Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Multilayer tablets, compression coated tablets and in lay tablets
Lorem Ipsum 3
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don't look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn't anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
Lorem Ipsum 4
Contrary to popular belief, Lorem Ipsum is not simply random text. It has roots in a piece of classical Latin literature from 45 BC, making it over 2000 years old. Richard McClintock, a Latin professor at Hampden-Sydney College in Virginia, looked up one of the more obscure Latin words, consectetur, from a Lorem Ipsum passage, and going through the cites of the word in classical literature, discovered the undoubtable source. Lorem Ipsum comes from sections 1.10.32 and 1.10.33 of "de Finibus Bonorum et Malorum" (The Extremes of Good and Evil) by Cicero, written in 45 BC. This book is a treatise on the theory of ethics, very popular during the Renaissance. The first line of Lorem Ipsum, "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet..", comes from a line in section 1.10.32.
Lorem Ipsum 14
On the other hand, we denounce with righteous indignation and dislike men who are so beguiled and demoralized by the charms of pleasure of the moment, so blinded by desire, that they cannot foresee the pain and trouble that are bound to ensue; and equal blame belongs to those who fail in their duty through weakness of will, which is the same as saying through shrinking from toil and pain. These cases are perfectly simple and easy to distinguish. In a free hour, when our power of choice is untrammelled and when nothing prevents our being able to do what we like best, every pleasure is to be welcomed and every pain avoided. But in certain circumstances and owing to the claims of duty or the obligations of business it will frequently occur that pleasures have to be repudiated and annoyances accepted. The wise man therefore always holds in these matters to this principle of selection: he rejects pleasures to secure other greater pleasures, or else he endures pains to avoid worse pains.
Amlenox Oral Paste
Composition
Amlexanox 5% w/w
Description
Amlexanox is a novel anti-inflammatory and antiallergic agent.
Structural Formula
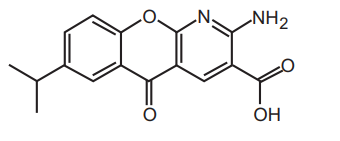
Molecular Formula :C16H14N2O4
Chemical Name : 2-amino-7-isopropyl-5-oxo-5H-chromeno[2,3-b]pyridine-3 carboxylic acid
Molecular Weight : 298.3 g/mol
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Antihistaminic action
- Inhibits IL-3 induced release of histamine from mast cells
- Inhibits the release of histamine and leukotrienes from neutrophils and basophils
Anti-inflammatory action
Potent inhibitor of the formation and/or antigen induced release of inflammatory mediators from cells including neutrophils and mast cells
Potent inhibitor of generation of 5- and 12- lipoxygenase
Increases levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) that inhibits the chemotactic and phagocytic activity of neutrophils
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After a single oral application of 100 mg of the paste (5 mg Amlexanox), maximum serum levels (Cmax) of 120 ± 70 ng/ml are observed at 2.4 ± 0.9 hours (Tmax). The area under the curve (AUC0-24h) values range from 30 to 973 ng.hr/mlwith amean value of 360 ± 240 ng.hr/ml.Most of the systemic absorption of Amlexanox is via the gastrointestinal tract, and the amount absorbed through the active ulceris not a significant portion of the applied dose.
Metabolism
The major metabolite of Amlexanox is its hydroxylated metabolite. Other metabolites include conjugates of the hydroxylated metabolite.
Excretion
A total of 17 ± 12% of the applied dose of Amlexanox from 100 mg of 5% Amlexanox paste was recovered in the urine within 24 hours after application. Amlexanox and its conjugates accounted for 7.8% of the dose; the hydroxylated metabolite accounted for 6.2% of the dose and an additional 3% of the dose was conjugates of the hydroxylated metabolite. The half-life for elimination (T½) is 3.5 ± 1.1 hours.
Indications
For aphthous ulcers in people with normal immune system
Contraindications
Amlenox is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to Amlexanox or other ingredients in the formulation.
Adverse Effects
Occurrence < 2%
Transient pain, stinging and/or burning at the site of application.
Occurrence < 1%
Contact mucositis, nausea, and diarrhea.
Dosage and Administration
The paste should be applied as soon as possible after noticing the symptoms of an aphthous ulcer and should be used four times daily, preferably following oral hygiene after breakfast, lunch, dinner, and at bedtime. Wash your hands before applying Amlenox. Dry the ulcer by gently patting it with a soft, clean cloth. Moisten the tip th of your index finger. Squeeze a dab of paste approximately 1/4 inch (0.5 cm) onto a finger tip. With gentle pressure dab the paste onto the ulcer. Repeat the process if you have more than one ulcer. If significant healing or pain relief has not occurred in 10 days, consult your dentist or physician.
Overdosage
There are no reports of human ingestion overdosage. Ingestion of a full tube of 5 grams of paste would result in systemic exposure well below the maximum non-toxic dose of Amlexanox in animals. Gastrointestinal upset such as diarrhea and vomiting could result from an overdose.
Precautions
Wash hands immediately after applying Amlenox directly to ulcers with finger tips. In the event that a rash or contact mucositis occurs, discontinue the use of Amlenox.
Use in Special Population
Pregnancy
The drug falls under category B. Since there are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women, Amlexanox should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers
Amlexanox was found in the milk of lactating rats; therefore caution should be exercised when administering Amlexanox oral paste 5% to a nursing mother.
Pediatric
Safety and effectiveness of Amlexanox oral paste 5% have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric
Clinical studies have established no significant differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, the dose selection for elderly patients should be done cautiously, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Storage
Store below 30°C. Do not freeze
Keep out of reach of children. Keep the tube tightly closed after use.
Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
Presentation
A tube of 5 g.
For More Information About This Product
Management 4
Management 4
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book.
Management 3
Management 3
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book.
Management 2
Management 2
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book.


