Lornit 150 mg Tablet
1.0 Generic name
L-Ornithine L-Aspartate tablet
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each film coated tablet contains:
L-Ornithine L-Aspartate 150mg/ 500 mg
Excipients q.s
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet 150 mg/ 500 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Treatment of associated conditions and sequelae of diseases with impaired hepatic detoxification (e.g. cirrhosis of the liver), when there are symptoms and signs of minimal or overt hepatic encephalopathy.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
2-3 tablets 3-4 times per day can be administered in mild to moderate liver disorders.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to LOLA or any other excipients of this product.
- Severe renal insufficiency (serum creatinine value > 3 mg/100 ml).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Monitoring of serum and urinary urea levels at regular intervals should be done.
- Should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits out-weigh the potential risk to the fetus.
4.5 Drugs interactions
No known drug-drug interaction.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy & Lactation
The administration in pregnancy and lactation should be avoided. If treatment is nevertheless
thought to be necessary, the benefits and risks should be carefully assessed.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effect on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed
4.8 Undesirable effects
Very rarely side effects like nausea and vomiting occur. These side effects are usually transient and do not necessitate the withdrawal of the drug.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There is no data available for LOLA tablet overdosage. If any patient consumes excess of drug, it should be managed symptomatically.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate is a stable salt of the amino acids ornithine and aspartic acid and provides substrates for urea genesis and glutamine synthesis, which are important mechanisms in ammonia detoxification.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
It is well known that both ornithine and aspartic acid play a key role in liver metabolism. Ornithine is the starting point of ammonia detoxification. It brings ammonia into the urea cycle, in which ammonia is converted into a non-toxic substance urea. It activates ornithine transcarbamoylase and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase and acts as a substrate for urea genesis. Hence, LOLA can activate the periportal urea cycle in the liver. The other component of the drug, aspartic acid, not only represents an important stage in the reaction sequence involved in the urea cycle, but also features in the tricarboxylic acid cycle as oxaloacetate formed by transamination, thereby improving the energy balance of diseased liver. Furthermore, aspartic acid promotes natural regeneration of liver cells by taking part in pyrimidine biosynthesis.
After conversion to α-ketoglutarate, aspartate and ornithine, act as carbon sources for perivenous glutamine synthesis. LOLA up-regulates glutamine synthesis in the skeletal muscle by substrate provision for glutamine synthetase. Ammonia is consumed during urea formation and glutamine synthesis, and thereby LOLA decreases blood ammonia levels.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
- L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate is rapidly absorbed and cleaved into L-Ornithine and L-Aspartate.
- Elimination half-life of each amino acid is short, approximately 40 min and bioavailability is 82.2 28% after oral administration.
- Some L-Aspartate appears unchanged in the urine.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
9.0 Patient counselling information
- You will be regularly monitored for blood creatinine and blood/urine urea levels.
- Inform your doctor if you are pregnant, planning a pregnancy, or breastfeeding.
- Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of its ingredients.
12.0 Date of revision
23.09.2024
About Leaflet
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Lornit is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you use Lornit
3. How to use Lornit
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Lornit
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Lornit is and what it is used for
Lornit contains the active substance L-Ornithine L-Aspartate. It is used to treat conditions associated with impaired liver detoxification, such as cirrhosis of the liver, when there are symptoms and signs of minimal or overt hepatic encephalopathy.
2. What you need to know before you take Lornit
Do not take Lornit if:
- You are allergic to L-Ornithine L-Aspartate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- You have severe renal insufficiency (serum creatinine value > 3 mg/100 ml).
Warnings and precautions:
- Regular monitoring of serum and urinary urea levels is necessary.
- Use during pregnancy should only be if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks to the fetus.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
Driving and using machines:
- Avoid using Lornit during pregnancy and breastfeeding unless deemed necessary by your doctor. Driving and using machines:
No studies have been performed on the effects of Lornit on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to take Lornit
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor if you are not sure.
Recommended dose:
- 2-3 tablets, 3-4 times per day for mild to moderate liver disorders.
If you use more Lornit than you should
Tell your doctor if you accidentally use more than you were told.
If you forget to use Lornit
If you forget to take at the right time, use it as soon as you remember, then carry on as before. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using Lornit
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Very rare side effects:
- Nausea and vomiting, which are usually transient and do not require stopping the medication.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page. Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Lornit
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after EXP.
- The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Lornit contains:
- The active substance is L-Ornithine L-Aspartate (150 mg or 500 mg per tablet).
For More Information About This Product
Enzelo 25000 Capsules
1.0 Generic name
Pancreatin
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
ENZELO 10000
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Pancreatin IP 170 mg
(As enteric coated pellets)
Declared enzyme activity
Amylase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 8000
Lipase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 10000
Protease (Ph.Eur.U)/U 600
Approved Colours used in capsule shell
ENZELO 25000
Each hard gelatin capsule contains: Pancreatin IP 350 mg
(As enteric coated pellets)
Declared enzyme activity
Amylase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 18000
Lipase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 25000
Protease (Ph.Eur.U)/U 1000
Approved Colours used in capsule shell
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Capsule
Pancreatin 170 mg / 350 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For the treatment of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults (including the elderly) and children:
Initially one or two capsules during each meal. Dose increases, if required, should be added slowly, with careful monitoring of response and symptomatology.
It is important to ensure adequate hydration of patients at all times whilst dosing Enzelo 25000.
Fibrosing colonopathy has been reported in patients with cystic fibrosis taking in excess of 10,000 units of lipase/kg/day
Method of administration
Oral use.
Capsule should be swallowed whole & not to be opened, chewed or crushed.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to Pancreatin of porcine origin or to any of the excipients
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Strictures of the ileo-caecum and large bowel (fibrosing colonopathy) have been reported in patients with cystic fibrosis taking high doses of pancreatin preparations. As a precaution, unusual abdominal symptoms or changes in abdominal symptoms should be medically assessed to exclude the possibility of fibrosing colonopathy, especially if the patient is taking in excess of 10,000 units of lipase/kg/day.
4.5 Drugs interactions
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
For pancreatic enzymes no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available.
Animal studies show no evidence for any absorption of porcine pancreatic enzymes. Therefore, no reproductive or developmental toxicity is to be expected.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing to pregnant women.
Nursing Mothers
No effects on the suckling child are anticipated since animal studies suggest no systemic exposure of the breast-feeding woman to pancreatic enzymes. Pancreatic enzymes can be used during breast-feeding.
If required during pregnancy or lactation Enzelo should be used in doses sufficient to provide adequate nutritional status.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Enzelo has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
| Organ system | Very common ≥ 1/10 | Common ≥ 1/100 to < 1/10 | Uncommon ≥ 1/1000 to < 1/100 | Frequency not known |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | abdominal pain* | nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal distention, diarrhoea* | strictures of the ileo-caecum and large bowel (fibrosing colonopathy) | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | rash | pruritus, urticaria | ||
| Immune system disorders | hypersensitivity (anaphylactic reactions). |
*Gastrointestinal disorders are mainly associated with the underlying disease. Similar or lower incidences compared to placebo were reported for abdominal pain and diarrhoea.
Strictures of the ileo-caecum and large bowel (fibrosing colonopathy) have been reported in patients with cystic fibrosis taking high doses of pancreatin preparations, see section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use.
Allergic reactions mainly but not exclusively limited to the skin have been observed and identified as adverse reactions during post-approval use. Because these reactions were reported spontaneously from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency.
Paediatric population
No specific adverse reactions were identified in the paediatric population. Frequency, type and severity of adverse reactions were similar in children with cystic fibrosis as compared to adults.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
4.9 Overdose
Extremely high doses of pancreatin have been reported to be associated with hyperuricosuria and hyperuricaemia.
Supportive measures including stopping enzyme therapy and ensuring adequate rehydration are recommended.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
The capsules dissolve rapidly in the stomach releasing plenty of minimicrospheres, a multidose principle which is designed to achieve good mixing with the chyme, emptying from the stomach together with the chyme and after release, good distribution of enzymes within the chyme.
When the minimicrospheres reach the small intestine the coating rapidly disintegrates (at pH > 5.5) to release enzymes with lipolytic, amylolytic and proteolytic activity to ensure the digestion of fats, starches and proteins. The products of pancreatic digestion are then either absorbed directly, or following further hydrolysis by intestinal enzymes.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Treatment with enzelo markedly improves the symptoms of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency including stool consistency, abdominal pain, flatulence and stool frequency, independent of the underlying disease.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Pharmacokinetic data are not available as the enzymes act locally in the gastro-intestinal tract. After exerting their action, the enzymes are digested themselves in the intestine.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Not applicable.
7.0 Description
Pancreatin is a pancreatic enzyme supplement, containing Lipase, Amylase, Protease
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on Pack
8.3 Packaging information
10 Blister strips of 10 capsules each
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C.
Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Capsule should be swallowed whole & not to be opened, chewed or crushed.
- Capsule should be taken with the first bite of a meal
- Should be taken with sufficient fluid, adequate hydration should be ensured
- Dosage should not be changed or increased without the physician direction
- Sporadic doses (not taken with food) should be avoided
- Do not take this medicine, if you are allergic to porcine pancreatin.
- Signs of an allergic reaction include a rash, itching or shortness of breath.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only.
- Do not pass it on to others.
- It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- ENZELO is a pancreatic enzyme supplement for people whose bodies do not make enough enzymes to digest their food.
- Take the number of capsules as prescribed by your doctor or dietician.
- ENZELO Capsule should be taken with the first bite of a meal or a snack and drink plenty of water.
- Do not take ENZELO if you are allergic to pork or any pig product.
- If you experience severe abdominal pain while taking ENZELO, contact your doctor immediately.
- Most people do not have problems taking ENZELO but side effects can occur.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What ENZELO is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take ENZELO
- How to take ENZELO
- Possible side effects
- How to store ENZELO
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Enzelo is and What It is Used for
What is ENZELO
- ENZELO is a high strength pancreatic enzyme supplement.
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements are used by people whose bodies do not make enough of their own enzymes to digest their food.
- ENZELO granules contain a mixture of the natural enzymes which are used to digest food.
- The enzymes are taken from pig pancreas glands.
How ENZELO works
The enzymes in ENZELO work by digesting food as it passes through the gut. So you must take ENZELO at the same time as eating a meal or a snack. This will allow the enzymes to mix thoroughly with the food.
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Enzelo
Do not use ENZELO
you are allergic to pork, any pig product, or to any of the other ingredients If the above applies to you do not take ENZELO. Talk to your doctor or dietician again.
Warnings and precautions
A rare bowel condition called “fibrosing colonopathy”, where gut is narrowed, has been reported in patients with cystic fibrosis taking high dose pancreatin products.
If you have cystic fibrosis and take in excess of 10,000 lipase units per kilogram per day and have unusual abdominal symptoms or changes in abdominal syptoms tell you doctor.
Talk to your doctor if:
- You are pregnant or trying to get pregnant (ENZELO can be used while breast feeding)
- Please tell your doctor dietician or pharmacist if you think that you should not take ENZELO for any other reason.
If you drive or use machines
It is unlikely that ENZELO will affect your ability to drive or operate tools or machines.
3. How to Use Enzelo
How much ENZELO to take
- Always follow your doctor or dietician’s advice on how many capsules to take.
- Initially one or two capsules during each meal.
- It is important to ensure adequate hydration of patients at all times whilst dosing Enzelo 25000.
- If your doctor advises you to increase the number of capsules you take, you should do so slowly with careful monitoring of response and symptomatology. If you still have fatty stools or abdominal pain, talk to your doctor or dietician.
When to take ENZELO
- ENZELO Capsule should be taken with the first bite of a meal or a snack and drink plenty of water
How to take ENZELO
- Swallow the capsules whole
- Drink plenty of liquid every day.
- Mixing with non-acidic food or liquid, crushing or chewing of the pellets may cause irritation in your mouth or change the way ENZELO works in your body.
- Do not hold ENZELO capsules or its content in your mouth.
How long to take ENZELO for?
You should take your medicine until your doctor tells you to stop. Many patients will need to take pancreatic enzymes supplements for the rest of their lives.
If you take too much ENZELO
If you take too much ENZELO you should drink plenty of water and see your doctor immediately.
If you forget a dose
If you forget to take your medicine, wait until your next meal and take your usual number of capsules.
Do not try to make up for the number of capsules that you have missed. Just take your next dose at the usual time.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, ENZELO can cause side effects (unwanted effects or reactions), but not everyone gets them.
If you have severe or long-lasting abdominal pain, contact your doctor immediately.
If you notice any unusual abdominal symptoms while taking ENZELO– contact your doctor.
Very common side effects (affect more than 1 in 10 patients):
- stomach pains
Common side effects (affect 1-10 patients of 100):
- diarrhoea
- constipation
- feeling or being sick
- bloating
Uncommon side effects (affect 1-10 patients of 1000):
- Skin reaction, such as a rash.
During use, some patients have also experienced the following, the frequency of which is unknown:
- itching with or without a rash
- allergic reactions (which may be severe)
- severe or long-lasting abdominal pain (Fibrosing colonopathy).
At extremely high doses, some patients have had high levels of uric acid in their blood and urine.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Enzelo
Store below 25°C.
Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What ENZELO contains
ENZELO 10000
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Pancreatin IP 170 mg
(As enteric coated pellets)
Declared enzyme activity
Amylase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 8000
Lipase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 10000
Protease (Ph.Eur.U)/U 600
Approved Colours used in capsule shell
ENZELO 25000
Each hard gelatin capsule contains: Pancreatin IP 350 mg
(As enteric coated pellets)
Declared enzyme activity Amylase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 18000
Lipase (Ph.Eur.U)/U 25000
Protease (Ph.Eur.U)/U 1000
Approved Colours used in capsule shell
Packaging:
10 Blister strips of 10 capsules each
For More Information About This Product
Elriz XL Tablets
1.0 Generic Name
Levocetirizine hydrochloride & Ambroxol Hydrochloride modified release (5 mg +75mg)
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each modified release uncoated bilayered tablet contains:
Levocetirizine Hydrochloride IP 5 mg
(As immediate release)
Ambroxol Hydrochloride IP 75 mg
(As prolonged release)
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset Yellow
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Modified release uncoated bilayered tablet
5mg + 75mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For symptomatic relief of productive cough associated with allergic rhinitis, when both antihistamine and mucolytic agents are desired.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and adolescents 12 years and above:1 tablet once a day
Elderly
Adjustment of the dose is recommended in elderly patients with moderate to severe renal impairment.
Renal impairment
The dosing intervals must be individualised according to renal function (eGFR – estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate). Refer to the following table and adjust the dose as indicated.
Dosing adjustments for patients with impaired renal function (as per Levocetirizine dose):
| Group | eGFR (ml/min) | Dosage and frequency |
| Normal | ≥ 90 | 1 tablet once daily |
| Mild | 60 – < 90 | 1 tablet once daily |
| Moderate | 30 – < 60 | 1 tablet once every 2 days |
| Severe | 15 - < 30 (not requiring dialysis) | 1 tablet once every 3 days |
| End-stage renal disease - | < 15 (requiring dialysis treatment) | Contra-indicated |
In paediatric patients suffering from renal impairment, the dose will have to be adjusted on an individual basis taking into account the renal clearance of the patient and his body weight. There are no specific data for children with renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with solely hepatic impairment. In patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment, adjustment of the dose is recommended (see Renal impairment above).
Method of administration - Oral
Tablet should be swallowed whole & not to be broken, crushed or chewed. It may be taken with or without food. It is recommended to take the daily dose in one single intake.
4.3 Contraindications
- Patients with history of hypersensitivity to any component of the product
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to cetirizine, to hydroxyzine, to any other piperazine derivatives or to any of the other excipients.
- Patients with end stage renal disease with eGFR below 10 ml/min (requiring dialysis treatment).
- Patients undergoing haemodialysis
- Children < 12 years of age
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Precaution is recommended with concurrent intake of alcohol.
- Caution should be taken in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia) as levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention.
- Caution should be taken in patients with epilepsy and patients at risk of convulsion as levocetirizine may cause seizure aggravation.
- Response to allergy skin tests are inhibited by antihistamines and a wash-out period (of 3 days) is required before performing them.
- Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
- Pruritus may occur when levocetirizine is stopped even if those symptoms were not present before treatment initiation. The symptoms may resolve spontaneously. In some cases, the symptoms may be intense and may require treatment to be restarted. The symptoms should resolve when the treatment is restarted.
- In clinical trials the occurrence of somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia has been reported in some patients under therapy with Elriz XL.
- Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of Elriz XL.
- Concurrent use of Elriz-XL with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
- The use of Elriz XL (Ambroxol) should be carefully considered in patients predisposed to peptic ulcers.
- Ciliary dyskinesia: In patients with ciliary dyskinesia the benefit of liquefaction of secretions should be carefully weighed against the risk of congestion of secretions.
Pediatric population
The use of ELRIZ®XL tablet is not recommended in children aged less than 12 years.
4.5 Drugs interactions
- No interaction studies have been performed with levocetirizine (including no studies with CYP3A4 inducers); studies with the racemate compound cetirizine demonstrated that there were no clinically relevant adverse interactions (with anti-pyrine, azithromycin, cimetidine, diazepam, erythromycin, glipizide, ketoconazole and pseudoephedrine). A small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine (16%) was observed in a multiple dose study with theophylline (400 mg once a day); while the disposition of theophylline was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
- In vitro data indicate that levocetirizine is unlikely to produce pharmacokinetic interactions through inhibition or induction of liver drug-metabolizing enzymes.
- In a multiple dose study of ritonavir (600 mg twice daily) and cetirizine (10 mg daily), the extent of exposure to cetirizine was increased by about 40% while the disposition of ritonavir was slightly altered (-11%) further to concomitant cetirizine administration.
- The extent of absorption of levocetirizine is not reduced with food, although the rate of absorption is decreased.
- In sensitive patients, the concurrent administration of cetirizine or levocetirizine and alcohol or other CNS depressants may cause additional reductions in alertness and impairment of performance.
- After administration of ambroxol concentrations of antibiotics (amoxicillin, cefuroxime, erythromycin) in broncho-pulmonary secretions and sputum is increased.
- Anti-tussives: Concomitant administration of anti-tussives may impair the expectoration of liquefied bronchial mucus due to inhibition of the cough reflex and cause congestion of secretions.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Caution is advised when Elriz-XL is used during pregnancy. Use during the first trimester of pregnancy is not recommended.
Breast-feeding
Cetirizine, the racemate of levocetirizine, has been shown to be excreted in human. Therefore, the excretion of levocetirizine in human milk is likely. Adverse reactions associated with levocetirizine may be observed in breastfed infants. Therefore, caution should be exercised when prescribing levocetirizine to lactating women.
Fertility
For levocetirizine no clinical data are available.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Comparative clinical trials have revealed no evidence that levocetirizine at the recommended dose impairs mental alertness, reactivity or the ability to drive. Nevertheless, some patients could experience somnolence, fatigue and asthenia under therapy with levocetirizine.
Therefore, patients intending to drive, engage in potentially hazardous activities or operate machinery should take their response to the medicinal product into account.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Levocetirizine
- Common adverse reactions with (≥1/100 to <1/10): Headache (3.2%), Somnolence (1.4%), dry Mouth (1.6%), and Fatigue (1.2%).
- The incidence of sedating adverse drug reactions such as somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia was altogether more common (8.1%) under compared to placebo (3.1%)
- Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100): asthenia or abdominal pain
Ambroxol
- Mild upper gastro-intestinal side effects primarily Taste disturbances, heartburn, dyspepsia, and occasionally nausea and vomiting have been reported.
- Allergic reactions have occurred rarely, primarily skin rashes.
- There have been extremely rare case reports of severe acute anaphylactic-type reactions but their relationship to Ambroxol is uncertain. Some of these patients have also shown allergic reactions to other substances.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms
Levocetirizine
- Symptoms of overdose may include drowsiness in adults. In children, agitation and restlessness may initially occur, followed by drowsiness.
Ambroxol
- There are no severe intoxications known following an overdose of Ambroxol. Manifestations that have been reported include short-term restlessness and diarrhoea. Consistent with the findings of preclinical studies, increased saliva production, nausea, vomiting, and a drop in blood pressure can be observed following extreme overdosing.
Therapeutic Measures: There is no known specific antidote. Should overdose occur, symptomatic or supportive treatment is recommended. Gastric lavage may be considered shortly after ingestion of the drug. Levocetirizine is not effectively removed by haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Levocetirizine, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, is a second- generation anti-histamine and a potent and selective antagonist of peripheral H1-receptors.
Ambroxol is frequently used as mucolytic and it also induces the synthesis of surfactant in lung alveolar type II cells. By this mechanism, it decreases the work and effort of breathing and can improve respiratory symptoms. It has also been proved to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
At half the dose, levocetirizine has comparable activity to cetirizine, both in the skin and in the nose. Levocetirizine shows receptor occupancy of 90% at 4 hours and 57% at 24 hours. The onset of action of levocetirizine 5 mg has been observed at 1-hour post drug intake.
Ambroxol is shown to exert several activities: i) secretolytic activity (i.e., promotes mucus clearance, facilitates expectoration, and eases productive cough); ii) anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity; and iii) a local anesthetic effect through sodium channel blocking at the level of the cell membrane.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Levocetirizine exhibited linear pharmacokinetics over the therapeutic dose range in adult healthy subjects.
| Pharmacokinetics parameters | Levocetirizine HCL (5 mg o.d. dose) | Ambroxol HCL |
| Bioavailability | 85% | 79% |
| Cmax | 270 ng/mL and 308 ng/mL | 169.03±23.42 ng/mL |
| Tmax | 0.5 hours | 1.20±0.22 hours |
| Volume of distribution | 0.4 L/kg | 552 L# |
| Protein binding | 91 to 92%, | 90% |
| Half life | 7.9 ± 1.9 hours | 7.07±1.54 hours |
| Excretion | Renal | Primarily metabolized in the liver |
Pharmacokinetics in special Populations
- Elderly Levocetirizine dose should be adjusted in accordance with renal function in elderly patients
- Hepatic Insufficiency No dose adjustment is needed in patients with solely hepatic impairment.
- Renal Insufficiency Dosage and frequency of administration of ELRIZ®XL should be reduced
- Dosage and frequency of administration of Levocetirizine should be reduced in patients with mild, moderate or severe renal impairment
- In patients with moderate to severe renal / hepatic impairment, a slower elimination rate may lead to the accumulation of ambroxol and/or ambroxol-metabolites formed in the liver.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential, toxicity to reproduction and development.
7.0 Description
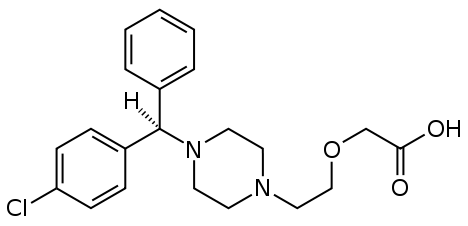
ELRIZ®XL is a fixed dose combination of a Levocetirizine Hydrochloride (5mg) and Ambroxol Hydrochloride (75mg).
Levocetirizine hydrochloride is an orally active H1-receptor antagonist.
Molecular Formula: C21H25ClN2O3•HCl
Chemical name: (R)-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl) phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] acetic acid hydrochloride.
Molecular weight: 461.82
Molecular Structure:
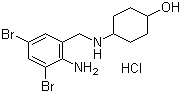
Ambroxol is a metabolite of bromhexine and is widely used as a mucolytic.
Molecular Formula: C13H18Br2N2O.HCl
Chemical name: trans-4-((2-amino-3,5-dibromobenzyl) amino) cyclohexanol hydrochloride
Molecular Weight: 414.56 g/mol
Molecular Structure:
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
10 blister strips of 10 tablets each
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
- Store in cool, dry and dark place.
- Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- ELRIZ®XL Tablet should be swallowed whole & not to be broken, crushed or chewed.
- Somnolence Caution patients against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of levocetirizine dihydrochloride.
- Concomitant Use of Alcohol and other Central Nervous System Depressants Instruct patients to avoid concurrent use of levocetirizine hydrochloride with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants because additional reduction in mental alertness may occur.
- Dosing of Tablets Do not exceed the recommended daily dose in adults and adolescents 12 years of age. Advise patients to not ingest more than the recommended dose of levocetirizine hydrochloride because of the increased risk of somnolence at higher doses.
- Do not take this medicine, if you are allergic to Levocetirizine and/or Ambroxol Signs of an allergic reaction include a rash, itching or shortness of breath.
- Advice patients to talk to your doctor or pharmacist, if you get any side effects. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
- Advice patients If they have any further questions, ask doctor or pharmacist.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1.What ELRIZ®XL is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you take ELRIZ®XL
3.How to take ELRIZ®XL
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store ELRIZ®XL
6.Contents of the pack and other information
1. What ELRIZ®XL is and what it is used for
ELRIZ®XL is a fixed dose combination of a Levocetirizine Hydrochloride (5mg) and Ambroxol Hydrochloride (75mg).
Levocetirizine, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, is a second-generation anti-histamine and a potent and selective antagonist of peripheral H1-receptors.
Ambroxol is frequently used as mucolytic and it also induces the synthesis of surfactant in lung alveolar type II cells. By this mechanism, it decreases the work and effort of breathing and can improve respiratory symptoms. It has also been proved to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the active ingredient of ELRIZ®XL.
ELRIZ®XL is used for symptomatic relief of productive cough associated with allergic rhinitis, when both antihistamine and mucolytic agents are desired.
2. What you need to know before you take ELRIZ®XL
Do not take ELRIZ®XL:
- If you are allergic to ELRIZ®XL or any of its ingredients.
- If you have a severe impairment of kidney function (severe renal failure with creatinine clearance below 10 ml/min).
- If you have a severe kidney disease requiring dialysis.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before taking ELRIZ®XL:
- If you are likely to be unable to empty your bladder (with conditions such as spinal cord injury or enlarged prostate), please ask your doctor for advice.
- If you suffer from epilepsy or are at risk of convulsions, please ask your doctor for advice as use of ELRIZ®XL may cause seizure aggravation.
- If you are scheduled for allergy testing, ask your doctor if you should stop taking ELRIZ®XL for several days before testing. This medicine may affect your allergy test results.
Tell your doctor immediately if during treatment you suffer from
Hypersensitivity reactions (swelling of the mouth, tongue, face and/or throat, breathing or swallowing difficulties, chest tightness or wheezing, hives, sudden fall in blood pressure)
At the first signs of a hypersensitivity reaction, stop taking ELRIZ®XL and tell your doctor.
Other medicines and ELRIZ®XL
Tell your doctor if you are taking or have taken the following medications.
- Ritonavir
- Antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Cefuroxime, Erythromycin)
- Antitussives
ELRIZ®XL with food, drink and alcohol
Take caution during the concurrent administration of ELRIZ®XL and alcohol or other agents.
ELRIZ®XL can be taken with or without food.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
You should not take ELRIZ®XL during pregnancy.
You should not breast-feed when taking ELRIZ®XL.
If you are pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Undesirable effects such as somnolence /drowsiness, tiredness and exhaustion are possible. You should not drive or operate machinery.
3. How to take ELRIZ®XL
Always take this medicine exactly as described in this leaflet or as your doctor, pharmacist or nurse has told you. Check with your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you are not sure.
The recommended dose for adults and children aged 12 years and over: one tablet daily. Swallow the tablet whole with some water.
Use in children
ELRIZ®XL is not used for children under 12 years of age.
Special dosage instructions for specific populations:
Renal and hepatic impairment
Patients with impaired kidney function may be given a lower dose according to the severity of their kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Patients who have severe impairment of kidney function must not take ELRIZ®XL.
Patients who only have impaired liver function should take the usual prescribed dose.
Patients who have both impaired liver and kidney function may be given a lower dose depending on the severity of the kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Elderly patients aged 65 years and above
No adaptation of the dose is necessary in elderly patients, provided their renal function is normal.
If you take more ELRIZ®XL than you should
If you take more ELRIZ®XL than you should, somnolence can occur in adults. Children may initially show excitation and restlessness followed by somnolence.
Tell your doctor or emergency department in hospital immediately.
If you forget to take ELRIZ®XL
If you forget to take ELRIZ®XL, or if you take a dose lower than that prescribed by your doctor, do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. Take your next dose at your normal time.
If you stop taking ELRIZ®XL
Stopping treatment should have no negative effects. However, rarely pruritus (intense itching) may occur if you stop taking ELRIZ®XL, even if those symptoms were not present before treatment initiation.
The symptoms may resolve spontaneously. In some cases, the symptoms may be intense and may require treatment to be restarted. The symptoms should resolve when the treatment is restarted.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist immediately if you notice any of these side effects during your treatment with ELRIZ®XL:
Levocetirizine
- Common adverse reactions with (≥1/100 to <1/10): Headache (3.2%), Somnolence (1.4%), dry Mouth (1.6%), and Fatigue (1.2%).
- The incidence of sedating adverse drug reactions such as somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia was altogether more common (8.1%) under compared to placebo (3.1%)
- Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100): asthenia or abdominal pain
Ambroxol
- Mild upper gastro-intestinal side effects primarily Taste disturbances, heartburn, dyspepsia, and occasionally nausea and vomiting have been reported.
- Allergic reactions have occurred rarely, primarily skin rashes.
- There have been extremely rare case reports of severe acute anaphylactic-type reactions but their relationship to Ambroxol is uncertain. Some of these patients have also shown allergic reactions to other substances.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store ELRIZ®XL
Store protected from light.
Store in cool and dry place.
Keep out of reach of children.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What ELRIZ®XL contains
Each modified release uncoated bilayered tablet contains:
Levocetirizine Hydrochloride IP 5 mg
(As immediate release)
Ambroxol Hydrochloride IP 75 mg
(As prolonged release)
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset Yellow
Pack size: 10 Blister strips of 10 tablets each
For More Information About This Product
Elriz Tablet
1.0 Generic Name
Levocetirizine Tablets IP 5 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each film coated tablet contains
Levocetirizine Hydrochloride IP 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film-coated tablet. 5 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
Therapeutic Indication
For allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria.
Posology and method of administration
- Adults and adolescents 12 years and above:
The daily recommended dose is 5 mg (1 tablet).
Elderly
Adjustment of the dose is recommended in elderly patients with moderate to severe renal impairment.
Renal impairment
The dosing intervals must be individualised according to renal function (eGFR – estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate). Refer to the following table and adjust the dose as indicated.
Dosing adjustments for patients with impaired renal function:
| Group | eGFR (ml/min) | Dosage and frequency |
| Normal | ≥ 90 | 1 tablet once daily |
| Mild | 60 – < 90 | 1 tablet once daily |
| Moderate | 30 – < 60 | 1 tablet once every 2 days |
| Severe | 15 - < 30 (not requiring dialysis) | 1 tablet once every 3 days |
| End-stage renal disease - | < 15 (requiring dialysis treatment) | Contra-indicated |
In paediatric patients suffering from renal impairment, the dose will have to be adjusted on an individual basis taking into account the renal clearance of the patient and his body weight. There are no specific data for children with renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with solely hepatic impairment. In patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment, adjustment of the dose is recommended (see Renal impairment above).
Paediatric population
Children aged 6 to 12 years:
The daily recommended dose is 5 mg (1 film-coated tablet).
For children aged 2 to 6 years no adjusted dosage is possible with the film-coated tablet formulation. It is recommended to use a paediatric formulation of Elriz.
Method of administration
The film-coated tablet must be taken orally, swallowed whole with liquid and may be taken with or without food. It is recommended to take the daily dose in one single intake.
Duration of use:
Intermittent allergic rhinitis (symptoms experienced for less than four days a week or for less than four weeks a year) has to be treated according to the disease and its history; it can be stopped once the symptoms have disappeared and can be restarted again when symptoms reappear. In case of persistent allergic rhinitis (symptoms experienced for more than four days a week or for more than four weeks a year), continuous therapy can be proposed to the patient during the period of exposure to allergens.
There is clinical experience with the use of levocetirizine for treatment periods of at least 6 months. In chronic urticaria and chronic allergic rhinitis, there is clinical experience of use of cetirizine (racemate) for up to one year.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to cetirizine, to hydroxyzine, to any other piperazine derivatives or to any of the other excipients.
Patients with end stage renal disease with estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) below 15 ml/min (requiring dialysis treatment).
Special warnings and precautions for use
Precaution is recommended with concurrent intake of alcohol.
Caution should be taken in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia) as levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention.
Caution should be taken in patients with epilepsy and patients at risk of convulsion as levocetirizine may cause seizure aggravation.
Response to allergy skin tests are inhibited by antihistamines and a wash-out period (of 3 days) is required before performing them.
Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Pruritus may occur when levocetirizine is stopped even if those symptoms were not present before treatment initiation. The symptoms may resolve spontaneously. In some cases, the symptoms may be intense and may require treatment to be restarted. The symptoms should resolve when the treatment is restarted.
Paediatric population
The use of the film-coated tablet formulation is not recommended in children aged less than 6 years since this formulation does not allow for appropriate dose adaptation. It is recommended to use a paediatric formulation of Elriz.
Drugs interactions
No interaction studies have been performed with levocetirizine (including no studies with CYP3A4 inducers); studies with the racemate compound cetirizine demonstrated that there were no clinically relevant adverse interactions (with antipyrine, azithromycin, cimetidine, diazepam, erythromycin, glipizide, ketoconazole and pseudoephedrine). A small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine (16%) was observed in a multiple dose study with theophylline (400 mg once a day); while the disposition of theophylline was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
In a multiple dose study of ritonavir (600 mg twice daily) and cetirizine (10 mg daily), the extent of exposure to cetirizine was increased by about 40% while the disposition of ritonavir was slightly altered (-11%) further to concomitant cetirizine administration.
The extent of absorption of levocetirizine is not reduced with food, although the rate of absorption is decreased.
In sensitive patients, the concurrent administration of cetirizine or levocetirizine and alcohol or other CNS depressants may cause additional reductions in alertness and impairment of performance.
Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data (less than 300 pregnancy outcomes) from the use of levocetirizine in pregnant women. However, for cetirizine, the racemate of levocetirizine, a large amount of data (more than 1000 pregnancy outcomes) on pregnant women indicate no malformative or feto/ neonatal toxicity. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryo/fetal development, parturition or postnatal development
The use of levocetirizine may be considered during pregnancy, if necessary.
Breast-feeding
Cetirizine, the racemate of levocetirizine, has been shown to be excreted in human. Therefore, the excretion of levocetirizine in human milk is likely. Adverse reactions associated with levocetirizine may be observed in breastfed infants. Therefore, caution should be exercised when prescribing levocetirizine to lactating women.
Fertility
For levocetirizine no clinical data are available.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Comparative clinical trials have revealed no evidence that levocetirizine at the recommended dose impairs mental alertness, reactivity or the ability to drive.
Nevertheless, some patients could experience somnolence, fatigue and asthenia under therapy with levocetirizine. Therefore, patients intending to drive, engage in potentially hazardous activities or operate machinery should take their response to the medicinal product into account.
Undesirable effects
Clinical studies
Adults and adolescents above 12 years of age
In therapeutic studies in women and men aged 12 to 71 years, 15.1% of the patients in the levocetirizine 5 mg group had at least one adverse drug reaction compared to 11.3% in the placebo group. 91.6 % of these adverse drug reactions were mild to moderate.
In therapeutic trials, the dropout rate due to adverse events was 1.0% (9/935) with levocetirizine 5 mg and 1.8% (14/771) with placebo.
Clinical therapeutic trials with levocetirizine included 935 subjects exposed to the medicinal product at the recommended dose of 5 mg daily. From this pooling, following incidence of adverse drug reactions were reported at rates of 1% or greater (common: ≥1/100 to <1/10) under levocetirizine 5 mg or placebo:
| Preferred Term (WHOART) | Placebo (n =771) | Levocetirizine 5 mg (n = 935) |
| Headache | 25 (3.2%) | 24 (2.6%) |
| Somnolence | 11 (1.4%) | 49 (5.2%) |
| Mouth dry | 12 (1.6%) | 24 (2.6%) |
| Fatigue | 9 (1.2%) | 23 (2.5%) |
Further uncommon incidences of adverse reactions (uncommon ≥1/1,000 to <1/100) like asthenia or abdominal pain were observed.
The incidence of sedating adverse drug reactions such as somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia was altogether more common (8.1%) under levocetirizine 5 mg than under placebo (3.1%).
Paediatric population
In two placebo-controlled studies in paediatric patients aged 6-11 months and aged 1 year to less than 6 years, 159 subjects were exposed to levocetirizine at the dose of 1.25 mg daily for 2 weeks and 1.25 mg twice daily respectively. The following incidence of adverse drug reactions was reported at rates of 1% or greater under levocetirizine or placebo.
|
System Organ Class and Preferred Term |
Placebo (n=83) |
Levocetirizine (n=159) |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
||
|
Diarrhoea |
0 |
3(1.9%) |
|
Vomiting |
1(1.2%) |
1(0.6%) |
|
Constipation |
0 |
2(1.3%) |
|
Nervous system disorders |
||
|
Somnolence |
2(2.4%) |
3(1.9%) |
|
Psychiatric disorders |
||
|
Sleep disorder |
0 |
2(1.3%) |
In children aged 6-12 years double blind placebo controlled studies were performed where 243 children were exposed to 5 mg levocetirizine daily for variable periods ranging from less than 1 week to 13 weeks. The following incidence of adverse drug reactions was reported at rates of 1% or greater under levocetirizine or placebo.
|
Preferred Term |
Placebo (n=240) |
Levocetirizine 5mg (n=243) |
|
Headache |
5(2.1%) |
2(0.8%) |
|
Somnolence |
1(0.4%) |
7(2.9%) |
Post-marketing experience
Adverse reactions from post-marketing experience are per System Organ Class and per frequency. The frequency is defined as follows: very common (≥1/10); common (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
- Immune system disorders: Not known: hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Not known: increased appetite
- Psychiatric disorders: Not known: aggression, agitation, hallucination, depression, insomnia, suicidal ideation, nightmare
- Nervous system disorders: Not known: convulsion, paraesthesia, dizziness, syncope, tremor, dysgeusia
- Ear and labyrinth disorders:Not known: vertigo
- Eyes disorders: Not known: visual disturbances, blurred vision, oculogyration
- Cardiac disorders: Not known: palpitations, tachycardia
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Not known: dyspnoea
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Not known: nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea
- Hepatobiliary disorders: Not known: hepatitis
- Renal and urinary disorders: Not known: dysuria, urinary retention
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Not known: angioneurotic oedema, fixed drug eruption, pruritus, rash, urticarial
- Musculoskeletal, connective tissues, and bone disorders: Not known: myalgia, arthralgia
- General disorders and administration site conditions: Not known: oedema
- Investigations: Not known: weight increased, abnormal liver function tests
- Description of selected adverse reactions After levocetirizine discontinuation, pruritus has been reported.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Overdose
Symptoms
Symptoms of overdose may include drowsiness in adults. In children, agitation and restlessness may initially occur, followed by drowsiness.
Management of overdoses
There is no known specific antidote to levocetirizine.
Should overdose occur, symptomatic or supportive treatment is recommended. Gastric lavage may be considered shortly after ingestion of the drug. Levocetirizine is not effectively removed by haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of Action
Levocetirizine hydrochloride, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, is a second-generation anti-histamine and a potent and selective antagonist of peripheral H1-receptors.
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antihistamine for systemic use, piperazine derivatives, ATC code: R06A E09.
Binding studies revealed that levocetirizine has high affinity for human H1-receptors (Ki = 3.2 nmol/l). Levocetirizine has an affinity 2-fold higher than that of cetirizine (Ki = 6.3 nmol/l). Levocetirizine dissociates from H1-receptors with a half-life of 115 ± 38 min.
After single administration, levocetirizine shows a receptor occupancy of 90% at 4 hours and 57% at 24 hours.
Pharmacodynamic studies in healthy volunteers demonstrate that, at half the dose, levocetirizine has comparable activity to cetirizine, both in the skin and in the nose.
The pharmacodynamic activity of levocetirizine has been studied in randomised, controlled trials:
In a study comparing the effects of levocetirizine 5 mg, desloratadine 5 mg, and placebo on histamine-induced wheal and flare, levocetirizine treatment resulted in significantly decreased wheal and flare formation which was highest in the first 12 hours and lasted for 24 hours, (p<0.001) compared with placebo and desloratadine.
The onset of action of levocetirizine 5 mg in controlling pollen-induced symptoms has been observed at 1 hour post drug intake in placebo controlled trials in the model of the allergen challenge chamber.
Clinical efficacy and safety
The efficacy and safety of levocetirizine has been demonstrated in several double-blind, placebo controlled, clinical trials performed in adult patients suffering from seasonal allergic rhinitis, perennial allergic rhinitis, or persistent allergic rhinitis. Levocetirizine has been shown to significantly improve symptoms of allergic rhinitis, including nasal obstruction in some studies.
Chronic idiopathic urticaria was studied as a model for urticarial conditions. Since histamine release is a causal factor in urticarial diseases, levocetirizine is expected to be effective in providing symptomatic relief for other urticarial conditions, in addition to chronic idiopathic urticaria.
ECGs did not show relevant effects of levocetirizine on QT interval.
Pharmacokinetic properties
The pharmacokinetics of levocetirizine are linear with dose- and time-independent with low inter-subject variability. The pharmacokinetic profile is the same when given as the single enantiomer or when given as cetirizine. No chiral inversion occurs during the process of absorption and elimination.
Absorption
Levocetirizine is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. In adults, peak plasma concentrations are achieved 0.9 h after dosing. Steady state is achieved after two days. Peak concentrations are typically 270 ng/ml and 308 ng/ml following a single and a repeated 5 mg o.d. dose, respectively. The extent of absorption is dose-independent and is not altered by food, but the peak concentration is reduced and delayed.
Distribution
No tissue distribution data are available in humans, neither concerning the passage of levocetirizine through the blood-brain-barrier. In rats and dogs, the highest tissue levels are found in liver and kidneys, the lowest in the CNS compartment.
In humans, levocetirizine is 90% bound to plasma proteins. The distribution of levocetirizine is restrictive, as the volume of distribution is 0.4 l/kg.
Biotransformation
The extent of metabolism of levocetirizine in humans is less than 14% of the dose and therefore differences resulting from genetic polymorphism or concomitant intake of enzyme inhibitors are expected to be negligible. Metabolic pathways include aromatic oxidation, N- and O- dealkylation and taurine conjugation. Dealkylation pathways are primarily mediated by CYP 3A4 while aromatic oxidation involved multiple and/or unidentified CYP isoforms. Levocetirizine had no effect on the activities of CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1 and 3A4 at concentrations well above peak concentrations achieved following a 5 mg oral dose.
Due to its low metabolism and absence of metabolic inhibition potential, the interaction of levocetirizine with other substances, or vice-versa, is unlikely.
Elimination
The plasma half-life in adults is 7.9 ± 1.9 hours. The half-life is shorter in small children.
The mean apparent total body clearance in adults is 0.63 ml/min/kg. The major route of excretion of levocetirizine and metabolites is via urine, accounting for a mean of 85.4% of the dose. Excretion via faeces accounts for only 12.9% of the dose. Levocetirizine is excreted both by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential, toxicity to reproduction and development.
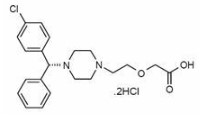
7.0 Description
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride, the active component of Elriz tablets and oral solution, is an orally active H1‑receptor antagonist. The chemical name is (R)-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl) phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] acetic acid dihydrochloride. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the R enantiomer of cetirizine hydrochloride, a racemic compound with antihistaminic properties. The empirical formula of levocetirizine dihydrochloride is C21H25ClN2O3•2HCl. The molecular weight is 461.82
Chemical structure is shown below:
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
Packaging information
2 Composite blister strips of 5 x 10 tablets each
Storage and handing instructions
- Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
- Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Somnolence
Caution patients against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of levocetirizine dihydrochloride.
Concomitant Use of Alcohol and other Central Nervous System Depressants
Instruct patients to avoid concurrent use of levocetirizine hydrochloride with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants because additional reduction in mental alertness may occur.
Dosing of Levocetirizine hydrochloride Tablets
Do not exceed the recommended daily dose in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older of 5 mg once daily in the evening. In children 6 to 11 years of age the recommended dose is 2.5 mg once daily in the evening. Advise patients to not ingest more than the recommended dose of levocetirizine hydrochloride because of the increased risk of somnolence at higher doses.
Do not take this medicine, if you are allergic to levocetirizine
Signs of an allergic reaction include a rash, itching or shortness of breath.
Advice patients to talk to your doctor or pharmacist, if you get any side effects. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Advice patients If they have any further questions, ask doctor or pharmacist.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What ELRIZ is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take ELRIZ
- How to take ELRIZ
- Possible side effects
- How to store ELRIZ
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Elriz is and What It is Used for
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the active ingredient of ELRIZ
ELRIZ is an anti-allergic medication.
For the treatment of signs of illness (symptoms) associated with:
- allergic rhinitis (including persistent allergic rhinitis);
- nettle rash (urticaria).
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Elriz
Do not use ELRIZ if you
- if you are allergic to levocetirizine dihydrochloride, to cetirizine, to hydroxyzine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
- if you have a severe impairment of kidney function (severe renal failure with creatinine clearance below 10 ml/min).
- if you have a severe kidney disease requiring dialysis.
Do not take ELRIZ tablets if any of the above applies to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking ELRIZ tablets.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before taking ELRIZ, especially if you
- If you are likely to be unable to empty your bladder (with conditions such as spinal cord injury or enlarged prostate), please ask your doctor for advice.
- If you suffer from epilepsy or are at risk of convulsions, please ask your doctor for advice as use of ELRIZ may cause seizure aggravation.
- If you are scheduled for allergy testing, ask your doctor if you should stop taking ELRIZ for several days before testing. This medicine may affect your allergy test results
Children and adolescents
The use of ELRIZ is not recommended in children less than 6 years since the film-coated tablets do not allow for dose adaptation.
Other medicines and ELRIZ
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
ELRIZ with food, drink and alcohol
Caution is advised if ELRIZ is taken at the same time as alcohol or other agents acting on the brain.
In sensitive patients, the concurrent administration of ELRIZ and alcohol or other agents acting on the brain may cause additional reductions in alertness and impairment of performance.
ELRIZ can be taken with or without food.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Some patients being treated with ELRIZ may experience somnolence / drowsiness, tiredness and exhaustion. Use caution when driving or operating machinery untill you know how this medicine affects you. However, special tests have revealed no impairment of mental alertness, the ability to react or the ability to drive in healthy test persons after taking levocetirizine in the recommended dosage.
3. How to Use Elriz
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose for adults and children aged 6 years and over is one tablet daily.
Special dosage instructions for specific populations:
Renal and hepatic impairment
Patients with impaired kidney function may be given a lower dose according to the severity of their kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Patients who have severe impairment of kidney function must not take ELRIZ.
Patients who only have impaired liver function should take the usual prescribed dose.
Patients who have both impaired liver and kidney function may be given a lower dose depending on the severity of the kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Elderly patients aged 65 years and above
No adaptation of the dose is necessary in elderly patients, provided their renal function is normal.
Use in children
ELRIZ is not recommended for children under 6 years of age.
How and when should you take ELRIZ?
For oral use only. ELRIZ tablets should be swallowed whole with water and may be taken with or without food.
How long should you take ELRIZ?
The duration of use depends on the type, duration and course of your complaints and is determined by your physician.
If you take more ELRIZ than you should
If you take more ELRIZ than you should, somnolence can occur in adults. Children may initially show excitation and restlessness followed by somnolence. If you think you have taken an overdose of ELRIZ, please tell your doctor who will then decide what action should be taken.
If you forget to take ELRIZ
If you forget to take ELRIZ, or if you take a dose lower than that prescribed by your doctor, do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. Take your next dose at your normal time.
If you stop taking ELRIZ
Stopping treatment should have no negative effects. However, rarely pruritus (intense itching) may occur if you stop taking ELRIZ, even if those symptoms were not present before treatment initiation.
The symptoms may resolve spontaneously. In some cases, the symptoms may be intense and may require treatment to be restarted. The symptoms should resolve when the treatment is restarted.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
Dry mouth, headache, tiredness and somnolence/drowsiness
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
Exhaustion and abdominal pain
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Other side effects such as palpitations, increased heart rate, fits, pins and needles, dizziness, syncope, tremor, dysgeusia (distortion of the sense of taste), sensation of rotation or movement, visual disturbances, blurred vision, oculogyration (eyes having uncontrolled circular movements), painful or difficult urination, inability to completely empty the bladder, oedema, pruritus (itchiness), rash, urticaria (swelling, redness and itchiness of the skin), skin eruption, shortness of breath, weight increase, muscular pain, joint pain, aggressive or agitated behaviour, hallucination, depression, insomnia, recurring thoughts of or preoccupation with suicide, nightmare, hepatitis, abnormal liver function, vomiting, increased appetite, nausea and diarrhoea have also been reported. Pruritus (intense itching) upon discontinuation.
At the first signs of a hypersensitivity reaction, stop taking ELRIZ and tell your doctor. Hypersensitivity reaction symptoms may include: swelling of the mouth, tongue, face and/or throat, breathing or swallowing difficulties (chest tightness or wheezing), hives, sudden fall in blood pressure leading to collapse or shock, which may be fatal.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly:Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Elriz
- Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C
- Keep out of reach of children
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister and the carton after “EXP”. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What ELRIZ contains
Each film coated tablet contains
Levocetirizine Hydrochloride IP-5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
2 Composite blister strips of 5 x 10 tablets each
For More Information About This Product
Elriz Syrup
1.0 Generic name
Levocetirizine syrup
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each 5 ml syrup contains:
Levocetirizine Hydrochloride 2.5 mg
Excipients …………………. q.s.
In a flavored syrup base.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral syrup, Levocetirizine 2.5mg/5ml
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and adolescents 12 years and above:
The daily recommended dose is 5 mg (10 ml of solution).
Elderly
Adjustment of the dose is recommended in elderly patients with moderate to severe renal impairment.
Renal impairment
The dosing intervals must be individualised according to renal function (eGFR – estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate). Refer to the following table and adjust the dose as indicated.
Dosing adjustments for patients with impaired renal function:
| Group | eGFR (ml/min) | Dosage and frequency |
| Normal renal function | ≥ 90 | 5 mg once daily |
| Mildly decreased renal function/td> | 60 – < 90 | 5 mg once daily |
| Moderately decreased renal function | 30 – < 60 | 5 mg once every 2 days |
| Severely decreased renal function | 15 – < 30 (not requiring dialysis) | 5 mg once every 3 days |
| End stage renal disease (ESRD) | < 15 (requiring dialysis treatment) | Contra-indicated |
In paediatric patients suffering from renal impairment, the dose will have to be adjusted on an individual basis taking into account the renal clearance of the patient and his body weight. There are no specific data for children with renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with solely hepatic impairment. In patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment, adjustment of the dose is recommended (see Renal impairment above).
Paediatric population
Children aged 6 to 12 years:
The daily recommended dose is 5 mg (10 ml of solution).
Children aged 2 to 6 years:
The daily recommended dose is 2.5 mg to be administered in 2 intakes of 1.25 mg (2.5 ml of solution twice daily).
Even if some clinical data are available in children aged 6 months to 12 years, these data are not sufficient to support the administration of levocetirizine to infants and toddlers aged less than 2 years.
Method of administration
An oral syringe is included in the package. The appropriate volume of oral solution should be measured with the oral syringe, and poured in a spoon or in a glass of water. The oral solution must be taken orally immediately after dilution, and may be taken with or without food.
Duration of use:
Intermittent allergic rhinitis (symptoms experienced for less than four days a week or for less than four weeks a year) has to be treated according to the disease and its history; it can be stopped once the symptoms have disappeared and can be restarted again when symptoms reappear. In case of persistent allergic rhinitis (symptoms experienced for more than four days a week or for more than four weeks a year), continuous therapy can be proposed to the patient during the period of exposure to allergens.
There is clinical experience with the use of levocetirizine for treatment periods of at least 6 months. In chronic urticaria and chronic allergic rhinitis, there is clinical experience of use of cetirizine (racemate) for up to one year.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to cetirizine, to hydroxyzine, to any other piperazine derivatives or to any of the other excipients.
Patients with end stage renal disease with estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) below 10 ml/min (requiring dialysis treatment).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Precaution is recommended with concurrent intake of alcohol.
Elriz contains methyl parahydroxybenzoate and propyl parahydroxybenzoate which may cause allergic reactions (possibly delayed).
Caution should be taken in patients with epilepsy and patients at risk of convulsion as levocetirizine may cause seizure aggravation.
Elriz contains maltitol liquid
Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not take this medicine.
Caution should be taken in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia) as levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention.
Response to allergy skin tests are inhibited by antihistamines and a wash-out period (of 3 days) is required before performing them.
Pruritus may occur when levocetirizine is stopped even if those symptoms were not present before treatment initiation. The symptoms may resolve spontaneously. In some cases, the symptoms may be intense and may require treatment to be restarted. The symptoms should resolve when the treatment is restarted.
Pediatric population
Even if some clinical data are available in children aged 6 months to 12 years, these data are not sufficient to support the administration of levocetirizine to infants and toddlers aged less than 2 years.
4.5 Drugs interactions
No interaction studies have been performed with levocetirizine (including no studies with CYP3A4 inducers); studies with the racemate compound cetirizine demonstrated that there were no clinically relevant adverse interactions (with antipyrine, azithromycin, cimetidine, diazepam, erythromycin, glipizide, ketoconazole and pseudoephedrine). A small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine (16%) was observed in a multiple dose study with theophylline (400 mg once a day); while the disposition of theophylline was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
In a multiple dose study of ritonavir (600 mg twice daily) and cetirizine (10 mg daily), the extent of exposure to cetirizine was increased by about 40% while the disposition of ritonavir was slightly altered (-11%) further to concomitant cetirizine administration.
The extent of absorption of levocetirizine is not reduced with food, although the rate of absorption is decreased.
In sensitive patients, the concurrent administration of cetirizine or levocetirizine and alcohol or other CNS depressants may cause additional reductions in alertness and impairment of performance.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data (less than 300 pregnancy outcomes) from the use of levocetirizine in pregnant women. However, for cetirizine, the racemate of levocetirizine, a large amount of data (more than 1000 pregnancy outcomes) on pregnant women indicate no malformative or feto/neonatal toxicity. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryo/fetal development, parturition or postnatal development.
The use of levocetirizine may be considered during pregnancy, if necessary.
Breast-feeding
Cetirizine, the racemate of levocetirizine, has been shown to be excreted in human. Therefore, the excretion of levocetirizine in human milk is likely. Adverse reactions associated with levocetirizine may be observed in breastfed infants. Therefore, caution should be exercised when prescribing levocetirizine to lactating women.
Fertility
For levocetirizine no clinical data are available.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Comparative clinical trials have revealed no evidence that levocetirizine at the recommended dose impairs mental alertness, reactivity or the ability to drive and use machines.
Nevertheless, some patients could experience somnolence, fatigue and asthenia under therapy with levocetirizine. Therefore, patients intending to drive, engage in potentially hazardous activities or operate machinery should take their response to the medicinal product into account.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Clinical studies
Adults and adolescents above 12 years of age In therapeutic studies in women and men aged 12 to 71 years, 15.1% of the patients in the levocetirizine 5 mg group had at least one adverse drug reaction compared to 11.3% in the placebo group. 91.6 % of these adverse drug reactions were mild to moderate. In therapeutic trials, the dropout rate due to adverse events was 1.0% (9/935) with levocetirizine 5 mg and 1.8% (14/771) with placebo. Clinical therapeutic trials with levocetirizine included 935 subjects exposed to the medicinal product at the recommended dose of 5 mg daily. From this pooling, following incidence of adverse drug reactions were reported at rates of 1% or greater (common: ≥ 1/100 to < 1/10) under levocetirizine 5 mg or placebo:
| Preferred Term (WHOART) | Placebo (n =771) | Levocetirizine 5 mg (n = 935) |
| Headache | 25 (3.2%) | 24 (2.6%) |
| Somnolence | 11 (1.4%) | 49 (5.2%) |
| Mouth dry | 12 (1.6%) | 24 (2.6%) |
| Fatigue | 9 (1.2%) | 23 (2.5%) |
Further uncommon incidences of adverse reactions (uncommon ≥ 1/1000 to < 1/100) like asthenia or abdominal pain were observed.
The incidence of sedating adverse drug reactions such as somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia was altogether more common (8.1%) under levocetirizine 5 mg than under placebo (3.1%).
Paediatric population
In two placebo-controlled studies in paediatric patients aged 6-11 months and aged 1 year to less than 6 years, 159 subjects were exposed to levocetirizine at the dose of 1.25 mg daily for 2 weeks and 1.25 mg twice daily respectively. The following incidence of adverse drug reactions was reported at rates of 1% or greater under levocetirizine or placebo.
| System Organ Class and Preferred Term | Placebo (n=83) | Levocetirizine (n=159) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhoea | 0 | 3(1.9%) |
| Vomiting | 1(1.2%) | 1(0.6%) |
| Constipation | 0 | 2(1.3%) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Somnolence | 2(2.4%) | 3(1.9%) |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Sleep disorder | 0 | 2(1.3%) |
In children aged 6-12 years double blind placebo controlled studies were performed where 243 children were exposed to 5 mg levocetirizine daily for variable periods ranging from less than 1 week to 13 weeks. The following incidence of adverse drug reactions was reported at rates of 1% or greater under levocetirizine or placebo.
| Preferred Term | Placebo (n=240) | Levocetirizine 5mg (n=243) |
| Headache | 5(2.1%) | 2(0.8%) |
| Somnolence | 1(0.4%) | 7(2.9%) |
Post-marketing experience
Adverse reactions from post-marketing experience are per System Organ Class and per frequency. The frequency is defined as follows: very common (≥1/10); common (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
- Immune system disorders:Not known: hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Not known: increased appetite
- Psychiatric disorders:Not known: aggression, agitation, hallucination, depression, insomnia, suicidal ideation, nightmare
- Nervous system disorders: Not known: convulsion, paraesthesia, dizziness, syncope, tremor, dysgeusia
- Ear and labyrinth disorders: Not known: vertigo
- Eyes disorders: Not known: visual disturbances, blurred vision, oculogyration
- Cardiac disorders: Not known: palpitations, tachycardia
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:Not known: dyspnoea
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Not known: nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea
- Hepatobiliary disorders: Not known: hepatitis
- Renal and urinary disorders: Not known: dysuria, urinary retention
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Not known: angioneurotic oedema, fixed drug eruption, pruritus, rash, urticarial
- Musculoskeletal, connective tissues, and bone disorders: Not known: myalgia, arthralgia
- General disorders and administration site conditions: Not known: oedema
- Investigations: Not known: weight increased, abnormal liver function tests
- Description of selected adverse reactions After levocetirizine discontinuation, pruritus has been reported.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms
Symptoms of overdose may include drowsiness in adults. In children, agitation and restlessness may initially occur, followed by drowsiness.
Management of overdoses
There is no known specific antidote to levocetirizine.
Should overdose occur, symptomatic or supportive treatment is recommended. Gastric lavage may be considered shortly after ingestion of the drug. Levocetirizine is not effectively removed by haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Levocetirizine hydrochloride, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, is a second-generation anti-histamine and a potent and selective antagonist of peripheral H1-receptors.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacodynamic effects
The pharmacodynamic activity of levocetirizine has been studied in randomised, controlled trials:
In a study comparing the effects of levocetirizine 5 mg, desloratadine 5 mg, and placebo on histamine-induced wheal and flare, levocetirizine treatment resulted in significantly decreased wheal and flare formation which was highest in the first 12 hours and lasted for 24 hours, (p<0.001) compared with placebo and desloratadine.
The onset of action of levocetirizine 5 mg in controlling pollen-induced symptoms has been observed at 1 hour post drug intake in placebo controlled trials in the model of the allergen challenge chamber.
In vitro studies (Boyden chambers and cell layers techniques) show that levocetirizine inhibits eotaxin-induced eosinophil transendothelial migration through both dermal and lung cells. A pharmacodynamic experimental study in vivo (skin chamber technique) showed three main inhibitory effects of levocetirizine 5 mg in the first 6 hours of pollen-induced reaction, compared with placebo in 14 adult patients: inhibition of VCAM-1 release, modulation of vascular permeability and a decrease in eosinophil recruitment.
Clinical efficacy and safety
The efficacy and safety of levocetirizine has been demonstrated in several double-blind, placebo controlled, clinical trials performed in adult patients suffering from seasonal allergic rhinitis, perennial allergic rhinitis, or persistent allergic rhinitis. Levocetirizine has been shown to significantly improve symptoms of allergic rhinitis, including nasal obstruction in some studies.
A 6-month clinical study in 551 adult patients (including 276 levocetirizine-treated patients) suffering from persistent allergic rhinitis (symptoms present 4 days a week for at least 4 consecutive weeks) and sensitized to house dust mites and grass pollen demonstrated that levocetirizine 5 mg was clinically and statistically significantly more potent than placebo on the relief from the total symptom score of allergic rhinitis throughout the whole duration of the study, without any tachyphylaxis. During the whole duration of the study, levocetirizine significantly improved the quality of life of the patients.
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial including 166 patients suffering from chronic idiopathic urticaria, 85 patients were treated with placebo and 81 patients with levocetirizine 5 mg once daily over six weeks. Treatment with levocetirizine resulted in significant decrease in pruritus severity over the first week and over the total treatment period as compared to placebo. Levocetirizine also resulted in a larger improvement of health-related quality of life as assessed by the Dermatology Life Quality Index as compared to placebo. Chronic idiopathic urticaria was studied as a model for urticarial conditions. Since histamine release is a causal factor in urticarial diseases, levocetirizine is expected to be effective in providing symptomatic relief for other urticarial conditions, in addition to chronic idiopathic urticaria.
ECGs did not show relevant effects of levocetirizine on QT interval.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
The pharmacokinetics of levocetirizine are linear with dose- and time-independent with low inter-subject variability. The pharmacokinetic profile is the same when given as the single enantiomer or when given as cetirizine. No chiral inversion occurs during the process of absorption and elimination.
Absorption
Levocetirizine is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. In adults, peak plasma concentrations are achieved 0.9 h after dosing. Steady state is achieved after two days. Peak concentrations are typically 270 ng/ml and 308 ng/ml following a single and a repeated 5 mg o.d. dose, respectively. The extent of absorption is dose-independent and is not altered by food, but the peak concentration is reduced and delayed.
Distribution
No tissue distribution data are available in humans, neither concerning the passage of levocetirizine through the blood-brain-barrier.
In rats and dogs, the highest tissue levels are found in liver and kidneys, the lowest in the CNS compartment. In humans, levocetirizine is 90% bound to plasma proteins. The distribution of levocetirizine is restrictive, as the volume of distribution is 0.4 l/kg.
Biotransformation
The extent of metabolism of levocetirizine in humans is less than 14% of the dose and therefore differences resulting from genetic polymorphism or concomitant intake of enzyme inhibitors are expected to be negligible. Metabolic pathways include aromatic oxidation, N- and Odealkylation and taurine conjugation. Dealkylation pathways are primarily mediated by CYP 3A4 while aromatic oxidation involved multiple and/or unidentified CYP isoforms. Levocetirizine had no effect on the activities of CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1 and 3A4 at concentrations well above peak concentrations achieved following a 5 mg oral dose. Due to its low metabolism and absence of metabolic inhibition potential, the interaction of levocetirizine with other substances, or vice-versa, is unlikely.
Elimination
The plasma half-life in adults is 7.9 ± 1.9 hours. The half-life is shorter in small children.
The mean apparent total body clearance in adults is 0.63 ml/min/kg. The major route of excretion of levocetirizine and metabolites is via urine, accounting for a mean of 85.4% of the dose. Excretion via faeces accounts for only 12.9% of the dose. Levocetirizine is excreted both by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
No carcinogenicity studies have been performed with levocetirizine. However, evaluation of cetirizine carcinogenicity studies are relevant for determination of the carcinogenic potential of levocetirizine. In a 2-year carcinogenicity study, in rats, cetirizine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, approximately 10 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age and approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis). In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in mice, cetirizine caused an increased incidence of benign hepatic tumors in males at a dietary dose of 16 mg/kg (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, approximately 4 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age, and approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m basis). No increased incidence of benign tumors was observed at a dietary dose of 4 mg/kg (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, equivalent to the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age and approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of these findings during long-term use of levocetirizine dihydrochloride is not known.
Levocetirizine was not mutagenic in the Ames test, and not clastogenic in the human lymphocyte assay, the mouse lymphoma assay, and in vivo micronucleus test in mice. In a fertility and general reproductive performance study in mice, cetirizine did not impair fertility at an oral dose of 64 mg/kg (approximately 25 times the recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m² basis)
7.0 Description
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride, the active component of Elriz oral solution, is an orally active H1‑receptor antagonist.
The chemical name is (R)-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl) phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] acetic acid dihydrochloride. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the R enantiomer of cetirizine hydrochloride, a racemic compound with antihistaminic properties.
The empirical formula of levocetirizine dihydrochloride is C21H25ClN2O3•2HCl.
The molecular weight is 461.82
Chemical structure is shown below:
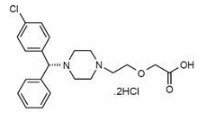
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging information
A bottle of 30 ml
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Somnolence
Caution patients against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of levocetirizine dihydrochloride.
Concomitant
Use of Alcohol and other Central Nervous System Depressants Instruct patients to avoid concurrent use of levocetirizine hydrochloride with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants because additional reduction in mental alertness may occur.
Dosing of Levocetirizine hydrochloride syrup
Do not exceed the recommended daily dose. Advise patients to not ingest more than the recommended dose of levocetirizine hydrochloride because of the increased risk of somnolence at higher doses.
Do not take this medicine, if you are allergic to levocetirizine
Signs of an allergic reaction include a rash, itching or shortness of breath.
Advice patients to talk to your doctor or pharmacist, if you get any side effects. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Advice patients if they have any further questions, ask doctor or pharmacist.
12.0 Date of revision
30.08.2024
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What Elriz is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Elriz
- How to take Elriz
- Possible side effects
- How to store Elriz
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Elriz is and what it is used for
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the active ingredient of Elriz. Elriz is an anti-allergic medication. It is used for the treatment of signs of illness (symptoms) associated with:
- allergic rhinitis (including persistent allergic rhinitis)
- nettle rash (urticaria).
2. What you need to know before you take Elriz
Do not take Elriz
- If you are allergic to levocetirizine dihydrochloride, to cetirizine, to hydroxyzine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- If you have a severe kidney disease requiring dialysis.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Elriz.
If you are likely to be unable to empty your bladder (with conditions such as spinal cord injury or enlarged prostate), please ask your doctor for advice.
If you suffer from epilepsy or are at risk of convulsions, please ask your doctor for advice as use of Elriz may cause seizure aggravation.
If you are scheduled for allergy testing, ask your doctor if you should stop taking Elriz for several days before testing. This medicine may affect your allergy test results.
Children
The use of Elriz is not recommended for infants and children under 2 years of age.
Other medicines and Elriz
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
Elriz with food, drink and alcohol
Caution is advised if Elriz is taken at the same time as alcohol or other agents acting on the brain. In sensitive patients, the concurrent administration of Elriz and alcohol or other agents acting on the brain may cause additional reductions in alertness and impairment of performance.
Elriz can be taken with or without food.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Some patients being treated with Elriz may experience somnolence/drowsiness, tiredness and exhaustion. Use caution when driving or operating machinery until you know how this medicine affects you. However, special tests have revealed no impairment of mental alertness, the ability to react or the ability to drive in healthy test persons after taking levocetirizine in the recommended dosage.
3. How to take Elriz
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose is:
Adults and adolescents from the age of 12 years: 10 ml solution once daily.
Special dosage instructions for specific populations:
Renal and hepatic impairment
Patients with impaired kidney function may be given a lower dose according to the severity of their kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Patients who have a severe kidney disease requiring dialysis must not take Elriz.
Patients who only have impaired liver function should take the usual prescribed dose.
Patients who have both impaired liver and kidney function may be given a lower dose depending on the severity of the kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Elderly patients aged 65 years and above
No adaptation of the dose is necessary in elderly patients, provided their renal function is normal.
Use in children
Children from the age of 6 to 12 years: 10 ml solution once daily.
Children from the age of 2 to 6 years: 2.5 ml solution twice daily.
The administration of Elriz to infants and toddlers aged less than 2 years is not recommended.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
Dry mouth, headache, tiredness and somnolence/drowsiness
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
Exhaustion and abdominal pain
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Other side effects such as palpitations, increased heart rate, fits, pins and needles, dizziness, syncope, tremor, dysgeusia (distortion of the sense of taste), sensation of rotation or movement, visual disturbances, blurred vision, oculogyration (eyes having uncontrolled circular movements), painful or difficult urination, inability to completely empty the bladder, oedema, pruritus (itchiness), rash, urticaria (swelling, redness and itchiness of the skin), skin eruption, shortness of breath, weight increase, muscular pain, joint pain, aggressive or agitated behaviour, hallucination, depression, insomnia, recurring thoughts of or preoccupation with suicide, nightmare, hepatitis, abnormal liver function, vomiting, increased appetite, nausea and diarrhea have also been reported. Pruritus (intense itching) upon discontiunation.
At the first signs of a hypersensitivity reaction, stop taking Elriz and tell your doctor. Hypersensitivity reaction symptoms may include swelling of the mouth, tongue, face and/or throat, breathing or swallowing difficulties (chest tightness or wheezing), hives, sudden fall in blood pressure leading to collapse or shock, which may be fatal.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly. Website: https://www.zuventus.com/ and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Elriz
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions. Do not use 3 months after first opening.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Elriz contains
Composition:
Each 5 ml contains:
Levocetirizine Hydrochloride -2.5 mg
Packing
A bottle of 30 ml


