolites are excreted mainly in the bile and faeces, with only small amounts appearing in the urine. There is some enterohepatic recycling but it is considered to have a negligible contribution to vitamin D status. Certain vitamin D substances may be distributed into breast milk.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Vitamin D is well known and is a widely used material and has been used in clinical practice for many years. As such toxicity is only likely to occur in chronic overdosage where hypercalcaemia could result.
Cholecalciferol has been shown to be teratogenic in high doses in animals (4-15 times the human dose). Offspring from pregnant rabbits treated with high doses of vitamin D had lesions anatomically similar to those of supravalvular aortic stenosis and offspring not showing such changes show vasculotoxicity similar to that of adults following acute vitamin D toxicity.
7.0 Description
Vitanova D3 contains cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3). Vitamin D3 is essential for the proper growth and development of the body. It is synthesized within the body after exposure to sunlight and is essential for many important functions of the human body. Vitamin D3 in Vitanova D3 also increases the Calcium absorption from the intestines. Chemical name- (1S,3Z)-3-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-7a-methyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-4-methylidenecyclohexan-1-ol
Chemical formula- C27H44O
Molecular weight- 384.6.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
24 months.
8.3 Packaging information
Amber-coloured bottle glass (15 mL) with silver cap and dropper.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Keep out of reach of children.
Any unused product should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Take exactly as directed by your doctor or on the label. Do not increase the dosage or take for longer than is recommended.
Instruct patients on the following points when administering the drug. Inform the patient not to take Cholecalciferol if they have
- allergic to vitamin D or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
- high levels of vitamin D in your blood
- kidney stones or serious kidney problems
- high levels of calcium in your blood and/or urine
Remind patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately before taking Cholecalciferol if they have
- problems with kidneys
- sarcoidosis
- they are already taking other medicines or supplements containing vitamin D.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
-Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
-If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, or pharmacist, or nurse.
-This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
-If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, or pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4
What is in this leaflet
1.What Vitanova®-D3 is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you use Vitanova®-D3
3.How to use Vitanova®-D3
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store Vitanova®-D3 Contents of the pack and other information
1.0 What Vitanova®-D3 is and what it is used for
Vitanova®-D3 800 IU Drops contains Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). Vitamin D3, is found in some foods and is mainly produced by the body when skin is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D3 helps the kidneys and intestine absorb calcium and it helps build bones. Vitamin D3 deficiency is the predominant cause of rickets (defective mineralization of bones in children) and osteomalacia (inadequate mineralization of bones in adults).
Vitanova®-D3 800 IU Drops, may be prescribed by your doctor to prevent and treat vitamin D3 deficiency in adults, adolescents and children with an identified risk of vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin-D deficiency may occur when your diet and lifestyle does not provide you enough Vitamin-D or when your body requires more Vitamin- (pregnancy). It may also be prescribed in for certain bone conditions such as thinning of bones (osteoporosis) when it is given with other medications.
2.0 Before you take Vitanova®-D3
Do not take Vitanova®-D3 if you
- are allergic (hypersensitive) to vitamin D or any of the other ingredients in the drops (these are listed in section 6, Further information)
- have high levels of vitamin D in your blood (hypervitaminosis D)
- have high blood levels of calcium (hypercalcaemia) or high urine levels of calcium (hypercalciuria)
- have kidney stones or serious kidney problems.
Check with your doctor before taking Vitanova®-D3 if
- You have kidney damage or disease. Your doctor may want to measure the levels of calcium in your blood or urine You are being treated for heart disease
- You have sarcoidosis (an immune system disorder which may affect your liver, lungs, skin or lymph nodes)
- You are already taking additional doses of calcium or vitamin D. Whilst you are taking Vitanova®-D3 drops your doctor will monitor your blood levels of calcium to make sure they are not too high.
Taking other medicines
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
In particular, the following medicines may interact with Vitanova®-D3
- Heart medicines (cardiac glycosides such as digoxin). Your doctor may monitor your heart with an electrocardiogram (ECG) and measure the levels of calcium in your blood.
- Medicines to treat epilepsy (such as phenytoin) or medicines to make you sleep (barbiturates such as phenobarbitone) as these medicines can decrease the effect of vitamin D.
- Glucocorticoids (steroids hormones such as hydrocortisone or prednisolone). These can decrease the effect of vitamin D.
- Laxatives (such as paraffin oil) or a cholesterol lowering drug called colestyramine may reduce the absorption of vitamin D.
- Actinomycin (a medicine used to treat some forms of cancer) and imidazole antifungals (medicines such as clotrimazole and ketoconazole used to treat fungal diseases) as they may interfere with the metabolism of vitamin D.
Taking Vitanova®-D3 with food and drink
You can take Vitanova®-D3 with or without food and drink.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant or you are breast-feeding, you should talk to you doctor or pharmacist before you take Vitanova®-D3 Drops. Vitanova®-D3 Drops should be used during pregnancy and breast-feeding only if recommended by your doctor.
Driving and using machines
Vitanova®-D3 drops should not affect your ability to drive or operate machinery.
3.0 How to take Vitanova®-D3
Always take Vitanova®-D3 exactly as your doctor has told you. The drops should be dispensed onto a spoon before taking.
Dose
Use in children and adolescents
Infants aged 0 up to 2 years’ old
To treat vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 0.5 to 1.25ml daily for up to 12 weeks, followed by a long term maintenance dose.
Long term maintenance and to prevent vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 0.25ml to 1.25 ml daily.
Children aged 2 years to 11 years old
To treat vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 0.5 ml to 2.5 ml daily for up to 12 weeks, followed by a long term maintenance dose.
Long term maintenance and to prevent vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 0.5 ml to 1.25 ml daily.
Adolescents aged 12 years to 18 years old
To treat vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 0.5 ml to 5 ml daily for up to 12 weeks, followed by a long term maintenance dose.
Long term maintenance and to prevent vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 0.5 ml to 2 ml daily.
In infants, children and adolescents the drops can be mixed with a small amount of children’s foods, yogurt, milk, cheese or other dairy products. The drops must not be mixed into a bottle of milk or container of soft foods in case the child does not consume the whole portion, and so does not then receive the full dose.
Use in adults and the elderly
To treat vitamin D deficiency: your doctor will usually prescribe 1 to 5 ml daily for up to 12 weeks, followed by a long term maintenance dose.
Long term maintenance and to prevent vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 1 to 2 ml daily.
In osteoporosis (you will also be taking other medicines for this): Your doctor will usually prescribe 1 ml daily.
Use in pregnancy and breast-feeding
To treat vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 1 to 5 ml daily for up to 12 weeks, followed by a long term maintenance dose.
Long term maintenance and to prevent vitamin D deficiency: Your doctor will usually prescribe 1 ml to 2 ml daily.
In adults, the drops can be mixed with a small amount of cold or lukewarm food immediately before taking.
You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
If you take more Vitanova®-D3 than you should
If you accidentally take one drop too many, nothing is likely to happen. If you accidentally take several drops too many tell your doctor or get other medical advice immediately. If possible, take the bottle, the box and this leaflet with you to show the doctor. If you take too many drops you may feel or be sick, become constipated or have stomach pains, weak muscles, tiredness, lack of appetite, kidney problems and in severe cases irregular heartbeats.
If you forget to take Vitanova®-D3
If you forget to take your drops, take them as soon as you can. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. After that, take the next dose in accordance with the instructions given to you by your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4.0 Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Vitanova®-D3 can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects with Vitanova®-D3 may include:
Uncommon side effects
(affecting less than 1 in 100 people)
- Too much calcium in your blood (Hypercalcaemia). You may feel or be sick, loose your appetite, have constipation, stomach ache, feel very thirsty, have muscle weakness, drowsiness or confusion
- Too much calcium in your urine (hypercalciuria).
Rare side effects
(affecting less than1 in 1000 people)
- Skin rash
- Itching
- Hives
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5.0 How to store Vitanova®-D3
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
Store below 25ºC.
Do not used Vitanova®-D3 after the expiry date which is stated on the carton as “EXP”. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Opened bottle should be used within 6 months.
Medicines should not be disposed or via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6.0 Contents of the pack and other information
What VITANOVA- D3 oral drops contains
Each ml contains:
Cholecalciferol IP 800 IU.
In a Flavoured base q.s.
Colour: Tartrazine Supra
Appropriate overages of vitamin added to compensate loss on storage.
What VITANOVA- D3 looks like and contents of pack
Amber-coloured bottle glass (15 mL) with silver cap and dropper.
Packaging: A bottle of 15 ml
For More Information About This Product
Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection
1.0 Generic Name
Cholecalciferol Injection IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each ml contains:
Cholecalciferol IP 6,00,000 IU (15mg)
Ethyl Oleate IP q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Ampoule, 6,00,000 IU
For intramuscular use only.
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
Indicated for the treatment of Vitamin D3 deficiency
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Vitamin D3 injection is administered intramuscularly as a single dose of 6,00,000 IU once only or repeated after 6 months to 1 year, depending upon clinical response and requirements. The serum calcium levels should be checked every 3 - 6 months and the dose adapted according to the values.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance(s) or to any of the excipients.
- Hypercalcaemia, evidence of vitamin D toxicity, hypervitaminosis D, decreased renal function, metastatic calcification.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Adequate dietary calcium is necessary for clinical response to Cholecalciferol therapy.
- Caution should be used when the injectable forms are used in patients with vitamin D resistant rickets as the range between the toxic and therapeutic dosage is narrow.
- Vitamin D should be administered with caution to infants and patients who may have an increased sensitivity to its effects. Use with care in patients with renal impairment, renal calculi or heart disease or arteriosclerosis who might be at increased risk of organ damage if hypercalcaemia were to occur.
- Cholecalciferol is not recommended for use in hypoparathyroidism. In the event of hypoparathyroidism when Cholecalciferol is used, calcium, parathyroid hormone or dihydrotachysterol may be required.
- Dosage should be individualised. Frequent serum and urinary calcium, phosphate and urea nitrogen determinations should be carried out. Adequate fluid intake should be maintained.
- Should hyperglycaemia develop, Cholecalciferol should be discontinued immediately.
- Because of the effect on serum calcium, Cholecalciferol should only be administered to patients with renal stones when potential benefits outweigh possible hazards.
- Vitamin D3 supplementation may worsen hypercalcemia and/or hypercalciuria when administered to patients with diseases associated with unregulated overproduction of calcitriol (e.g., leukemia, lymphoma, sarcoidosis). Urine and serum calcium should be monitored in these patients.
- It should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment or calculi, heart disease, sarcoidosis, pseudo hypoparathyroidism and who might be at increased risk of organ damage if hypercalcemia occurred.
- Plasma calcium and phosphate concentrations should be controlled during vitamin D3 therapy to reduce the risk of ectopic calcification.
4.5 Drugs interactions
- Rifampicin and isoniazid may reduce the effectiveness of vitamin D3.
- Corticosteroids may counteract the effect of vitamin D3. Cholecalciferol and
- Magnesium-containing antacids: hypermagnesaemia may develop in patients on chronic renal dialysis.
- Digitalis glycosides: hypercalcaemia in patients on digitalis may precipitate cardiac arrhythmias.
- Verapamil: atrial fibrillation has recurred when supplemental calcium and Cholecalciferol have induced hypercalcaemia.
- Anti-convulsants: Vitamin D requirements may be increased in patients taking anti-convulsants (e.g. carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone).
- Thiazide diuretics: hypoparathyroid patients on Cholecalciferol may develop hypercalcaemia.
4.6 Use in special populations
- Pregnancy :- There are no or limited amount of data from the use of ergocalciferol in pregnant women. Cholecalciferol Injection should not be used in pregnancy unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential hazards to the foetus.
- Nursing Mothers :- Vitamin D3 and some of its active metabolites pass into breast milk. Infants should be closely monitored for hypercalcemia or clinical manifestations of vitamin D toxicity if the mother is taking pharmacological doses of vitamin D3.
- Infants:- Vitamin D3 should be used with caution in infants.
- Elderly: Requirements of vitamin D3 are increased in the elderly patients.
- Renal Insufficiency:- Patients with renal insufficiency will have decreased ability to form calcitriol metabolite, the effect on the calcium and phosphate balance should be supervised.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cholecalciferol injection have no influence on the ability to drive and use machines. If patient feels drowsiness, affected patients should not drive or operate machinery.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Adverse events are generally associated with excessive intake of Cholecalciferol leading to the development of hypercalcaemia.
Signs and symptoms of vitamin D intoxication associated with hypercalcemia include muscle weakness, apathy, headache, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, bone pain, ectopic calcification, proteinuria, hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias. Chronic hypercalcemia can lead to generalized vascular calcification, nephrocalcinosis, and rapid deterioration of renal function.
| System Organ Class | Adverse event | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Hypercalcaemia | Very common |
| Hypercholesterolaemia† | Not known | |
| Muscle weakness§ | Not known | |
| Muscle pain§ | Not known | |
| Mild acidosis† | Not known | |
| Polydipsia† | Not known | |
| Anorexia† | Not known | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Overt psychosis† | Rare |
| Somnolence§ | Not known | |
| Nervous system disorders | Headache§ | Not known |
| Endocrine disorders | Hypoparathyroidism* pseudohypopathyroidism* | Very common |
| Eye disorders | Conjunctivitis (calcific) | Not known |
| Photophobia | Not known | |
| Cardiac disorders | Cardiac arrhythmias | Not known |
| Rebal disorders | Elevated serum creatinine levels* | Very common |
| Vascular disorders | Generalised vascular calcification† | Not known |
| Hypertension† | Not known | |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Rhinorrhoea† | Not known |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Pancreatitis† | Not known |
| Nausea§ | Not known | |
| Vomiting§ | Not known | |
| Dry mouth§ | Not known | |
| Constipation§ | Not known | |
| Diarrhoea§ | Not known | |
| Abdominal pain§ | Not known | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Pruritus† | Not known |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Bone pain§ | Not known |
| Ectopic calcification† | Not known | |
| Renal and urinary disorders | Polyuria† | Not known |
| Nocturia† | Not known | |
| Nephrocalcinosis† | Not known | |
| Albuminuria† | Not known | |
| Reversible azotemia† | Not known | |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | Decreased libido† | Not known |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Hyperthermia† | Not known |
| Fatigue§ | Not known | |
| Irritability† | Not known | |
| Weakness§ | Not known | |
| Investigations | Elevated AST † | Not known |
| Elevated ALT† | Not known | |
| Elevated BUN† | Not known | |
| Weight loss† | Not known | |
| Surgical and medical procedures | Metallic taste§ | Not known |
*In clinical studies on hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypopathyroidism, hypercalcaemia was noted on at least one occasion in about 1 in 3 patients and hypercalciuria in about 1 in 7. Elevated serum creatinine levels were observed in about 1 in 6 patients (approximately one half of whom had normal levels at baseline).
§ Possible early symptoms of hypercalcaemia
†Possible late symptoms of hypercalcaemia
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
- Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: www.medico@zuventus.com
- Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms
Administration to patients in excess of their daily requirement can cause hypercalcaemia, hypercalciuria and hyperphosphataemia. Concomitant high intake of calcium and phosphate may lead to similar abnormalities.
Management
Treatment of chronic overdose with resulting hypercalcaemia consists of immediate withdrawal of the vitamin, a low calcium diet and generous fluid intake. Severe cases may require hydration with intravenous saline together with symptomatic and supportive treatment as indicated by the patient's clinical condition. Plasma calcium should be monitored.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
In its biologically active form vitamin D3 stimulates intestinal calcium absorption, incorporation of calcium into the osteoid, and release of calcium from bone tissue. In the small intestine it promotes rapid and delayed calcium uptake. The passive and active transport of phosphate is also stimulated. In the kidney, it inhibits the excretion of calcium and phosphate by promoting tubular resorption. The production of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in the parathyroids is inhibited directly by the biologically active form of vitamin D3. PTH secretion is inhibited additionally by the increased calcium uptake in the small intestine under the influence of biologically active vitamin D3.
The mechanism of action of 1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol) is mediated by the interaction of calcitriol with the vitamin D receptor (VDR). Calcitriol binds to cytosolic VDRs within target cells, and the receptor-hormone complex translocates to the nucleus and interacts with DNA to modify gene transcription. The VDR belongs to the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor supergene family. Calcitriol also exerts nongenomic effects that may require the presence of a functional VDR.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Vitamin D3 is converted to 25‑hydroxyvitamin D3 in the liver. Conversion to the active calcium-mobilizing hormone 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) in the kidney is stimulated by both parathyroid hormone (PTH) and hypophosphatemia. The known sites of action of calcitriol are intestine, bone, kidney and parathyroid gland. The principal action of calcitriol is to increase intestinal absorption of both calcium and phosphate as well as regulate serum calcium, renal calcium and phosphate excretion, bone formation and bone resorption.
Vitamin D is required for normal bone formation. Vitamin D insufficiency develops when both sunlight exposure and dietary intake are inadequate. Insufficiency is associated with negative calcium balance, increased PTH levels, bone loss, and increased risk of skeletal fracture. In severe cases, deficiency results in more severe hyperparathyroidism, hypophosphatemia, proximal muscle weakness, bone pain and osteomalacia.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
After absorption, Vitamin D3 is rapidly distributed to the liver and lesser amount distributed to adipose tissue, and stored as vitamin D3 at these sites for later release into the circulation. Circulating vitamin D3 is bound to vitamin D-binding protein.
Vitamin D3 is rapidly metabolized by hydroxylation in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcidiol), and subsequently metabolized in the kidney to calcitriol, which represents the biologically active form. Further hydroxylation occurs prior to elimination. A small percentage of vitamin D3 undergoes glucuronidation prior to elimination.
The mean urinary excretion of Vitamin D3 after 48 hours is 2.4% of the administered dose, and the mean fecal excretion after 48 hours is 4.9% of the administered dose as metabolites of the parent drug.
It was observed that, after intramuscular administration of 6,00,000 IU vitamin D3 in elderly patients, mean serum calcidiol concentration increases to 32.72±9.0 ng/ml at 6th week and up to 52.34±14.2 ng/ml at 12th week from baseline (11.76±7.6 ng/ml).
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
None stated.
7.0 Description
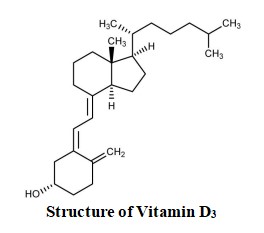
Cholecalciferol is the naturally occurring form of vitamin D, also called vitamin D3. It is produced from 7-dehydrocholesterol, a sterol present in mammalian skin, after being exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None stated.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging information
3 ampoules of 1 ml each
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light. After opening the residual must be discarded. Caution: Do not use if solution is not clear or has suspended matter.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Vitanova-D3 6L injection may interfere with cholesterol tests, hence please inform your physician and laboratory staff that you are taking Vitanova-D3 6L injection before undergoing blood tests.
- Clinical monitoring of serum electrolyte concentrations and cardiac function is recommended.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
-Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
-If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, or pharmacist, or nurse.
-This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
-If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, or pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4
What is in this leaflet
1.What Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you use Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection
3.How to use Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection
6.Contents of the pack and other information
What Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection is and what it is used for
This medicine contains the active ingredient Cholecalciferol Injection which is a form of vitamin D. It belongs to a group of medicines called vitamin D and analogues. Cholecalciferol increases levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood by increasing their absorption from the gut and reducing the amount removed by the kidneys. Cholecalciferol is used for the treatment of severe Vitamin-D deficiency. Few examples are as follows:
-Weak bones and teeth (called ‘Rickets’)
-Low levels of phosphate in the blood
-Other problems with how bones are formed (osteomalacia).
These disorders are due to poor absorption of vitamin D within the body usually caused by diseases of the gut, liver or gall bladder.
It is important that you have this medicine so that your bones and teeth form properly.
1. What you need to know before you use Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection
Do not use Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection:
• if you are allergic to vitamin D3 or any of the other ingredients of this medicine;
• if you have high levels of calcium in your blood (hypercalcaemia) or urine (hypercalciuria);
• if you have kidney stones (renal calculi) or serious kidney problems;
• if you have high levels of vitamin D3 in your blood (Hypervitaminosis D).
• if you have an accumulation of calcium salts in the body's tissue. If any of the above applies to you talk to your doctor or nurse.
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse before using Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection if you:
• if you have heart disease, problems with your kidneys or with your circulation
• if you have kidney stones
• if you have low levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH)
• if you already have high levels of vitamin D in your blood or if you are especially sensitive to vitamin D.
It is important that you are taking enough calcium in your diet so that your body can respond properly to your medicine.
Other medicines and Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
• Medicines for heart disease such as digoxin or verapamil as these can cause high levels of calcium in the blood leading to an irregular or fast heartbeat.
• Antacids containing magnesium for indigestion. If you are on kidney dialysis this can lead to high levels of magnesium in the blood which causes muscle weakness, low blood pressure, depression and coma.
• Thiazide diuretics (‘water tablets’) to relieve water retention such as bendroflumethiazide as these can lead to high levels of calcium if your body does not produce enough parathyroid hormone (PTH).
• Phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone or phenobarbital used for the treatment of epilepsy as these may cause Cholecalciferol to be lost from the body too quickly.
• Any other medicine, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
If any of the above applies to you talk to your doctor or nurse before being given Cholecalciferol.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before being given this medicine. Your doctor will tell you if you need to have Cholecalciferol when you are pregnant. You should not be given Cholecalciferol if you are breast-feeding. This medicine will be given to you in pregnancy only if your doctor decides it is necessary.
Driving and using machines
There is limited information on the possible effects of this medicine on your ability to drive. However, it is not expected that it would affect your ability to drive or to operate machinery.
2. How you will be given Cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol will be given to you by your doctor or nurse. Important: Your doctor will choose the dose that is right for you. You will be given Cholecalciferol by your doctor or nurse as an injection into a muscle. You may be given it just once or it may be repeated depending on how much your body needs. Your doctor may also prescribe for you other medicines containing calcium and phosphorus.
The recommended dose: a single dose of 6,00,000 IU intramuscularly once only or repeated after 6 months to 1 year, depending upon clinical response and requirements.
Medical check-ups
While you are receiving this medicine, your doctor will test your blood and urine regularly. This is to make sure that your medicine is working properly and that the dose you are taking is right for you. If the level of sugar in your blood becomes higher than normal your doctor will stop your treatment with Cholecalciferol.
If you are given more Cholecalciferol than you should
If you think you have been given too much Cholecalciferol you should tell your doctor.
If you have too much Cholecalciferol you may get increased calcium levels in your blood which may lead to the following: feeling sick, feeling weak, weight loss, stiffness, constipation, diarrhoea, hallucinations, fainting, increased levels of urination or feeling thirsty.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
3. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Side effects include:
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
• Too much calcium in blood (hypercalcaemia)
• Decrease activity of parathyroid gland (hypoparathyroidism)
• Disturbed parathyroid hormone metabolism (pseudohypoparathyroidism)
• Increased levels of creatinine in the blood which may indicate kidney problems.
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
• Psychosis – changes in abilities and personality
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Effects on the heart and blood:
• Hardening of the blood vessels, Irregular heart beat
• High blood pressure, High cholesterol, Imbalanced salt levels.
Effects on liver or kidneys:
• Kidney problems including kidney stones
• Increase in liver enzymes
• Protein in the urine.
Effects on the stomach and bowel:
• Inflammation of the pancreas, which causes severe pain in the abdomen and back
• Feeling sick or being sick
• Constipation, Diarrhoea
• Loss of appetite, Weight loss.
Effects on thirst and urinating:
• Dry mouth, a metallic taste, Drinking a lot
• Passing a lot of urine especially at night.
Effects on the eyes and skin:
• Conjunctivitis, Sensitivity to light, Itchy skin.
Effects on mood
• Being irritable, Loss of sex drive.
Effects on the nervous system:
• Weakness, Headache, Dizziness, Sleepiness.
Other effects:
• Calcium deposits in parts of the body other than bone
• Muscle pain, Bone pain, Tiredness, Feeling too hot, Runny nose.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4. How to store VITANOVA- D3
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and container after "Exp". The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
- After opening the residual must be discarded. Do not use this medicine if you notice the solution is cloudy
- Caution: Do not use if solution is not clear or has suspended matter.
- Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
- Do not freeze or refrigerate.
5. Contents of the pack and other information
What Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection contains
Each ml contains:
Cholecalciferol IP 6,00,000 IU (15mg)
Ethyl Oleate IP q.s.
What Vitanova®-D3 6L Injection looks like and contents of pack
Packaging: 3 ampoules of 1 ml each
For More Information About This Product
TumsUP Drops
1.0 Generic name
Simethicone, Dill Oil and Fennel Oil Liquid
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each ml contains :
Simethicone Emulsion
equivalent to Simethicone USP 40 mg
Dill Oil BP 0.005 ml
Fennel Oil 0.0007 ml
In Syrupy Base
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral drops
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Treatment of infantile colic
4.2 Posology and method of administration
For paediatric use only formulation.
Infants (below 6 months) : 5-10 drops 4 times daily, 15 minutes before feed.
Infants (6-12 months) : 10-20 drops 4 times daily, 15 minutes before feed.
Children (over 1 year) : 20 drops 4 times daily, 15 minutes before feed or as directed by the Physician.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Shake well before use.
- Cap should be tightly closed immediately after every use.
- Use calibrated dropper provided in this pack.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Levothyroxine may bind to Simethicone. Absorption of Levothyroxine may be impaired if the preparation is given concurrently to infants treated for thyroid disorders.
4.6 Use in special populations
For paediatric use only.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Not applicable
4.8 Undesirable effects
Simethicone does not have any serious side effects.
Minor adverse effects : Nausea, Mild diarrhea and Constipation. Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions such as rash, pruritis, facial oedema, tongue oedema and respiratory difficulty have been reported.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
Website : http ://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In the event of deliberate or accidental overdose, treat symptoms on appearance.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Excessive swallowing of air results in collection of gas in the intestine. This can be the result of too rapid eating, breast feeding babies where they inhale air along with the milk, excessive use of a pacifier (dummy), finger sucking or yelling. Simethicone, Dill Oil and Fennel Oil Liquid Relieves Infant Colic, Griping Pain & Flatulence When the swallowed air is in the intestine, bubbles are formed, which makes it more difficult for the gas to pass through the intestine canal, resulting in abdominal distension and pain.
Simethicone
Simethicone is used to relieve painful pressure caused by excess gas in the stomach and intestines. Simethicone is a surface active substance which changes the surface tension of the intestinal mucus allows gas bubbles in the stomach and intestines to come together. Thus, the air bubbles burst and the gas is released for easier passage of gas. The elimination of the gas, air or foam from the gastro-intestinal tract, relieves abdominal distension and dyspepsia.
Dill oil and fennel oil
Contains volatile oils that produce smooth muscle relaxation, an antispasmodic effect and increases intestinal motility. Dill and Fennel Oils are also used for digestion problems including intestinal gas (flatulence) and constipation.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Simethicone reduces surface tension and collapses gas bubbles, thus act as an 'antifoaming agent' and relieve flatulence. Dill Oil and Fennel Oil produce an antispasmodic effect and increases intestinal motility.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Physiologically the active ingredient Simethicone is a chemically inert. Simethicone is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is excreted unchanged in the faeces.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
7.0 Description
TumsUp drops is a fixed dose combination of Simethicone (40 mg) + Dill Oil (0.005 ml) + Fennel Oil (0.0007 ml) per ml. Simethicone is inert oil, which is tissue adherent and water repellent, it is therefore mucosal protective. Dill and Fennel Oils are essential oils extracted from the seeds or leaves/stems of Anethum Graveolens (Dill plant) and Foeniculum Vulgare respectively. Dill (Anethum Graveolens) has seeds containing volatile oils rich in carvone. Fennel (Foeniculum Vulgare) seeds hold another Volatile Oil, Anethole.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
24 Months
8.3 Packaging information
A glass bottle of 30 ml.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light. Do not Freeze. KEEP AWAY FROM THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Ask the patient to report any adverse events.
- Not to exceed the stated recommended daily dose.
12.0 Date of issue
05 February 2022
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What TumsUP Drops are and what are they used for
2. What you need to know before you take TumsUP Drops
3. How to take TumsUP Drops
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store TumsUP Drops
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What TumsUP Drops is and what it is used for
TumsUP Drops contains Simethicone, Dill Oil and Fennel Oil Liquid.
Simethicone belongs to a group of medicines called surface active substances. It works by helping to release trapped wind. This helps to relieve tummy pain and indigestion. Dill oil and fennel oil contains volatile oils that produce smooth muscle relaxation, an antispasmodic effect and increases intestinal motility. Dill and fennel oils are also used for digestion problems including intestinal gas and constipation.
TumsUP Drops are for the gentle relief of wind and griping pains and flatulence in babies.
This medicine can be used from birth onwards.
2. What you need to know before you use TumsUP Drops
Do not give TumsUP Drops if your baby is being treated for a thyroid disorder, seek advice from your doctor instead.
Do not give TumsUP Drops if you think your baby might be allergic (hypersensitive) to Simethicone, Dill Oil and Fennel Oil Liquid.
Taking other medicines
If your baby is being treated with levothyroxine for a thyroid disorder, using TumsUP Drops might reduce the amount of this type of medicine that is absorbed, weakening the effect of their treatment.
3. How to take TumsUP Drops
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
For paediatric use only formulation.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE.
Use calibrated dropper provided in this pack.
In infants (below 6 months) 5-10 drops should be given 4 times daily, 15 minutes before feed.
In Infants (6-12 months) 10-20 drops should be given 4 times daily, 15 minutes before feed. 4
Children (over 1 year) should be given 20 drops 4 times daily, 15 minutes before feed or as directed by the Physician.
Replace cap tightly immediately after each use.
If you use more TumsUP Drops than you should, contact your health advisor for advice.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you notice any signs of allergy, stop using the product and seek medical advice.
Minor adverse effects: nausea, mild diarrhoea and constipation. Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions such as rash, itching, facial swelling, tongue oedema and respiratory difficulty have been reported.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store TumsUP Drops
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in a cool place. Away from light.
Do not take Tumps UP Drops after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month after EXP.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist on how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What TumsUP Drops contains
Each ml contains:
Simethicone Emulsion equivalent to Simethicone USP 40 mg
Dill Oil BP 0.005 ml
Fennel Oil 0.0007 ml
In syrupy base
Packaging
A bottle of 30 ml
For More Information About This Product
Soventus®-LS Syrup
1.0 Generic Name
Levosalbutamol, Ambroxol Hydrochloride & Guaiphenesin Syrup
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each 5 ml Contains:
Levosalbutamol sulphate
equivalent to levosalbutamol 1 mg
Ambroxol Hydrochloride BP 30 mg
Guaiphenesin 50 mg
Excipient q. s.
Colour Tartrazine Supra
In a flavoured syrup base
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Syrup
100 ml bottle
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the symptomatic relief of bronchospasm in bronchial asthma & chronic bronchitis.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Children between 2 to 6 years: 2.5 ml to be administered 3 times daily.
Children between 6 to 12 years: 5 ml to be administered 3 times daily.
Adults and children above 12 years: 10 ml to be administered 3 times daily.
Soventus®-LS Syrup not be used with other cough and cold medicines. Do not exceed the stated dose. It is recommended to take Soventus®-LS Syrup with food.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to levosalbutamol, ambroxol, guaiphenesin or to any component of the formulation.
- Cardiac disease, and in patients with significant risk factors for myocardial ischemia.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Levosalbutamol
Levosalbutamol, as with all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; hyperthyroidism; diabetes mellitus; hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines; and convulsive disorders.
Significant changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure have been observed and may be expected to occur in some patients after use of any beta-adrenergic bronchodilators.
Patients with underlying severe heart disease (e.g., ischemic heart disease, arrhythmia or severe heart failure) should be warned to seek medical advice if they experience chest pain or other symptoms of worsening heart disease.
Attention should be paid to assessment of symptoms such as dyspnoea and chest pain, as they may be of either respiratory or cardiac origin. Due to the positive inotropic effects, beta 2-agonists should not be used in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Due to the hyperglycemic effects of β-2-agonists, additional blood glucose controls are recommended initially in diabetic patients. Potentially serious hypokalaemia may result from beta 2-agonist therapy. Particular caution is recommended in acute severe asthma as the associated risk may be augmented by hypoxia. The hypokalemic effect may be potentiated by concomitant treatments. It is recommended that serum potassium levels be monitored in such situations.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Ambroxol should be used with caution in patients with gastric ulceration. Care to be taken to avoid contact with eye, skin, serious ingestion or inhalation. In patients with symptoms of chronic impairment of mucus production and/or clearance, ambroxol should be used with caution. In patients with malignant cilia syndrome, the advantages of mucus liquefaction should be carefully weighed against the risk of a secretory obstruction.
The secretolytic effect of ambroxol may be supported by adequate fluid intake. The simultaneous administration of antitussives should definitely be avoided due to the risk of secretory obstruction.
There have been very rare reports of severe skin lesions such as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN, Lyell's Syndrome) in temporal association with the administration of mucolytic substances such as ambroxol hydrochloride. Mostly these could be explained by the severity of the underlying disease or concomitant medication. During the early phase of a Stevens-Johnson Syndrome or TEN, a patient may first experience nonspecific influenza-like prodromal symptoms e.g., fever, body ache, rhinitis, cough, and sore throat. If new skin or mucosal lesions occur, treatment with ambroxol hydrochloride should be discontinued as a precaution.
Guaiphenesin
Caution should be exercised in the presence of severe renal or severe hepatic impairment. The concomitant use of cough suppressants is not recommended. Guaiphenesin should not be administered in patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance. Guaiphenesin is considered to be unsafe in patients with porphyria.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Levosalbutamol
Other Adrenergic Bronchodilator Drugs: Other short-acting sympathomimetic bronchodilators or epinephrine should be used with caution with levosalbutamol. If additional adrenergic drugs are to be administered by any route, they should be used with caution to avoid deleterious cardiovascular effects.
Beta-blockers: Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists such as levosalbutamol, but may also produce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients.
Diuretics: Diuretics (such as loop or thiazide diuretics) can be acutely worsened by beta-agonists. Hence, caution is advised in the co-administration of beta-agonists with non-potassium sparing diuretics.
Digoxin: Digoxin levels were demonstrated after single-dose intravenous and oral administration of racemic salbutamol, hence it is advisable to carefully evaluate the serum digoxin levels in patients who are currently receiving digoxin and levosalbutamol.
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors or Tricyclic Antidepressants: Levosalbutamol should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of levosalbutamol on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Antibiotics: After using ambroxol, the concentrations of antibiotics such as amoxycillin, cefuroxime, and erythromycin in bronchial secretions and sputum are increased.
Antitussives: Concomitant administration of antitussives may impair the expectoration of liquefied bronchial mucus due to inhibition of the cough reflex and cause accumulation of secretions.
No clinically relevant interactions with other medications have been reported.
Guaiphenesin
Paracetamol: Guaiphenesin may increase the rate of absorption of paracetamol.
Laboratory Tests: If urine is collected within 24 hours of a dose of guaiphenesin, its metabolite may cause a color interference with laboratory determinations of urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA).
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnant Women
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of this combination in pregnant women. Transient hypoglycaemia has been reported in new-born preterm infants after maternal beta 2- agonist treatment. Ambroxol crosses the placenta. Animal studies do not show either direct or indirect harmful effects on pregnancy, embryo foetal development, parturition or postnatal development. Comprehensive controlled studies in pregnant women after the 28th week have not shown any harmful effects on the foetus. Use of ambroxol during the first trimester of pregnancy is not recommended. Guaiphenesin has been linked with an increased risk of neural tube defects in a small number of women with febrile illness in the first trimester of pregnancy. Soventus LS syrup should not be used during the first trimester of pregnancy. Caution is advised when Soventus®-LS Syrup is used during second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Lactating Women
It is not known whether levosalbutamol is excreted in human milk. Although ambroxol is excreted in the breast milk, adverse effects on the infants are unlikely. There is no information regarding effect of guaiphenesin on lactation. Use of Soventus®-LS Syrup is not recommended during lactation. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Patients
Safety and efficacy of this formulation in neonates and children below 2 years of age has not been established. Thus, Soventus®-LS Syrup is not recommended for use in paediatric patients below 2 years of age.
Geriatric Patients
Elderly patients with normal renal and hepatic function may be given the same dose as recommended for adults. Levosalbutamol is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Renal Impairment Patients
In severe renal impairment, accumulation of ambroxol metabolites has been reported. Therefore, caution should be exercised while using Soventus LS syrup in patients with significant renal dysfunction. Dose should be reduced or the dosing interval must be extended in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment Patients
In severe hepatic impairment, Soventus LS syrup should be used with caution.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have not been performed with Soventus®-LS Syrup. Ambroxol hydrochloride or guaiphenesin has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines. In some individuals, levosalbutamol may cause nervousness, headache, dizziness, fatigue and sleeplessness. Thus, caution should be exercised while taking Soventus LS syrup. If affected by dizziness, patients should avoid potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a vehicle or operating machinery.
4.8 Undesirable Effects
Levosalbutamol
The most frequent side effects are palpitation, fine tremors of the skeletal muscle (particularly the hand) and muscle cramps. The other likely side effects are gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, burning substernal or epigastric pain and diarrhoea. In some cases, nervousness, headache, dizziness, fatigue and sleeplessness may occur. Potentially serious hypokalaemia may result from β 2-agonist therapy. This effect may be potentiated by hypoxia. Particular caution is advised in severe asthma; in such cases, monitoring of serum potassium levels is recommended.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Occasional gastrointestinal side effects may occur, but these are normally mild. With prolonged administration in large doses, pain in epigastrium, nausea, vomiting can appear. Additional adverse effects reported rarely with ambroxol include:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and abdominal pain.
Respiratory, mediastinal, and thoracic disorders: Oral and pharyngeal hypoaesthesia, dry mouth, and dry throat.
Nervous system disorders: Dysgeusia (e.g., changed taste).
Immune system disorders: Anaphylactic reactions including anaphylactic shock.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Angioedema, rash, urticaria, pruritus, and other hypersensitivity reactions.
Allergic reactions: In patients having hypersensitivity to ambroxol, skin rash, nettle-rash, and angioneurotic oedema may occur.
Guaiphenesin
Side effects resulting from guaiphenesin administration are very rare. Guaiphenesin has occasionally been reported to cause gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, particularly in very high doses. Hypersensitivity reactions may occur. Allergic reactions, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, dyspnoea (reported in association with other symptoms of hypersensitivity), nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, rash, and urticaria have been reported very rarely with the use of guaiphenesin.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Ambroxol: Symptoms largely correspond with the known adverse effects in case of unintentional overdosing and/or medication errors. Symptomatic treatment is recommended if manifestations of poisoning do occur.
The expected symptoms with overdosage are those of excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation and/or occurrence or exaggeration of any of the side effects, e.g. tachycardia, nervousness, headache, tremor, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, and sleeplessness. Hypokalaemia may also occur. As with all sympathomimetic medications, cardiac arrest and even death may be associated with the abuse of levosalbutamol. Treatment consists of discontinuation of levosalbutamol together with appropriate symptomatic therapy. The judicious use of a cardio-selective beta-receptor blocker may be considered, bearing in mind that such medication can produce bronchospasm. There is insufficient evidence to determine if dialysis is beneficial for overdosage of levosalbutamol.
The effects of acute toxicity from Guaifenesin may include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea and drowsiness. The drug is, however, rapidly metabolised and excreted in the urine.
Patients should be kept under observation and symptomatic and supportive treatment is advised.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Levosalbutamol
Levosalbutamol is a selective beta 2-receptor agonist. Levosalbutamol produces bronchodilation through stimulation of beta 2-adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscles, thereby causing relaxation of bronchial muscle fibres. Activation of beta 2- adrenergic receptors on airway smooth muscle leads to the activation of adenyl cyclase and to an increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic-3′, 5′-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP). The increase in cyclic AMP is associated with the activation of protein kinase A, which in turn, inhibits the phosphorylation of myosin and lowers intracellular ionic calcium concentrations, resulting in muscle relaxation. Levosalbutamol relaxes the smooth muscles of all airways, from the trachea to the terminal bronchioles.
Levosalbutamol also has a mild anti-inflammatory activity. This is because increased concentration of cyclic AMP is associated with inhibition of the release of inflammatory/bronchoconstrictor mediators from mast cells and eosinophils in the airways.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Ambroxol causes an increase of secretion in the respiratory tract. It enhances pulmonary surfactant production and stimulates ciliary activity. These actions result in improved mucus flow and transport (mucociliary clearance). Improvement of mucociliary clearance has been shown in clinical pharmacologic studies. Enhancement of fluid secretion and mucociliary clearance facilitates expectoration and reduces cough.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin is thought to exert its expectorant action by stimulating receptors in the gastric mucosa. This increases the output from secretory glands of the gastrointestinal system and increases the flow of fluids from glands lining the respiratory tract. The result is an increase in volume and decrease in viscosity of bronchial secretions. Another possible mechanism by which it acts is by increasing the water bonding in the sputum, thereby decreasing its viscosity and leading to an increase in mucokinesis.
Other actions may include stimulation of vagal nerve endings in bronchial secretory glands and stimulating certain centers in the brain, which in turn enhance respiratory fluid flow.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Levosalbutamol
Levosalbutamol, the (R)-enantiomer of salbutamol, is a selective beta 2-receptor agonist. Levosalbutamol has approximately 2-fold greater affinity than racemic salbutamol for the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and approximately 100-fold greater affinity than S-salbutamol. Levosalbutamol is a single isomer beta 2-agonist that differs from racemic salbutamol by elimination of (S)-salbutamol. Levosalbutamol is an effective bronchodilator whose primary mechanism of action is unimpeded by (S)-salbutamol. Therefore, when compared with racemic salbutamol, clinically comparable bronchodilation can be achieved with lesser doses of levosalbutamol. Further, levosalbutamol also substantially decreases beta-mediated side effects associated with racemic salbutamol.
Levosalbutamol has bronchodilator, bronchoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and anti-edematous properties.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Ambroxol is the active metabolite of bromhexine. Ambroxol is more effective than bromhexine and is non-toxic and well tolerated. Ambroxol possesses mucolytic, mucokinetic (improvement in mucus transport), and secretolytic properties. It promotes the removal of tenacious secretions from the respiratory tract and reduces mucus stasis (arresting the secretion of mucus). Ambroxol also exhibits anti-oxidant activity.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin produces its expectorant action by increasing the volume of respiratory tract fluid and reducing the viscosity of tenacious secretions.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Levosalbutamol
Levosalbutamol [(R)-salbutamol] appears to be stereochemically stable in vivo and does not appear to interconvert metabolically to (S)-salbutamol.
Absorption: Whether administered alone or as the racemate, salbutamol enantiomers are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and have time to maximum drug concentration (Tmax) values ranging from 45 to 360 minutes. The bioavailability of levosalbutamol increases from 9% after a single oral dose to 30% at steady state.
Distribution: The blood to plasma ratio for total salbutamol appears to be near unity (0.96 ± 0.13) in healthy volunteers, suggesting that the total blood clearance of salbutamol is equal to the total plasma clearance once steady state has been reached. Values for binding to blood components, along with similar volumes of distribution for salbutamol enantiomers, suggest that protein binding plays a relatively minor role in the disposition of salbutamol enantiomers.
Metabolism: The intestine is the main site of enantio-selective presystemic metabolism of salbutamol for drug absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The clearance of salbutamol by the human body is to a major extent is dependent on sulphate conjugation, in particular after oral dosing. Racemic salbutamol is metabolized by sulphotranferase 1A3 (SULT1A3) to an inactive metabolite in human tissues. However, (R)-salbutamol (levosalbutamol) is sulphated 8-fold faster than (S)-salbutamol because of its higher binding affinity for the enzyme.
Elimination: Calculated renal clearance values for both enantiomers were significantly larger than creatinine clearance, indicating active renal excretion. This leads to relatively higher concentrations of the drug in urine than in plasma.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Ambroxol is absorbed rapidly and almost completely after oral administration. Oral bioavailability is approximately 60% owing to the first-pass effect. Bioavailability of ambroxol hydrochloride is not affected by food. Plasma concentrations are in a linear relationship to the dose. Peak plasma levels are attained after 0.5 to 3 hours. Plasma protein binding is around 90% in the therapeutic range. After oral, intravenous, and intramuscular administration, ambroxol is distributed swiftly and extensively from the blood into the tissues. The highest active ingredient concentrations have been measured in the lung.
Ambroxol is metabolized in the liver mainly by conjugation. Studies in human liver microsomes showed that CYP3A4 is the predominant isoform for ambroxol metabolism. Around 30% of an oral dose is eliminated via the first-pass effect. The terminal half-life is about 10 hours. Total clearance is 660 ml/min approximately, and renal clearance is 8% of the total clearance.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. However, limited information is available regarding its pharmacokinetics. After the administration of 600 mg guaiphenesin to healthy adult volunteers, the Cmax was approximately 1.4 mcg/ml, Tmax occurred approximately 15 minutes after drug administration, t½ was approximately 1 hour and the drug was not detectable in the blood after approximately 8 hours. Guaiphenesin appears to undergo both oxidation and demethylation.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Levosalbutamol
Carcinogenicity: Although there have been no carcinogenesis studies with levosalbutamol, racemic salbutamol Sulphate has been evaluated for its carcinogenic potential. In a 2-year study in Sprague-Dawley rats, dietary administration of racemic salbutamol Sulphate resulted in a significant dose-related increase in the incidence of benign leiomyomas of the mesovarium at doses of 2 mg/kg/day and greater. In an 18- month study in CD-1 mice and a 22-month study in the golden hamster, dietary administration of racemic salbutamol Sulphate showed no evidence of tumorigenicity. Dietary doses in CD-1 mice were up to 500 mg/kg/day and doses
in the golden hamster study were up to 50 mg/kg/day. Mutagenesis: Levosalbutamol HCl was not mutagenic in the Ames test or the CHO/HPRT Mammalian Forward Gene Mutation Assay. Levosalbutamol was not clastogenic in the in vivo micronucleus test in mouse bone marrow. Racemic salbutamol Sulphate was not clastogenic in an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in CHO cell cultures. Impairment of Fertility: No fertility studies have been conducted with levosalbutamol. Reproduction studies in rats using racemic salbutamol sulphate demonstrated no evidence of impaired fertility at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day. Teratogenicity: In animal studies, oral administration of levosalbutamol HCl to regnant New Zealand White rabbits found no evidence of teratogenicity at doses up to 25 mg/kg/day. However, other studies demonstrated that racemic salbutamol Sulphate was teratogenic in mice and rabbits at doses comparable to the human therapeutic range. Pregnant mice administered racemic salbutamol Sulphate subcutaneously (s.c.) had a dose-related increased incidence of cleft palate in their fetuses. The drug did not induce cleft palate formation when administered subcutaneously at a dose of 0.025 mg/ kg/day. In addition, oral administration of racemic salbutamol Sulphate to pregnant rabbits resulted in an increased incidence of cranioschisis in foetuses.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Toxicity: Ambroxol hydrochloride has a low index for acute toxicity. In repeat-dose studies, oral doses of 150 mg/kg/day (mouse, 4 weeks), 50 mg/kg/day (rat, 52 and 78 weeks), 40 mg/kg/day (rabbit, 26 weeks) and 10 mg/kg/day (dog, 52 weeks) were the no-observed adverse effect level (NOAEL). No toxicological target organs were detected. Four-week intravenous toxicity studies with ambroxol hydrochloride in rats (4, 16 and 64 mg/kg/day) and in dogs (45, 90 and 120 mg/kg/day (infusion 3 h/day)) showed no severe local and systemic toxicity including histopathology. All adverse effects were reversible. At 500 mg/kg/day, ambroxol hydrochloride was slightly toxic for dams and pups, as shown by a retarded body-weight development and reduced litter size.
Carcinogenicity: Ambroxol hydrochloride did not show any tumorigenic potential in carcinogenicity studies in mice (50, 200 and 800 mg/kg/day) and rats (65, 250 and 1000 mg/kg/day) when treated with a dietary admixture for 105 and 116 weeks, respectively. Mutagenesis: Genotoxicity studies in vitro (Ames and chromosome aberration test) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus test) did not reveal any mutagenic potential of ambroxol hydrochloride.
Impairment of Fertility: The fertility of male and female rats was not affected up to 500 mg/kg/day. The NOAEL in the peri- and post-natal development study was 50 mg/kg/day. Teratogenicity: Ambroxol hydrochloride was neither embryotoxic nor teratogenic when tested at oral doses up to 3000 mg/kg/day in rats and up to 200 mg/kg/day in rabbits.
Guaiphenesin
There is no relevant information available.
7.0 Description
Each 5 ml of Soventus LS syrup contain 1 mg of levosalbutamol, 30 mg of ambroxol hydrochloride, and 50 mg of guaiphenesin for oral administration. Levosalbutamol Levosalbutamol, also called as levalbuterol, is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist used as a bronchodilator.
Molecular Weight: 337.39 g/mol. Molecular Formula: C13H23NO7S. Chemical Name: 4-[(1R)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol; sulfuric acid.
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Ambroxol hydrochloride is a metabolite of bromhexine that stimulates mucociliary action and clears the air passages in the respiratory tract. Molecular Weight: 414.56 g/mol. Molecular Formula: C13H19Br2ClN2O. Chemical Name: 4-[(2-amino-3,5-dibromophenyl)methylamino]cyclohexan-1 ol; hydrochloride.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin, also called as Guaiphenesin or glyceryl guaiacolate, is an expectorant which promotes or facilitates the removal of secretions from the respiratory tract. Guaiphenesin is a white or slightly gray crystalline substance with a slightly bitter aromatic taste. Molecular Weight: 198.21 g/mol. Molecular Formula: C10H14O4. Chemical Name: 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
8.2 Shelf life
Refer on Pack
8.3 Storage and handling information
Store below 25°C.
Protect from light.
Do not freeze.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What Soventus®-LS Syrup is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take Soventus®-LS Syrup
3. How to take Soventus®-LS Syrup
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Soventus®-LS Syrup
6. Contents of the pack and other Information
1. What is Soventus®-LS Syrup and what it is used for
Soventus®-LS Syrup is the combination of Levosalbutamol, Ambroxol Hydrochloride & Guaiphenesin Syrup. These active ingredients belong to a group of medicines known as bronchodilators, mucolytic and mucokinetic used to treat asthma, bronchospasm and reversible airways obstruction by widening the airways of the lungs. It is suitable for children or adults who prefer liquid medicines or are unable to use an inhaler device.
Ambroxol hydrochloride widely used as a mucolytic. It increases secretion in the respiratory tract and stimulates ciliary activity. These actions result in improved mucus flow and clearance. Enhancement of fluid secretion and mucociliary clearance facilitates expectoration and reduces cough. Levosalbutamol is used as a bronchodilator, used to treat bronchospasm and symptoms of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. It relaxes the muscles in the airways and increases airflow to the lungs. Levosalbutamol makes breathing easier by widening the airways. By bronchodilator action, it also increases mucociliary clearance, suppression of oedema and exerts anti- allergic effects. Guaifenesin is an expectorant that also has some muscle relaxing action. It is used in many cough preparations. This increases the flow of fluids from glands lining the respiratory tract. This results in an increase in volume and decrease in viscosity of bronchial secretions.
2. What you need to know before you take Soventus®-LS Syrup
Do not take Soventus®-LS Syrup if you:
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formulation.
- Pre-existing ischaemic heart disease or those patients with significant risk factors for ischaemic heart disease.
- Gastric ulceration.
Warnings and precautions
In cases of severe renal failure, an accumulation of metabolites formed in the liver must be considered, and a reduction in the maintenance dose of Ambroxol or an increase in the dose interval must be performed. In patients with a tendency for peptic ulcers, the use of Ambroxol hydrochloride should be carefully considered.
For Levosalbutamol, caution should be observed in patients with thyrotoxicosis. Cardiovascular effects may be seen with sympathomimetic drugs, including Levosalbutamol.
Guaifenesin should not be used for persistent or chronic cough, such as occurs with asthma, or where cough is accompanied by excessive secretions, unless directed by a physician. Caution should be exercised in the presence of severe renal or severe hepatic impairment. The concomitant use of cough suppressants is not recommended.
Other medicines and Soventus®-LS Syrup
The concomitant use of antitussives along with ambroxol may impair the coughing up of the liquefied bronchial mucous and cause a secretory obstruction.
The administration of ambroxol with antibiotics (amoxicillin, cefuroxime, and erythromycin) increases the concentration of antibiotics in bronchopulmonary secretions and sputum.
Levosalbutamol and non-selective β-blockers should not be administered concurrently. Levosalbutamol should be used with caution in patients receiving other sympathomimetic.
Levosalbutamol should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of these agents, since the action of Levosalbutamol on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Soventus®-LS Syrup with food and drink
It is recommended to take Soventus®-LS Syrup with food.
Use in Special Population:
Pregnancy
Since there are no adequate and well-controlled studies of this combination in pregnant women, this medicine should be administered with caution.
Lactation
Levosalbutamol is secreted into breast milk, but any effect on the infant is unlikely at therapeutic doses. Transient hypoglycaemia has been reported in new-born preterm infants after maternal β-2 agonist treatment. Since Guaifenesin is excreted in breast milk in small amounts, decision must be made to continue with the medicine if benefit of drug outweighs the risks of treatment.
Geriatric Population
They are more sensitive to the effects of Levosalbutamol; hence a lower dose may be required.
Pediatric population
Not recommended for children below 2 years of age.
Hepatic & Renal Insufficiency
Caution should be exercised in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment and liver disease.
Effects on ability to drive and use machine
Patients should be cautioned against engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery until their response to Soventus syrup is known.
3. How to take Soventus®-LS Syrup
Always take Soventus syrup exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Taking this medicine
- Take this medicine by mouth.
- If you feel that this medicine is too weak or too strong, do not change the dose yourself, but ask your doctor.
How much to take
Children between 2 to 6 years: 2.5 ml to be administered 3 times daily.
Children between 6 to 12 years: 5 ml to be administered 3 times daily.
Adults and children above 12 years: 10 ml to be administered 3 times daily.
If you take more Soventus®-LS Syrup than you should
If you take more Soventus syrup than you should, tell a doctor or go to a hospital casualty department straight away. Take the medicine pack with you. This is so the doctor knows what you have taken.
If you forget to take Soventus®-LS Syrup
If you forget a dose, do not worry. Just wait until the next dose is due. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
4. Possible Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions with Ambroxol are nausea, oral and pharyngeal hypoesthesia, dyspepsia, dry mouth, abdominal pain and allergic reactions such as skin rash or urticaria can also occur.
Tremor and headache are the most common adverse events observed with Levosalbutamol administration. Tachycardia, palpitations, muscle spasms and hypokalaemia are few other common adverse reactions observed.
Guaifenesin has occasionally been reported to cause gastro-intestinal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, particularly in very high doses. Allergic reactions, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, dyspnoea (reported in association with other symptoms of hypersensitivity), nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, rash and urticaria may also occur.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Soventus®-LS Syrup
- Store below 250C, protected from light & moisture.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
- Keep away from the reach of children. Do not freeze.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Soventus®-LS Syrup contains:
Each 5 ml Contains:
Levosalbutamol sulphate
equivalent to levosalbutamol IP 1 mg
Ambroxol Hydrochloride IP 30 mg
Guaiphenesin IP 50 mg
Excipients q. s.
1x100ml, PET Bottle
For More Information About This Product
Soventus® Jr. Syrup
1.0 Generic Name
Ambroxol Hydrochloride, Terbutaline Sulphate & Guaiphenesin syrup
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each 5 ml contains:
10 mg
Terbutaline Sulphate USP 0.5 mg
Guaiphenesin USP 25 mg
Excipients q. s.
In a mentholated flavoured syrup base.
3.0 Dosage form and Strength
Syrup, 60ml
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For symptomatic relief of bronchospasm in bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Children (under 6 years): 5 - 10 ml thrice daily
Children (6-12 years): 10 ml thrice daily
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formulation
- Patients with pre-existing ischaemic heart disease or those patients with significant risk factors for ischaemic heart disease
- Gastric ulceration
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Terbutaline
As for all beta 2-agonists caution should be observed in patients with thyrotoxicosis.
Cardiovascular effects may be seen with sympathomimetic drugs, including terbutaline. There is some evidence from post-marketing data and published literature of myocardial ischaemia associated with beta agonists. Terbutaline, like all other beta-adrenergic agonists, can produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by pulse rate, blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Although such effects are uncommon after administration of terbutaline at recommended doses, if they occur, the drug may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta-agonists have been reported to produce electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, such as flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Therefore, terbutaline, like all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypertension.
Due to the positive inotropic effect of beta 2-agonists, these drugs should not be used in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Terbutaline, as with all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; hyperthyroidism; diabetes mellitus; hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines; and convulsive disorders. Significant changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure have been seen and could be expected to occur in some patients after use of any beta-adrenergic bronchodilator.
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions and exacerbation of bronchospasm have been reported after terbutaline administration. Beta-adrenergic agonist medications may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects. The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation.
Large doses of intravenous terbutaline have been reported to aggravate preexisting diabetes and ketoacidosis.
Tocolysis
Terbutaline should be used with caution in tocolysis and supervision of cardiorespiratory function, including ECG monitoring, should be considered. Treatment should be discontinued if signs of myocardial ischaemia (such as chest pain or ECG changes) develop. Terbutaline should not be used as a tocolytic agent in patients with significant risk factors for or pre-existing heart disease.
During infusion treatment in pregnant women with beta 2-stimulants in combination with corticosteroids a rare complication with a pathological picture resembling pulmonary oedema, has been reported.
Increased tendency to uterine bleeding has been reported in connection with Caesarean section. However, this can be effectively stopped by propranolol 1-2 mg injected intravenously.
Respiratory indications
Patients with underlying severe heart disease (e.g. ischaemic heart disease, arrhythmia or severe heart failure) who are receiving Terbutaline should be warned to seek medical advice if they experience chest pain or other symptoms of worsening heart disease.
Attention should be paid to assessment of symptoms such as dyspnoea and chest pain, as they may be of either respiratory or cardiac origin.
Due to the hyperglycaemic effects of beta 2-agonists, additional blood glucose controls are recommended initially in diabetic patients.
Potentially serious hypokalaemia may result from beta 2-agonist therapy. Particular caution is recommended in acute severe asthma as the associated risk may be augmented by hypoxia.
The hypokalaemic effect may be potentiated by concomitant treatments. It is recommended that serum potassium levels are monitored in such situations.
If a previously effective dosage regimen no longer gives the same symptomatic relief, the patient should urgently seek further medical advice. Consideration should be given to the requirements for additional therapy (including increased dosages of anti-inflammatory medication). Severe exacerbations of asthma should be treated as an emergency in the usual manner.
There have been rare reports of seizures in patients receiving terbutaline; seizures did not recur in these patients after the drug was discontinued.
Ambroxol
Care to be taken to avoid contact with eye, skin, serious ingestion or inhalation.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin should be not used for persistent or chronic cough, such as occurs with asthma, or where cough is accompanied by excessive secretions, unless directed by a physician. A persistent cough may be a sign of a serious condition. If cough persists for more than 7 days, tends to recur, or is accompanied by a fever, rash, or persistent headache, a physician should be consulted. Caution should be exercised in the presence of severe renal or severe hepatic impairment. The concomitant use of cough suppressants is not recommended. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not take this medicine. Not more than 4 doses should be given in any 24 hours. Avoid with any other cough and cold medicine. Consult a pharmacist or other healthcare professional before use in children under 6 years. Stop use and ask a healthcare professional if your cough lasts for more than 5 days, comes back, or is accompanied by a fever, rash, or persistent headache. Do not take with a cough suppressant. Do not give this medicine with any other cough or cold medicines.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Terbutaline
Beta-blocking agents (including eye drops); especially the non-selective ones such as propranolol, may partially or totally inhibit the effect of beta-stimulants. Therefore, terbutaline preparations and non-selective beta-blockers should not normally be administered concurrently. Terbutaline should be used with caution in patients receiving other sympathomimetics.
Halogenated Anaesthetics
Halothane anaesthesia should be avoided during beta 2-agonists treatment, since it increases the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Other halogenated anaesthetics should be used cautiously together with beta 2-agonists.
Potassium depleting agents and hypokalaemia
Owing to the hypokalaemic effect of beta-agonists, concurrent administration with terbutaline of serum potassium depleting agents known to exacerbate the risk of hypokalaemia, such as diuretics, methyl xanthines and corticosteroids, should be administered cautiously after careful evaluation of the benefits and risks with special regard to the increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias arising as a result of hypokalaemia. Hypokalaemia also predisposes to digoxin toxicity. Hypokalaemia may result from beta 2-agonist therapy and may be potentiated by concomitant treatment with xanthine derivatives, corticosteroids and diuretics.
Terbutaline should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, since the action of terbutaline on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Ambroxol
No data available
Guaiphenesin
If urine is collected within 24 hours of a dose of Guaiphenesin, its metabolite may cause a colour interference with laboratory determinations of urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA).
Others
Soventus Jr. Syrup should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus, serious cardiovascular disorders, hypertension, hyperthyroidism and peptic ulcers.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
However, there are no adequate and well-controlled studies of this combination in pregnant women. Hence this combination should be administered with caution in pregnancy.
Lactation
It is not known whether this combination is secreted in breast milk. However, terbutaline is secreted in breast milk, but effect on the infant is unlikely at therapeutic doses. Therefore, this combination should be used with caution in nursing mothers.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Patients should be cautioned against engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery until their response to Soventus Jr syrup is known.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Under individual hypersensitivity to Ambroxol allergic reactions such as skin rash, nettle-rash, and angioneurotic oedema are possible. Under the prolonged administration in large doses pain in epigastrial area, nausea, vomiting can appear.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and abdominal pain.
Respiratory, Mediastinal and Thoracic Disorders: Oral and pharyngeal hypoaesthesia, dry mouth and dry throat.
Nervous System Disorders: Dysgeusia (e.g., changed taste).
Immune System Disorders: Anaphylactic reactions including anaphylactic shock.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Angioedema, rash, urticaria, pruritus and other hypersensitivity.
Terbutaline Sulphate
Most of the adverse reactions are characteristic of sympathomimetic amines. The majority of these effects have reversed spontaneously within the first 1-2 weeks of treatment. The frequency of side-effects is low at the recommended doses.
The common adverse reactions to terbutaline are tremor, headache, tachycardia, palpitations, muscle spasms and hypokalaemia, nervousness, somnolence, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia, extra systoles ventricular, vasodilations, nausea, dry mouth, asthenia, sweating.
The following adverse effects each occurred in fewer than 1% of patients: hallucinations, rash, paraesthesia, hypertonia, (muscle cramps), vomiting.
There have been rare reports of elevation in liver enzymes and of hypersensitivity vasculitis.
Rare cases of arrhythmias e.g. atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and extra systoles, myocardial ischaemia, peripheral vasodilation, hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema, bronchospasm, hypotension, collapse, nausea, mouth and throat irritation, sleep disorder, behavioural disturbances such as agitation and restlessness, paradoxical bronchospasm, urticaria and rash.
Guaiphenesin
Side effects resulting from Guaiphenesin administration are very rare. Guaiphenesin has occasionally been reported to cause gastro-intestinal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, gastrointestinal discomfort particularly in very high doses. Also, hypersensitivity reactions may occur. The frequency of these guaiphenesin-related adverse reactions is unknown but based on estimate from post-marketing data are likely to be rare: Allergic reactions, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, dyspnoea (reported in association with other symptoms of hypersensitivity), nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, rash, urticaria.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Terbutaline
Possible Symptoms and Signs: Headache, anxiety, tremor, nausea, tonic cramp, palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmia. A fall in blood pressure sometimes occurs.
Laboratory findings like hypokalaemia, hyperglycaemia and lactic acidosis sometimes occur.
Treatment
Mild and moderate cases: Reduce the dose.
Severe cases: Gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal. Determination of acid-base balance, blood sugar and electrolytes, particularly serum potassium levels. Monitoring of the heart rate and rhythm and blood pressure. Metabolic changes should be corrected.
A cardioselective beta-blocker (e.g. metoprolol) is recommended for the treatment of arrhythmias causing haemodynamic deterioration. The beta-blocker should be used with care because of the possibility of inducing bronchoconstriction: use with caution in patients with a history of bronchospasm. If the beta 2-mediated reduction in the peripheral vascular resistance significantly contributes to the fall in blood pressure, a volume expander should be given.
Preterm labour: Pulmonary oedema: discontinue administration. A normal dose of loop diuretic (e.g. Furosemide) should be given intravenously.
Increased bleeding in connection with Caesarian section: propranolol, 1-2mg intravenously.
Ambroxol
Acute potential health effects include skin irritation, eye irritation, respiratory tract irritation, gastrointestinal tract irritation with decreased motility or constipation, ulceration or bleeding from the stomach or duodenum, peritonitis. It may even affect behavior/central nervous system (tremor, convulsions, ataxia, and somnolence), respiration (dyspnea, respiratory stimulation), liver, blood (changes if white blood cell count), and urinary system. No data available on chronic potential health effects.
Guaiphenesin
The effects of acute toxicity from Guaiphenesin may include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea and drowsiness. The drug is, however, rapidly metabolised and excreted in the urine. Patients should be kept under observation and treated symptomatically. Overdosage may also give rise to nausea and vomiting. Treatment need only be symptomatic and supportive.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Terbutaline
Terbutaline is a selective beta 2 - adrenergic causing bronchodilation; increase in mucociliary clearance; suppression of oedema and anti-allergic effects.
The pharmacologic effects of beta-adrenergic agonist drugs, including terbutaline, are at least in part, attributable to stimulation through beta-adrenergic receptors on intracellular adenyl cyclase, the enzyme that catalyses the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic-3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP). Increased cyclic AMP levels are associated with relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and inhibition of release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity from cells, especially from mast cells.
Ambroxol
Ambroxol (group of benzilamides) belongs to secretolitical and secretomotoric medicinal products. It possesses expressed expectorant effect. Mechanism of action of the medicinal product is stipulated by stimulation of serous cells of tonsils of bronchial tubes' mucous membrane, increasing of mucous secretion content and changing of correlation of serous and mucous components of phlegm, breached under pathological processes in lungs. Under this hydrolyzing ferments activate and releasing of lizosoms from Clark's cells strengthens, that causes decreasing of viscosity of phlegm. Ambroxol increases content of surfactant in lungs, which is dealt with strengthening of synthesis of the last and secretion in alveolar pneumocytes, and also with breach of its disintegration. The medicinal product increases mucociliar transport of phlegm. It suppresses coughing insignificantly. Ambroxol well penetrates through the placenta barrier, improving synthesis of surfactants during uterine life of foetus, and also it has an ability to warn syndrome of insufficient breathing in newborn. The medicinal product does not cause immense creating of secretion, reduces spastic hyperactivity of bronchial tubes- one of the main factors of developing of bronchial asthma under allergy. Ambroxol is more effective, than its predecessor - Bromhexine; it is non-toxic one and well endured by patients. Action of retard form of Ambroxol is kept in 9-10 hours after administration inside.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin is thought to exert its pharmacological action by stimulating receptors in the gastric mucosa. This increases the output from secretory glands of the gastrointestinal system and reflexly increases the flow of fluids from glands lining the respiratory tract. The result is an increase in volume and decrease in viscosity of bronchial secretions. Other actions may include stimulating vagal nerve endings in bronchial secretory glands and stimulating certain centres in the brain, which in turn enhance respiratory fluid flow. Guaiphenesin produces its expectorant action within 24 hours.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Terbutaline
Basic parameters have been evaluated in man after oral administration of therapeutic doses, e.g.
Renal clearance (CLR): 1.925/ml/min (males)
Renal clearance (CLR): 2.32ml/min (females)
Terminal half-life T½ has been determined after single and multiple dosing (mean values varied between 16-20 h)
Bioavailability: Food reduces bioavailability following oral dosing (10% on average). Fasting values of 14-15% have been obtained.
Metabolism: The main metabolite after oral dosing is the sulphate conjugate and also some glucoronide conjugate can be found in the urine.
Ambroxol
Absorption: Ambroxol is rapidly absorbed (70 - 80%) after oral administration. The time to reach peak plasma concentration is approximately 2 hours.
Distribution: The distribution half-life of ambroxol is around 1.3 hours.
Metabolism: Metabolite is dibromoanthranilic acid (activity unspecified).
Excretion: Excretion is primarily via the kidneys. Renal clearance (rate) is approximately 53 ml/minute; approximately 5-6% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. The elimination half-life of ambroxol is biphasic, with an alpha half-life of 1.3 hours and a beta half-life of 8.8 hours.
Guaiphenesin
Absorption: Guaiphenesin is well absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract following oral administration, although limited information regarding its pharmacokinetics is available. After the administration of 600 mg Guaiphenesin to healthy adult volunteers, the C max was approximately 1.4ug/ml, with t max occurring approximately 15 minutes after drug administration.
Distribution: No information is available on the distribution of Guaiphenesin in humans.
Metabolism and elimination: Guaiphenesin appears to undergo both oxidation and demethylation. Following an oral dose of 600 mg Guaiphenesin to 3 healthy male volunteers, the t½ was approximately 1 hour and the drug was not detectable in the blood after approximately 8 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in Renal/Hepatic Impairment: There have been no specific studies of Guaiphenesin in subjects with renal or hepatic impairment. Caution is therefore recommended when administering this product to subjects with severe renal or hepatic impairment.
6.0 Preclinical safety data
Not Applicable
7.0 Description
Soventus Jr. Syrup is a combination of Terbutaline sulphate, Ambroxol hydrochloride and Guaiphenesin.
Terbutaline sulphate is a beta-adrenergic agonist bronchodilator available as syrup for oral administration. Terbutaline sulphate is ±-alpha-[(tert-butylamino) methyl]-3,5-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol sulphate (2:1) (salt).
The empirical formula is (C12H19NO3)2H2SO4 and the structural formula is

Guaiphenesin, a member of methoxybenzenes is an expectorant. The physiologic effect of guaifenesin is by means of decreased respiratory secretion viscosity, and increased respiratory secretions.

Chemical Name: 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propane-1,2-diol
Molecular formula: C10H14O4
Molecular Weight: 198.22 g/mol
Ambroxol hydrochloride is an aromatic amine. A metabolite of Bromhexine that stimulates mucociliary action and clears the air passages in the respiratory tract. It is usually administered as the hydrochloride.
Chemical Name: 4-[(2-amino-3,5-dibromophenyl)methylamino]cyclohexan-1-ol;hydrochloride
Molecular Formula: C13H19Br2ClN2O
Molecular Weight: 414.56 g/mol

8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 List of excipients
Menthol, Disodium Edetate, Sodium Benzoate, Sucralose, Glycerol,Propylene Glycol, Liquid Sorbitol (Non Crystallising), Hydroxyethyl Cellulose , Potassium Sorbate, Colour Tartrazine Supra Soluble , Flavour Honey, Flavour Lemon Lime AF- 2422, Flavour Mixed Fruit AF-2270 ,, Sodium Citrate, Citric Acid Monohydrate.
8.2 Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
8.3 Shelf life
24 months
8.4 Nature and contents of container
Soventus Junior: PET Bottle 1x60ml
8.5 Special precautions for storage and handling
Protect from light. Store below 250C. Keep out of reach of children. No special requirements for disposal. Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. Shake Well Before Use.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Do not take with any other cough or cold medicines.
Avoid contact with eye, skin and serious ingestion or inhalation of the Syrup.
Avoid taking the it if you have severe renal or severe hepatic impairment.
Do not take it if you are pregnant or breast-feeding without consulting doctor.
Stop taking Soventus Jr syrup and inform your doctor if your cough persists for more than 1 week, tends to recur, or is accompanied by a fever, rash or persistent headache.
In some patients it may cause common side effects like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, allergic reaction, dizziness, headache, rash, urticaria, tremor, palpitations, muscle cramp and increased heart rate. Inform your doctor if you experience any persistent problem while taking this medicine.
If you miss a dose of Soventus Jr syrup, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not double the dose.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, please ask your child’s doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as your child’s.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your child’s doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
- The full name of this medicine is Ambroxol Hydrochloride, Terbutaline Sulfate, & Guaiphenesin Syrup but within the leaflet it will be referred to as Soventus Jr syrup.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What Soventus® Jr. Syrup is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before your child takes Soventus® Jr. Syrup
3. How to take Soventus® Jr. Syrup
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Soventus® Jr. Syrup
6. Contents of the pack and other Information
1. What is Soventus® Jr. Syrup and what it is used for
Soventus Jr Syrup is a combination of Terbutaline sulphate, ambroxol hydrochloride and Guaiphenesin.
Terbutaline is a selective beta 2 -adrenergic agonist which predominantly stimulates beta 2-receptors, thus producing relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle. Ambroxol possesses mucokinetic (improvement in mucus transport) and secretolytic (liquifies secretions) properties. It promotes the removal of tenacious secretions in the respiratory tract and reduces mucus stasis (arresting the secretion of mucus). Besides that, Ambroxol also exhibits anti-oxidant activity. Guaiphenesin, by increasing respiratory tract fluid, reduces the viscosity of tenacious secretions and acts as an expectorant. Another possible mechanism by which it acts is by increasing the water bonding in the sputum, thereby decreasing its viscosity and leading to an increase in mucokinesis. Guaiphenesin is effective in both productive and non-productive coughs.
Soventus Jr syrup is used for the symptomatic relief of bronchospasm in bronchial asthma & chronic bronchitis.
Your child’s doctor will determine how Soventus Jr syrup should be used depending on the symptoms and severity of your child’s disease.
2. What you need to know before you take Soventus® Jr. Syrup
Do not take Soventus Jr syrup if your child is:
- hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formulation.
- pre-existing ischaemic heart disease or those patients with significant risk factors for ischaemic heart disease.
- gastric ulceration.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your child’s doctor, pharmacist or nurse before using Soventus® Jr. Syrup
Terbutaline
As for all beta 2-agonists caution should be observed in patients with thyrotoxicosis.
Cardiovascular effects may be seen with sympathomimetic drugs, including terbutaline. There is some evidence from post-marketing data and published literature of myocardial ischaemia associated with beta agonists. Terbutaline, like all other beta-adrenergic agonists, can produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by pulse rate, blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Although such effects are uncommon after administration of terbutaline at recommended doses, if they occur, the drug may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta-agonists have been reported to produce electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, such as flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Therefore, terbutaline, like all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypertension.
Due to the positive inotropic effect of beta 2-agonists, these drugs should not be used in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Terbutaline, as with all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; hyperthyroidism; diabetes mellitus; hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines; and convulsive disorders. Significant changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure have been seen and could be expected to occur in some patients after use of any beta-adrenergic bronchodilator.
Beta-adrenergic agonist medications may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects. The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Large doses of intravenous terbutaline have been reported to aggravate pre-existing diabetes and ketoacidosis.
Respiratory indications
Patients with underlying severe heart disease (e.g. ischaemic heart disease, arrhythmia or severe heart failure) who are receiving Terbutaline should be warned to seek medical advice if they experience chest pain or other symptoms of worsening heart disease.
Attention should be paid to assessment of symptoms such as dyspnoea and chest pain, as they may be of either respiratory or cardiac origin.
Due to the hyperglycaemic effects of beta 2-agonists, additional blood glucose controls are recommended initially in diabetic patients.
Potentially serious hypokalaemia may result from beta 2-agonist therapy. Particular caution is recommended in acute severe asthma as the associated risk may be augmented by hypoxia. The hypokalaemic effect may be potentiated by concomitant treatments. It is recommended that serum potassium levels are monitored in such situations.
If a previously effective dosage regimen no longer gives the same symptomatic relief, the patient should urgently seek further medical advice. Consideration should be given to the requirements for additional therapy (including increased dosages of anti-inflammatory medication). Severe exacerbations of asthma should be treated as an emergency in the usual manner.
There have been rare reports of seizures in patients receiving terbutaline; seizures did not recur in these patients after the drug was discontinued.
Ambroxol
Care to be taken to avoid contact with eye, skin, serious ingestion or inhalation.
Guaiphenesin
Guaiphenesin should be not used for persistent or chronic cough, or where cough is accompanied by excessive secretions, unless directed by a physician. A persistent cough may be a sign of a serious condition. If cough persists for more than 7 days, tends to recur, or is accompanied by a fever, rash, or persistent headache, a physician should be consulted.
Caution should be exercised in the presence of severe renal or severe hepatic impairment. The concomitant use of cough suppressants is not recommended.
Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not take this medicine. Not more than 4 doses should be given in any 24 hours. Avoid with any other cough and cold medicine.
Consult a healthcare professional before use in children under 6 years. Stop use and ask a healthcare professional if your cough lasts for more than 7 days, comes back, or is accompanied by a fever, rash, or persistent headache. Do not take with a cough suppressant. Do not give this medicine with any other cough or cold medicines.
Other medicines and Soventus Jr syrup
Terbutaline
Beta-blocking agents (including eye drops); especially the non-selective ones such as propranolol, may partially or totally inhibit the effect of beta-stimulants. Therefore, terbutaline preparations and non-selective beta-blockers should not normally be administered concurrently. Terbutaline should be used with caution in patients receiving other sympathomimetics.
Potassium depleting agents and hypokalaemia
Owing to the hypokalaemic effect of beta-agonists, concurrent administration with terbutaline of serum potassium depleting agents known to exacerbate the risk of hypokalaemia, such as diuretics, methyl xanthines and corticosteroids, should be administered cautiously after careful evaluation of the benefits and risks with special regard to the increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias arising as a result of hypokalaemia. Hypokalaemia also predisposes to digoxin toxicity. Hypokalaemia may result from beta 2-agonist therapy and may be potentiated by concomitant treatment with xanthine derivatives, corticosteroids and diuretics.
Terbutaline should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, since the action of terbutaline on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Ambroxol
No data available
Guaiphenesin
If urine is collected within 24 hours of a dose of Guaiphenesin, its metabolite may cause a colour interference with laboratory determinations of urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA).
Others
Soventus Jr. Syrup should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus, serious cardiovascular disorders, hypertension, hyperthyroidism and peptic ulcers.
USE IN SPECIAL POPULATION:
Pregnancy
However, there are no adequate and well-controlled studies of this combination in pregnant women. Hence this combination should be administered with caution in pregnancy.
Lactation
It is not known whether this combination is secreted in breast milk. However, terbutaline is secreted in breast milk, but effect on the infant is unlikely at therapeutic doses. Therefore, this combination should be used with caution in nursing mothers.
Effects on ability to drive and use machine
Patients should be cautioned against engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery until their response to Soventus Jr syrup is known.
3. How to Take Soventus Jr Syrup
- Always use this medicine exactly as your child’s doctor has told you. Check with your child’s doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- This medicine is to be given to a child under adult supervision.
- It should be taken even when your child has no symptoms.
- To be taken by mouth
How much to take
Children (under 6 years) 5 - 10 ml thrice daily
Children (6-12 years) 10 ml thrice daily
Always take the product exactly as advised. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Only to be taken by mouth. Shake the bottle well before measuring the dose in the measuring cap provided with bottle.
If you take more Soventus Jr syrup than you should
Contact your child’s doctor immediately for advice. Take the medicine pack with you. This is so the doctor knows what you have taken.
If you forget to take Soventus Jr syrup
Try to give Soventus Jr syrup as prescribed. However, if your child misses a dose, just resume the usual schedule. Do not give a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
4. Possible Side Effects
Ambroxol Hydrochloride
Under individual hypersensitivity to Ambroxol allergic reactions such as skin rash, nettle-rash, and angioneurotic oedema are possible. Under the prolonged administration in large doses pain in epigastric area, nausea, vomiting can appear.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and abdominal pain. Respiratory Disorders: Oral and pharyngeal hypoaesthesia, dry mouth and dry throat.
Nervous System Disorders: dysgeusia (e.g., changed taste).
Immune System Disorders: Anaphylactic reactions including anaphylactic shock. Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Angioedema, rash, urticaria, pruritus and other hypersensitivity.
Terbutaline Sulphate
Most of the adverse reactions are characteristic of sympathomimetic amines. The majority of these effects have reversed spontaneously within the first 1-2 weeks of treatment. The frequency of side-effects is low at the recommended doses.
The common adverse reactions to terbutaline are tremor, headache, tachycardia, palpitations, muscle spasms and hypokalaemia, nervousness, somnolence, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia, extra systoles ventricular, vasodilations, nausea, dry mouth, asthenia, sweating. The following adverse effects each occurred in fewer than 1% of patients: hallucinations, rash, paraesthesia, hypertonia, (muscle cramps), vomiting.
There have been rare reports of elevation in liver enzymes and of hypersensitivity vasculitis. Rare cases of arrhythmias e.g. atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and extra systoles, myocardial ischaemia, peripheral vasodilation, hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema, bronchospasm, hypotension, collapse, nausea, mouth and throat irritation, sleep disorder, behavioural disturbances such as agitation and restlessness, paradoxical bronchospasm, urticaria and rash.
Guaiphenesin
Side effects resulting from Guaiphenesin administration are very rare. Guaiphenesin has occasionally been reported to cause gastro-intestinal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, gastrointestinal discomfort particularly in very high doses. Also, hypersensitivity reactions may occur. The frequency of these Guaiphenesin-related adverse reactions is unknown but based on estimate from post-marketing data are likely to be rare: Allergic reactions, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, dyspnoea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, rash, urticaria.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to Store Soventus Jr Syrup
- Store protected from light & moisture. Store below 250C. Shake well before use.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
- Keep away from the reach of children.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Soventus Jr syrup contains
Each 5 ml contains:
Ambroxol Hydrochloride 10 mg
Terbutaline Sulphate 0.5 mg
Guaiphenesin IP 25 mg
Excipients (q.s.)
A bottle of 60 ml.
For More Information About This Product
Maxtra Gargle
1.0 Generic Name
Benzydamine Mouthwash BP 0.15% w/v
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Benzydamine Hydrochloride BP 0.15% w/v
Hydrochloric flavoured vehicle containing Ethanol IP 10% q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Liquid external (Mouthwash)
0.15% w/v
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1. Therapeutic indication
Benzydamine Mouthwash is a locally acting analgesic and anti-inflammatory treatment for the relief of painful inflammatory conditions of the mouth and throat including:
- Traumatic Conditions: Pharyngitis following tonsillectomy or the use of a naso-gastric tube;
- Inflammatory Conditions: Pharyngitis, aphthous ulcers and oral ulceration due to radiation therapy;
- Dentistry: For use after dental operations.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Rinse or gargle with 15 mL solution for 20-30 seconds every 1.5 to 3 hours as required for pain relief. The solution should be expelled from the mouth after use. Benzydamine Mouthwash should generally be used undiluted, but if ‘stinging’ occurs the rinse may be diluted with water.
4.3. Contraindications
Use in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the active ingredient, benzydamine hydrochloride, or to any of the other ingredients.
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use
- Benzydamine Mouthwash is for oromucosal use only and should not be swallowed.
- Benzydamine use is not advisable in patients with hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
- Avoid contact with eyes.
- Bronchospasm may be precipitated in patients suffering from or with a previous history of bronchial asthma. Caution should be exercised in these patients.
4.5. Drugs interactions
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6. Use in special populations
There is no information as regards use of benzydamine in pregnancy. Benzydamine Mouthwash should not be used in pregnancy or lactation unless considered essential by the physician.
4.7. Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Benzydamine Mouthwash has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8. Undesirable effects
The most common side effects are numbness and a stinging feeling in the mouth. The adverse reactions reported are classified by system organ class.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Laryngospasm or bronchospasm.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Oral numbness (hypoesthesia) and a stinging feeling in the mouth (oral pain), dryness of mouth
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions which may be associated with pruritus, urticaria, photosensitivity reaction and rash, Angioedema
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactic reactions (which can be potentially life-threatening), hypersensitivity reactions
The small amount of alcohol in this medicine will not have any noticeable effects.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com.
Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
4.9. Overdose
Intoxication is only expected in case of accidental ingestion of large quantities of benzydamine (> 300 mg).
Very rarely symptoms of overdosing such as excitation, convulsions, sweating, ataxia, tremor and vomiting have been reported after the oral administration of benzydamine dosages much larger than recommended. In the event of acute overdose only symptomatic treatment is possible; the stomach should be emptied by inducing vomiting or by gastric lavage, and the patient carefully observed and given supportive treatment. Adequate hydration must be maintained.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1. Mechanism of Action
The indazole analogue benzydamine has physicochemical properties and pharmacological activities which differ from those of the aspirin-like NSAIDs. Unlike aspirin-like NSAIDs which are acids or metabolised to acids, benzydamine is a weak base. In further contrast, benzydamine is a weak inhibitor of the prostaglandin synthesis. Only at concentration of 1 mM and above benzydamine effectively inhibits cyclooxygenase and lipooxygenase enzyme activity. It mostly exerts its effects through inhibition of the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) without significantly affecting other pro-inflammatory (IL-6 and 8) or anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, IL-1 receptor antagonist). Further mechanisms of action are hypothesised including the inhibition of the oxidative burst of neutrophils as well as membrane stabilisation as demonstrated by the inhibition of granule release from neutrophils and the stabilisation of lysosomes. The local anaesthetic activity of the compound has been related to an interaction with cationic channels.
5.2. Pharmacodynamic properties
Benzydamine specifically acts on the local mechanisms of inflammation such as pain, oedema or granuloma. Benzydamine topically applied demonstrates antiinflammatory activity reducing oedema as well as exudate and granuloma formation. Further, it exhibits analgesic properties if pain is caused by an inflammatory condition and local anaesthetic activity. Hyperthermia, which is indicative of systemic functional involvement, is poorly affected by benzydamine.
5.3. Pharmacokinetic properties
Oral doses of benzydamine are well absorbed and plasma drug concentrations reach a peak fairly rapidly and then decline with a half-life of about 13 hours. Less than 20% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins. Although local drug concentrations are relatively large, the systemic absorption of mouthwash-gargle doses of benzydamine is relatively low compared to oral doses. This low absorption should greatly diminish the potential for any systemic drug side-effects when benzydamine is administered by this route. Benzydamine is metabolized primarily by oxidation, conjugation and dealkylation.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1. Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Non-Clinical Data reveal no special hazards for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated toxicity, genotoxicity, cardiogenic potential, and toxicity to reproduction.
7.0 Description
Benzydamine belongs to the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Molecular Formula: C19H23N3O·HCl
Molecular Weight: 345.87 g/mol
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1. Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
8.2. Shelf-life
24 months
8.3. Packaging information
PET clear 120 mL bottle with silver cap and 15 mL measuring cup
8.4. Storage and handing instructions
Store in cool place. Do not refrigerate or freeze.
FOR MOUTHWASH USE ONLY.
DO NOT SWALLOW.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE.
FOR EXTERNAL USE ONLY
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Instruct patients on the following points when administering the drug.
- If a dose of this medication is missed, it is not necessary to make up the missed dose. Skip the missed dose and continue with the next scheduled dose. Do not double doses.
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
- Instruct patients to this medicine is for oromucosal use only and should not be swallowed.
- Remind patient to tell about asthmatic condition
- Remind patient to tell about allergic condition to acetylsalicylic acid or to other anti-inflammatory painkillers called NSAIDs
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Always use this medicine exactly as described in this leaflet or as your doctor, pharmacist or nurse have told you.
- This medicine is available without prescription. However, you still need to use it carefully to get the best results.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- Ask your doctor, dentist or pharmacist if you need more information or advice.
- You must contact a doctor if your symptoms worsen or do not improve.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
3. How to use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
6. Contents of the pack and other information.
1. What Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse is and what it is used for
Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse contains the active substance Benzydamine hydrochloride which is a locally acting analgesic and anti-inflammatory. Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse used for the relief of painful inflammatory conditions of the mouth and throat including:
- Sore throat following removal of the tonsils
- Mouth ulcers, Sore throat, Mouth ulcers due to radiation therapy
- For use after dental operations, discomfort associated with Dentures or dental work
2. What you need to know before you use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
Do not use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse if:
- you are allergic to benzydamine hydrochloride
- you are allergic to any of the other ingredients of Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse (see section 6).
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before using Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse:
- If you have a history of asthma
- If you are allergic to acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drugs
If any of these apply to you, talk to your doctor, dentist or pharmacist.
Other medicines and Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility If you are pregnant or breast -feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast -feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
3. How to use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
Important:
Always use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse exactly as your Doctor/Pharmacist has told you. You should check with your doctor, dentist or pharmacist if you are not sure.
If you get Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse in your eyes
Do not use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse in or near your eyes.
If any Oral Rinse gets in your eyes, wash them immediately with cold water.
How much Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse to use
- Adults, adolescents and elderly: The usual dose is 15 ml of solution to be used every 1½ to 3 hours. Use the measuring cup provided to measure the dose.
- Children: This medicine is not suitable for children aged 12 years or under.
How to use the Oral Rinse
The solution should be rinsed around the mouth or used as a gargle for 20 to 30 seconds and then spat out.
This solution should not be swallowed. This solution should not be used for more than 7 days unless your doctor or dentist tells you to.
If your symptoms worsen or do not improve contact your doctor.
If you use more Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse than you should
If you take too much or you accidentally swallow large quantities of your medicine, contact immediately your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
If you forget to use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose. Simply take the next dose as planned. If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects could be serious. If you have any of the side effects listed below, seek immediate medical help:
- Serious allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock), signs of which may include difficulty breathing, chest pain or chest tightness, and/or feeling dizzy/faint, severe itching of the skin or raised lumps on the skin, swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat, and which may be potentially life threatening.
Other side effects include the following, if they get serious, please tell your doctor: Uncommon (affects 1 in 1,000 people):
- Numbness and/or stinging in the mouth and/or throat.
Very rare (affects less than 1 in 10,000 people):
- Difficulty breathing and wheezing
- Itching
- Skin rash.
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Skin redness or swelling
- Allergic reaction (Hypersensitivity).
If this solution stings your mouth, the next dose can be diluted with some water to reduce this effect.
Some people may react after using the product with a severe allergic reaction experiencing symptoms as described above (a so called anaphylactic reaction) which may be potentially life-threatening. In this case you should seek immediate medical assistance.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse
- Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse after the expiry date on the bottle. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- If you store the product without the original carton, make sure it is kept out of the direct sunlight.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste.
- Return any medicine you no longer need to your pharmacist.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse contains:
The active substance is benzydamine hydrochloride.
Benzydamine Hydrochloride BP0.15% w/v
Hydrochloric flavoured vehicle containing Ethanol IP 10% q.s.
The other ingredients are tartrazine supra & brilliant blue FCF.
For advice on what to do if you are allergic to any of these ingredients see section 2.
What Maxtra Gargle Oral Rinse looks like
It comes in a PET clear 120 ml bottle with silver cap and 15 ml measuring cup
For More Information About This Product
Nukast 4 mg Syrup
1.0 Name of the medicinal product
Montelukast Sodium & Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Syrup
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each 5 ml contains: Montelukast Sodium USP Equivalent to Montelukast 4 mg Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride USP 2.5 mg
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Syrup
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For relief of symptoms of allergic rhinitis (seasonal and perennial).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Children (2-5 years): 5 ml syrup as measured from the given cup once daily.
4.3 Contraindications
- known hypersensitivity to montelukast, levocetirizine, to other piperazine derivatives or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation.
- severe renal impairment at less than 10 ml/min creatinine clearance.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Montelukast
Eosinophilic Conditions
In rare cases, patients on therapy with montelukast may present with systemic eosinophilia sometimes presenting with clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition, which is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients. A causal association between, montelukast and those underlying conditions has not been established.
Patients with known aspirin sensitivity should continue avoidance of aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents while taking montelukast.
Neuropsychiatric Events
Neuropsychiatric events have been reported in adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients taking montelukast. Post-marketing reports with montelukast use include agitation, aggressive behaviour or hostility, anxiousness, depression, disorientation, dream abnormalities, hallucinations, insomnia, irritability, restlessness, somnambulism, suicidal thinking and behaviour (including suicide), and tremor. The clinical details of some post-marketing reports involving montelukast appear consistent with a drug-induced effect.
Patients and prescribers should be alert for neuropsychiatric events. Patients should be instructed to notify their prescriber if these changes occur. Prescribers should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing treatment with montelukast if such events occur.
Levocetirizine
Comparative clinical trials have revealed no evidence that levocetirizine at the recommended dose impairs mental alertness, reactivity or the ability to drive. In clinical trials the occurrence of somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia has been reported in some patients under therapy with levocetirizine. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness and motor co-ordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of levocetirizine. Concurrent use of levocetirizine with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Montelukast
Montelukast may be administered with other therapies routinely used in the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma. In drug-interactions studies, the recommended clinical dose of montelukast did not have clinically important effects on the pharmacokinetics of the following medicinal products: theophylline, prednisone, prednisolone, oral contraceptives (ethinyl estradiol/norethindrone 35/1), terfenadine, digoxin and warfarin.
The area under the plasma concentration curve (AUC) for montelukast was decreased approximately 40% in subjects with co-administration of phenobarbital, since montelukast is metabolised by CYP 3A4, caution should be exercised, particularly in children, when montelukast is co-administered with inducers of CYP 3A4, such as phenytoin, phenobarbital and rifampicin.
In vitro studies have shown that montelukast is a potent inhibitor of CYP 2C8. However, data from a clinical drug-drug interaction study involving montelukast and rosiglitazone (a probe substrate representative of medicinal products primarily metabolised by CYP 2C8) demonstrated that montelukast does not inhibit CYP 2C8 In vivo. Therefore, montelukast is not anticipated to markedly alter the metabolism of medicinal products metabolised by this enzyme (e.g paclitaxel, rosiglitazone and repaglinide.)
Levocetirizine
In vitro data indicate that levocetirizine is unlikely to produce pharmacokinetic interactions through inhibition or induction of liver drug-metabolizing enzymes. No in vivo drug-drug interaction studies have been performed with levocetirizine.
Drug interaction studies have been performed with racemic cetirizine.
Pharmacokinetic interaction studies performed with racemic cetirizine demonstrated that cetirizine did not interact with antipyrine, pseudoephedrine, erythromycin, azithromycin, ketoconazole and cimetidine. There was a small decrease (~ 16%) in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of theophylline. It is possible that higher theophylline does could have a greater effect.
The extent of absorption of levocetirizine is not reduced with food although the rate of absorption is decreased.
Ritonavir increased the plasma AUC of cetirizine by about 42% accompanied by an increase in half-life (53%) and a decrease in clearance (29%) of cetirizine. The disposition of ritonavir was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
In sensitive patients the simultaneous administration of cetirizine or levocetirizine and alcohol or other CNS depressants may have effects on the central nervous system, although it has been shown that the racemate cetirizine does not potentiate the effect of alcohol.
Renal Impairment
Levocetirizine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidneys and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Dosage adjustment may be required in patients with impaired renal function. Hence this combination is not recommended in patients with impaired renal function.
Hepatic Impairment
As levocetirizine is mainly excreted unchanged by the kidneys, it is unlikely that the clearance of levocetirizine is significantly decreased in patients with solely hepatic impairment. But montelukast is mainly excreted through bile; caution is to be exercised while prescribing this combination in patients with impaired hepatic function. The pharmacokinetics of montelukast in patients with more severe hepatic impairment or with hepatitis has not been evaluated.
4.6 Use in special populations (such as pregnant women, lactating women, paediatric patients, geriatric patients etc.)
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well controlled studies of either montelukast or levocetirizine in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this combination should be used during pregnancy only if it is considered to be clearly essential.
Lactation
It is not known if montelukast is excreted in human milk. Cetirizine has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk. Because levocetirizine is also expected to be excreted in human milk this combination is not recommended during lactation.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of montelukast in children with perennial allergic rhinitis below 6 months of age has not been established. The safety and effectiveness of levocetirizine in pediatric patients under 2 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Montelukast
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Levocetirizine
Clinical studies of levocetirizine for each approved indication did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious usually star ting at the low end of the dosing range reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Montelukast
Montelukast is not expected to affect a patient's ability to drive a car or operate machinery. However, in very rare cases, individuals have reported drowsiness or dizziness.
Levocetirizine
Comparative clinical trials have revealed no evidence that levocetirizine at the recommended dose impairs mental alertness, reactivity or the ability to drive. Nevertheless, some patients could experience somnolence, fatigue and asthenia under therapy with levocetirizine.
Therefore, patients intending to drive, engage in potentially hazardous activities or operate machinery should take their response to the medicinal product into account.
4.8 Undesirable effects
There is no data available on undesirable effects of this combination. However, side effects have been reported with individual molecules.
Montelukast
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and greater than placebo; listed in descending order of frequency) in controlled clinical trials were: upper respiratory infection, fever, headache, pharyngitis, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, otitis media, influenza, rhinorrhea, sinusitis, otitis.
Montelukast has been evaluated in 280 pediatric patients 2 to 14 years of age in a 2-week, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group safety study. Montelukast
administered once daily in the evening had a safety profile similar to that of placebo. In this study, the following events occurred with a frequency ≥ 2% and at an incidence greater than placebo: headache, otitis media, pharyngitis, and upper respiratory infection.
The safety in patients 2 to 14 years of age with perennial allergic rhinitis is supported by the safety in patients 2 to 14 years of age with seasonal allergic rhinitis. The safety in patients 6 to 23 months of age is supported by data from pharmacokinetic and safety and efficacy studies in asthma in this pediatric population and from adult pharmacokinetic studies.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in post-marketing use:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Increased bleeding tendency.
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, hepatic eosinophilic infiltration.
Psychaitric disorders: Agitation including aggressive behaviour or hostility, anxiousness, depression, disorientation, dream abnormalities, hallucinations, insomnia, irritability, restlessness, somnambulism, suicidal thinking and behaviour (including suicide), tremor.
Nervous system disorder: Drowsiness, Paresthesia /hypoesthesia, seizure.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Epistaxis
Cardiac disorders: Palpitations.
Gastro-intestinal disorders: Diarrhoea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting.
Hepatobiliary disorders: Elevated levels of serum transminases (ALT, AST), rare cases of cholestatic hepatitis, hepatocellular liver-injury, and mixed-pattern liver injury have been reported in patients treated with montelukast. Most of these occurred in combination with other confounding factors, such as use of other medications, or when montelukast was administered to patients who had underlying potential for liver disease, such as alcohol use or other forms of hepatitis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders : Angioedema, bruising, urticaria, pruritus, rash, erythema nodosum.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders : Arthralgia, myalgia including muscle cramps
General disorders and administration site conditions : Asthenia/fatigue, malaise, oedema.
Patients with asthma on therapy with montelukast may present with systemic eosinophilia. Sometimes presenting with clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition which is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction of oral cor ticosteroid therapy. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients.
Levocetirizine
Use of levocetirizine has been associated with somnolence, fatigue, nasopharyngitis, dry mouth and pharyngitis in subjects 12 years of age and older. Further uncommon incidences of adverse reactions like asthenia, abdominal pain, syncope and weight- increase were observed.
Adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2% of pediatric subjects aged 1-6 years exposed to levocetirizine 1.25 mg twice daily in a 2-week placebo-controlled clinical trial were pyrexia, diarrhea, vomiting and otitis media while in pediatric subjects 6-12 years of age exposed to levocetirizine 5 mg once daily in placebo-controlled clinical trials 4 and 6 weeks in duration were pyrexia, cough, somnolence, epitaxis. In pediatric subjects 6 months to 11 months receiving 1.25 mg levocetirizine once daily in a 2 week placebo controlled double blind safety trial the common side effects (≥ 3% subjects) were diarrhea and constipation.
In addition to the adverse reactions reported during clinical studies and listed above very rare cases of the following adverse drug reactions have been reported in post-marketing experience:
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis
Psychiatric disorders: Aggression, agitation, hallucination, depression
Nervous System disorders: Convulsion
Eyes disorders: Visual disturbances
Cardiac disorders: Palpitations, tachycardia.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnoea
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatitis Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Angioneurotic edema, fixed drug eruption, pruritus, rash urticaria
Musculoskeletal, connective tissues, and bone disorders: Myalgia
Investigations: Weight Increased, abnormal liver functions tests
4.9 Overdose
There is no data reported on the overdosage of this combination. However, overdosage has been reported with individual molecules.
Montelukast
No specific information is available on the treatment of overdosage with montelukast. In chronic asthma studies, montelukast has been administered at doses up to 200 mg/day to adult patients for 22 weeks and, in short-term studies, up to 900 mg/day to patients for approximately a week without clinically important adverse experiences.
There have been reports of acute overdosage in post-marketing experience and clinical studies with montelukast. These include reports in adults and children with a dose as high as 100 mg. The clinical and laboratory findings observed were consistent with the safety profile in adults and pediatric patients. There were no adverse experiences in the majority of overdosage reports. The most frequently occurring adverse experiences were consistent with the safety profile of montelukast and included abdominal pain, somnolence, thirst, headache, vomiting and psychomotor hyperactivity.
In the event of overdose, it is reasonable to employ the usual supportive measures : e.g., remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring, and institute supportive therapy, if required.
It is not known whether montelukast is removed by peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis.
Levocetirizine
Symptoms of overdose may include drowsiness in adults and initially agitation and restlessness, followed by drowsiness in children. There is no known specific antidote to levocetirizine. Should overdose occur, symptomatic or supportive treatment is recommended. Gastric lavage should be considered following short-term ingestion. Levocetirizine is not effectively removed by haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
The cysteinyl leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) are potent inflammatory eicosanoids released from various cells including mast cells and eosinophils. These important pro-asthmatic mediators bind to cysteinyl leokotriene (CysLT) receptors.
The CysLT type-1 (CysLT1) receptor is found in the human airway (including airway smooth muscle cells and airway macrophages) and on other pro-inflammatory cells (including eosinophils and certain myeloid stem cells). CysLTs have been correlated with the pathophysiology of asthma and allergic rhinitis.
In allergic rhinitis, CysLTs are released from the nasal mucosa after allergen exposure during both early and late-phase reactions and are associated with symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Intranasal challenge with CysLTs has been shown to increase nasal airway resistance and symptoms of nasal obstructions.
Montelukast is an orally active compound that binds with high affinity and selectivity to the CysLT1 receptor. Montelukast inhibits physiologic actions of LTD4 at the CysLT1 receptor without any agonist activity. In patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis aged 15 years and older who received montelukast, a mean increase of 0.2% in peripheral blood eosinophil counts was noted, compared with a mean increase of 12.5% in placebo-treated patients, over the double-blind treatment periods; this reflects a mean difference of 12.3% in favour of montelukast. The relationship between these observations and the clinical benefits of montelukast noted in the clinical trials is not known.
Levocetirizine
Levocetirizine, the R-enantiomer of cetirizine, is a potent and selective antagonist of peripheral H1-receptors. Binding studies revealed that levocetirizine has high affinity for human H1-receptors (Ki=3.2 nmol/l). Levocetirizine has an affinity 2-fold higher than that of cetirizine (Ki=6.3 nmol/1). Levocetirizine dissociates from H1 - receptors with a half-life of
115±38 min. After single administration, levocetirizine shows receptor occupancy of 90% at 4 hours and 57% at 24 hours.
The onset of action of levocetirizine 5 mg in controlling pollen-induced symptoms has been observed at 1 hour post drug intake in placebo controlled trials in the model of the allergen challenge chamber.
In vitro studies (Boyden chambers and cell layers techniques) show that levocetirizine inhibits eotaxin-induced eosinophil transendothelial migration through both dermal and lung cells. A pharmacodynamic experimental study in vivo (skin chamber technique) showed three main inhibitory effects of levocetirizine 5 mg in the first 6 hours of pollen-induced reaction compared with placebo in 14 adult patients: Inhibition of VCAM-1 release, modulation of vascular permeability and a decrease in eosinophil recruitment.
Pharmacodynamic studies in healthy volunteers demonstrate that at half the dose levocetirizine has comparable activity to cetirizine, both in the skin and in the nose.
A QT/QTc study using a single dose of 30 mg of levocetirizine did not demonstrate an effect on the QTc interval. While a single dose of levocetirizine had no effect, the effects of levocetirizine may not be at steady state following single dose. The effect of levocetirizine on the QTc interval following multiple dose administration is unknown. Levocetirizine is not expected to have QT/QTc effects because of the results of QTc studies with cetirizine and the long post-marketing history of cetirizine without reports of QT prolongation.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Montelukast
Absorption
Montelukast is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. For the 4 mg chewable tablet, the mean Cmax is achieved 2 hours after administration in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age in the fasted state.
The 4 mg oral granule formulation is bioequivalent to the 4 mg chewable tablet when administered to adults in the fasted state. The co-administration of the oral granule formulation with applesauce did not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of montelukast. A high fat meal in the morning did not affect the AUC of montelukast oral granules; however, the meal decreased Cmax by 35% and prolonged Tmax from 2.3 ± 1.0 hours to 6.4 ± 2.9 hours.
The safety and efficacy of montelukast in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were demonstrated in clinical trials in which the 10 mg film-coated tablet was administered in the morning or evening without regard to the time of food ingestion.
Distribution
Montelukast is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The steady state volume of distribution of montelukast averages 8 to 11 liters. Studies in rats with radiolabeled montelukast indicate minimal distribution across the blood-brain barrier.
In addition, concentrations of radiolabeled material at 24 hours post dose were minimal in all other tissues.
Metabolism
Montelukast is extensively metabolized. In studies with therapeutic doses, plasma concentrations of metabolites of montelukast are undetectable at steady state in adults and pediatric patients.
In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicate that cytochromes P450 3A4 and 2C9 are involved in the metabolism of montelukast. Clinical studies investigating the effect of known inhibitors of cytochromes P450 3A4 (e.g ketoconazole, erythromycin) or 2C9 (e.g., fluconazole) on montelukast pharmacokinetics have not been conducted. Based on further in vitro results in human liver microsomes, therapeutic plasma concentrations of montelukast do not inhibit cytochromes P450 3A4, 2C9, 1A2, 2A6, 2C19 or 2D6. However, in vitro studies have shown that montelukast is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450 2C8; however, data from a clinical drug-drug interaction study involving montelukast and rosiglitazone (a probe substrate representative of drugs primarily metabolized by CYP 2C8) demonstrated that montelukast does not inhibit CYP 2C8 in vivo, and therefore is not anticipated to alter the metabolism of drugs metabolized by this enzyme.
Elimination
The plasma clearance of montelukast averages 45 mL/min in healthy adults. Following an oral dose of radiolabeled montelukast, 86% of the radioactivity was recovered in 5-day fecal collection and <0.2% was recovered in urine. Coupled with estimates of montelukast oral bioavailability, this indicates that montelukast and its metabolites are excreted almost exclusively via the bile.
In several studies, the mean plasma half-life of montelukast ranged from 2.7 to 5.5 hours in healthy young adults. The pharmacokinetics of montelukast is nearly linear for oral doses up to 50 mg. During once-daily dosing with 10 mg montelukast, there is little accumulation of the parent drug in plasma (14%).
Levocetirizine
The pharmacokinetics of levocetirizine is linear with dose and time independent with low inter-subject variability. The pharmacokinetic profile is the same when given as the single enantiomer or when given as cetirizine. No chiral inversion occurs during the process of absorption and elimination.
Absorption
Levocetirizine is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are achieved 0.9 h after dosing. Steady state is achieved after two days. Peak concentrations are typically 270 ng/ml and 308 ng/ml following a single and a repeated 6 mg o.d. dose, respectively. The extent of absorption is dose-independent and is not altered by food, but the peak concentration is reduced and delayed.
Distribution
No tissue distribution data are available in humans, neither concerning the passage of levocetirizine through the blood-brain-barrier. Levocetirizine in 90% bound to plasma proteins. The distribution of levocetirizine is restrictive, as the volume of distribution is 0.4 l/kg.
Biotransformation
The extent of metabolism of levocetirizine in humans is less than 14% of the dose and therefore differences resulting from genetic polymorphism or concomitant intake of enzyme inhibitors are expected to be negligible. Metabolic pathways include aromatic oxidation, N and O-dealkylation and taurine conjugation. Dealkylation pathways are primarily mediated by CYP 3A4 while aromatic oxidation involved multiple and/or unidentified CYP isoforma. Levocetirizine had no effect on the activities of CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C0, 2C19, 2D8, 2E1 and 3A4 at concentrations well above peak concentrations achieved following a 6 mg oral dose.
Due to its low metabolism and absence of metabolic inhibition potential, the interaction of levocetirizine with other substances or vice-versa, is unlikely.
Elimination
The plasma half-life in adults is 7.9 ± 1.9 hours. The half-life is shorter in small children. The mean apparent total body clearance is 0.63 ml/min kg. The major route of excretion of levocetirizine and metabolites is via urine, accounting for a mean of 85.4% of the dose. Excretion via faeces accounts for only 12.9% of the dose. Levocetirizine is excreted both by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Montelukast sodium was found not to be genotoxic. Montelukast sodium was negative in microbial and mammalian cell mutagenesis assays, with and without metabolic activation. There was no evidence of clastogenic activity in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells, with or without a microsomal enzyme activation system, or of DNA damage in the in vitro alkaline elution assay in rat hepatocytes. Similarly, there was no induction of chromosomal aberrations in bone marrow cells of male or female mice.
Montelukast sodium was not carcinogenic when administered at oral doses of up to 200 mg/kg/day in 104-week study in rats, nor at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day in a 91-week study in mice. Systemic exposure in these studies, in terms of the plasma AUC for parent drug, was at least 30 times higher than that in humans at recommended dose levels.
Levocetirizine
Levocetirizine is the R-enantiomer of the marketed cetirizine. The long term oral toxicity, fertility and early developmental and prenatal postnatal developmental toxicity studies with cetirizine represent the toxicity profile of levocetirizine with supplemental bridging toxicity, developmental and genotoxicity studies conducted with levocetirizine. In genotoxicity studies, cetirizine was negative in the Ames, Human Peripheral Lymphocytes Chromosomal Aberration, Mouse Lymphoma and Mouse Micronucleus assays. Levocetirizine, In the carcinogenicity studies in rodents, the dietary doses were 1, 4 and 16 mg/kg for the mouse and 3, 8 and 20 mg/kg for the rat. The rats showed liver toxicity (hypertrophy, vacuolation and fat deposit). No tumors were seen in rats that were clinically significant, while male mice showed benign liver tumors which were due to enzyme induction.
6.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
6.1 List of excipients
Methylparaben Sodium, Propylparaben Sodium, Polyoxyl 40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil, Glycerol, Saccharin Sodium, Mango Flavour RSV, Colour Quinoline Yellow WS, Colour Erythrosine Supra, Disodium Edetate, Sodium Hydroxide, Hydrochloric Acid
6.2 Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
6.3 Shelf life
24 MONTHS
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Protect from light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container Nukast Syrup:
1x60ml, PET Bottle 6.6Special precautions for disposal and other handling No special requirements for disposal. Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
10.0 Date of revision of the text
Nov 2020
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
- What Nukast-4 Syrup is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Nukast-4 Syrup
- How to take Nukast -4 Syrup
- Possible side effects
- How to store Nukast -4 Syrup
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Nukast -4 Syrup is and what it is used for
What Nukast -4 Syrup is
Nukast is combination of Montelukast and Levocetirizine. Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist that blocks substances called leukotrienes. Levocetirizine is an anti-allergic medication. Nukast-4 Syrup is used in children for the treatment of signs of illness (symptoms) associated with allergic rhinitis (including persistent allergic rhinitis)
2. What you need to know before you take Nukast
Tell your doctor about any medical problems or allergies you have now or have had.
Do not take Nukast
If you are allergic to montelukast/ levocetrizine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine. Severe renal impairment (Creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min)
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Nukast.
Montelukast
Acute Asthma: Montelukast is not indicated for use in the reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthma attacks, including status asthmatics. Patients who have exacerbations of asthma after exercise should have available for rescue a short-acting inhaled β2-agonist.
Concomitant Corticosteroid Use: While the dose of inhaled corticosteroid may be reduced gradually under medical supervision, montelukast should not be abruptly substituted for inhaled or oral corticosteroids.
Aspirin Sensitivity: Patients with known aspirin sensitivity should continue avoidance of aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents while taking montelukast.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients.
Neuropsychiatric Events: Prescribers should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing treatment with montelukast if such events occur.
Phenylketonuria: Phenylketonuric patients should be informed about the presence of phenylalanine (a component of aspartame) in this product.
Levocetirizine
Somnolence: Concurrent use of levocetirizine with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
Urinary Retention: Levocetirizine should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia) as levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention. Discontinue, if urinary retention occurs.
Pediatric
The safety and efficacy of levocetirizine in pediatric patients under 2 years of age have not been established.
Pregnancy
No clinical studies available in human pregnancy. Therefore, NUKAST syrup should not be used in pregnancy.
Lactation
It is not known if montelukast is excreted in human milk. Cetirizine has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk. Because levocetirizine is also expected to be excreted in human milk this combination is not recommended during lactation.
Hepatic insufficiency
As levocetirizine is mainly excreted unchanged by the kidneys, it is unlikely that the clearance of levocetirizine is significantly decreased in patients with solely hepatic impairment. But montelukast is mainly excreted through bile; caution is to be exercised while prescribing this combination in patients with impaired hepatic function. The pharmacokinetics of montelukast in patients with more severe hepatic impairment or with hepatitis has not been evaluated.
Renal impairment
Levocetirizine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidneys and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Dosage adjustment may be required in patients with impaired renal function. Hence this combination is not recommended in patients with impaired renal function.
Other medicines and Nukast
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken or might take any other medicines including those obtained without a prescription.
Some medicines may affect how Nukast works, or Nukast may affect how other medicines work.
Tell your doctor if you are taking the following medicines before starting Montelukast:
- Phenobarbital (used for treatment of epilepsy)
- Phenytoin (used for treatment of epilepsy)
- Rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis and some other infections)
- Gemfibrozil (used for treatment of high lipid levels in plasma)
Taking Nukast with food and drink
Nukast-4 syrup may be taken with or without food.
Driving and using machines
Nukast-4 syrup has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines. However, individuals have reported drowsiness or dizziness. Therefore, patients intending to drive, engage in potentially hazardous activities or operate machinery should take their response to the medicinal product into account.
3. How to take Nukast
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- You should take only one tablet of Nukast once a day as prescribed by your doctor.
- It should be taken even when you have no symptoms or have an acute asthma attack.
For Children (2-5 years): 5 ml syrup as measured from the given cup once daily.
Nukast-4 syrup can be taken with or without food.
Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic insufficiency.
If you are taking Nukast-4 syrup, be sure that you do not take any other products that contain the same active ingredient, montelukast and levocetirizine.
This medicine is for oral use.
You can take Nukast-4 syrup with or without food.
If you take more Nukast-4 syrup than you should
Contact your doctor immediately for advice.
There were no side effects reported in the majority of overdose reports. The most frequently occurring symptoms reported with overdose in adults and children included abdominal pain, somnolence, thirst, headache, vomiting and psychomotor hyperactivity.
In the event of overdose, it is reasonable to employ the usual supportive measures; e.g., remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring, and institute supportive therapy, if required. Gastric lavage should be considered following short-term ingestion of Nukast.
If you forget to take Nukast-4 syrup
Try to take Nukast-4 syrup as prescribed. However, if you miss a dose, just resume the usual schedule of 5 ml syrup as measured from the given cup once daily.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Nukast
Nukast-4 syrup can treat your rhinitis (inflammation of nasal mucosa) only if you continue to take it. It is important to continue taking Nukast for as long as your doctor prescribes. It will help control your rhinitis.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Serious side effects
Talk with your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects, which may be serious, and for which you may need urgent medical treatment.
Pediatric Patients: 2 to 5 Years of Age (≥ 2%):
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, rhinorrhea, sinusitis, otitis, influenza, rash, ear pain, gastroenteritis, eczema, urticaria, varicella, pneumonia, dermatitis, and conjunctivitis, thirst.
Levocetirizine:
Use of levocetirizine has been associated with somnolence, fatigue, asthenia, and urinary retention.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Nukast-4 syrup?
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Store below 30°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last date of that month.
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Nukast-4 Syrup contains:
The active substance is montelukast and levocetirizine.
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains Montelukast sodium equivalent to Montelukast 4 mg
Levocetirizine hydrochloride 2.5 mg Excipients q.s.


