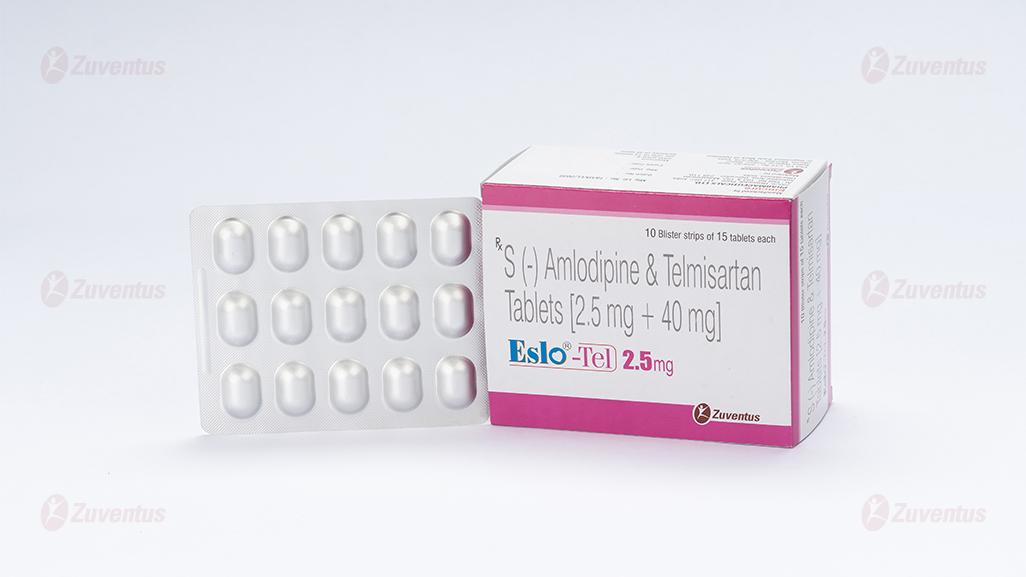
Eslo Tel 2.5mg & 5mg Tablets
Therapy Area
Cardiology
Composition
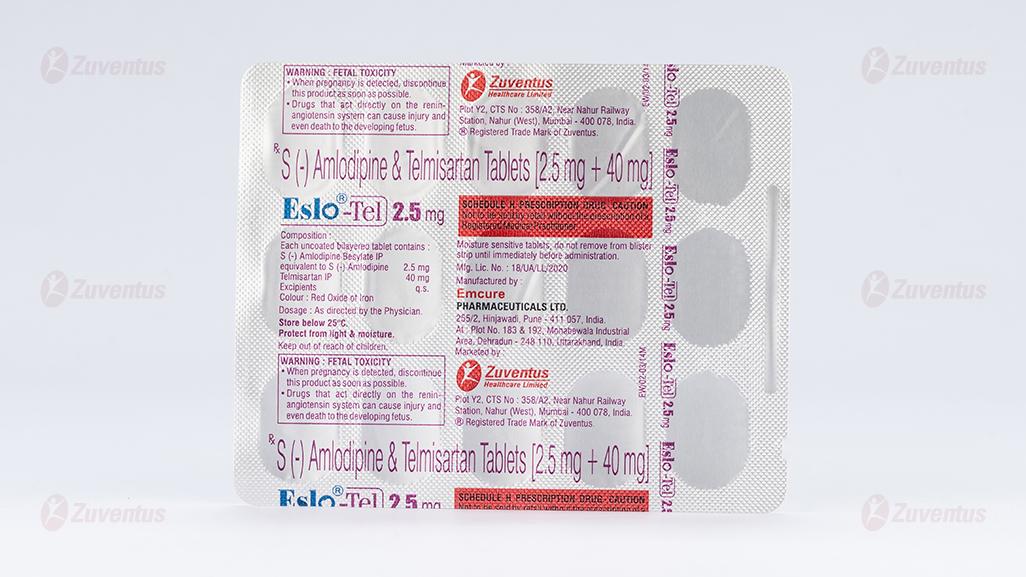
Eslo Tel 2.5 mg
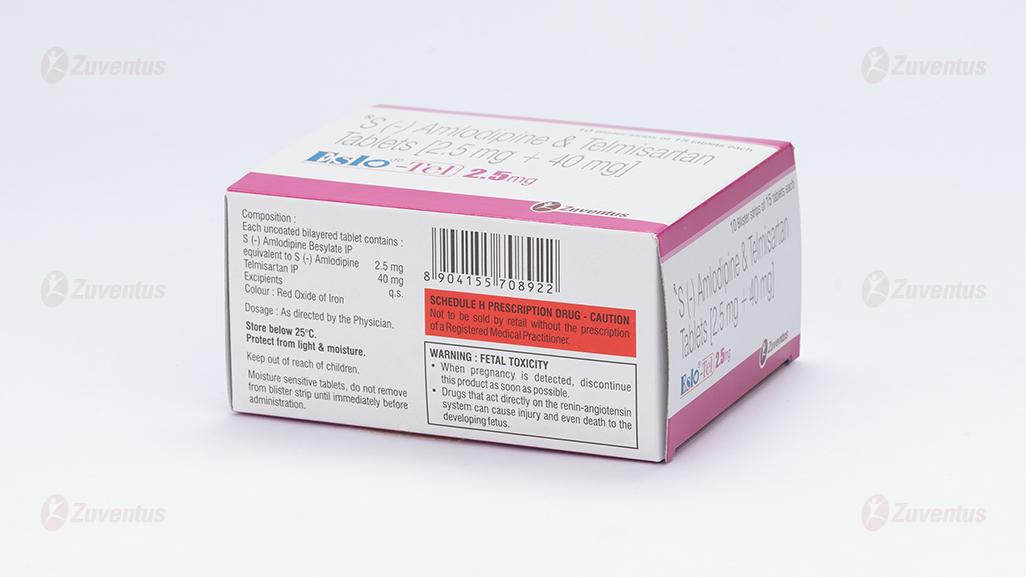
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains :
S (-) Amlodipine Besylate IP
equivalent to S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg
Telmisartan IP 40 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Iron Oxide Red
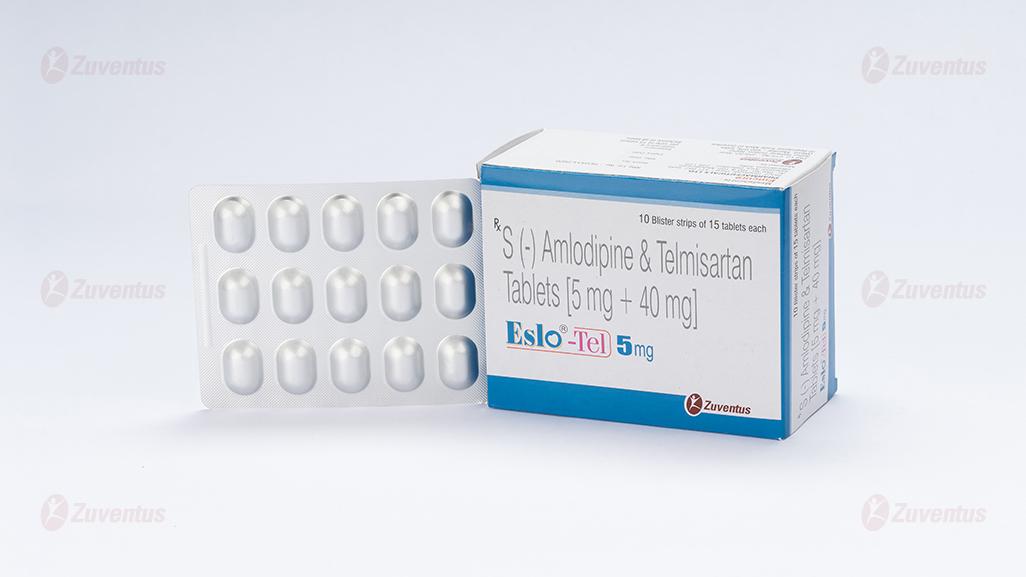
Eslo Tel 5 mg
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains :
S (-) Amlodipine Besylate IP
equivalent to S (-) Amlodipine 5 mg
Telmisartan IP 40 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Iron Oxide Yellow
Pharmacotherapeutic Group
Antihypertensive agent
Eslo Tel combines two antihypertensive compounds with complementary mechanisms to control blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension : an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, Telmisartan, and a dihydropyridinic calcium channel blocker, S (-) Amlodipine. The combination of these agents has an additive antihypertensive effect, reducing blood pressure to a greater degree than either component alone. Eslo Tel once daily produces effective and consistent reductions in blood pressure across the 24-hour therapeutic dose range.
Description
Clinical Pharmacology:
Pharmacodynamics
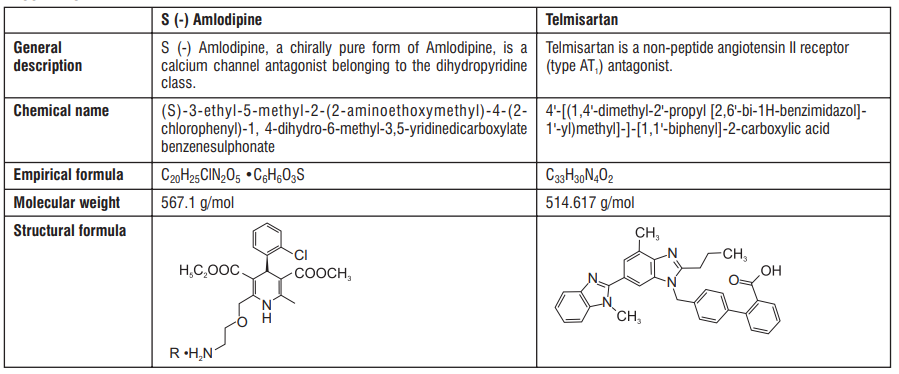
S (-) Amlodipine
Amlodipine is a racemic mixture of R and S enantiomers in 1:1 ratio. S-enantiomer of Amlodipine is active and R-enantiomer is inactive. The S (-) isomer of Amlodipine is found to possess greater pharmacological effects than R (+) Amlodipine. S (-) Amlodipine is 1000 times more potent than the R (+) isomer in binding to the dihydropyridine receptor. Therefore this is the only form which produces its therapeutic effects. In humans, the dominant effects of S (-) Amlodipine are consequent to vasodilation. S (-) Amlodipine lowers peripheral vascular resistance without causing a reflex tachycardia. In patients with angina pectoris S (-) Amlodipine reduces the myocardial oxygen demand by causing a direct vasodilation of the coronary artery and arterioles.
Telmisartan
Telmisartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. There is also an AT2 receptor found in many tissues, but AT2 is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Telmisartan has much greater affinity (>3,000 fold) for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction also catalyzed by ACE.
Because Telmisartan does not inhibit ACE (kininase II), it does not affect the response to bradykinin. Telmisartan does not bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Pharmacokinetics:
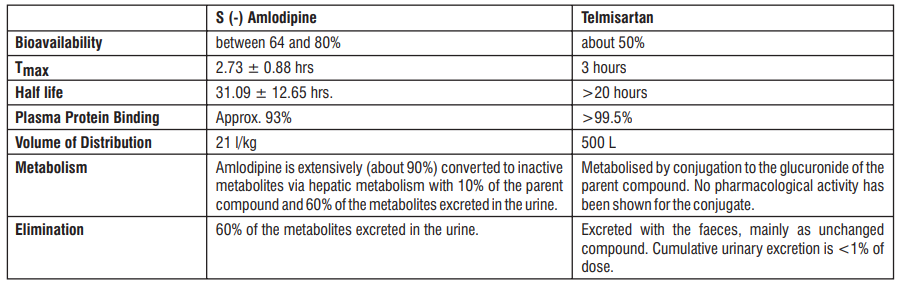
Paediatric population (age below 18 years)
No pharmacokinetic data are available in the paediatric population.
Elderly
The pharmacokinetics of Telmisartan does not differ in young and elderly patients. In elderly patients, Amlodipine clearance tends to decline with resulting increases in AUC and elimination half-life.
Renal impairment
In patients with mild to moderate and severe renal impairment, doubling of plasma concentrations of Telmisartan was observed. However, lower plasma concentrations were observed in patients with renal insufficiency undergoing dialysis. Telmisartan is highly bound to plasma protein in renal-insufficient subjects and cannot be removed by dialysis. The elimination half-life is not changed in patients with renal impairment. The pharmacokinetics of S (-) Amlodipine is not significantly influenced by renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
Pharmacokinetic studies in patients with hepatic impairment showed an increase in absolute bioavailability of Telmisartan up to nearly 100%. The elimination half-life of Telmisartan is not changed in patients with hepatic impairment. Patients with hepatic insufficiency have decreased clearance of Amlodipine with resulting increase of approximately 40-60% in AUC.
Indication
Treatment of essential hypertension
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substances, to dihydropyridine derivatives or to any of the excipients.
Second and third trimesters of pregnancy
Biliary obstructive disorders and severe hepatic impairment
Shock (including cardiogenic shock)
Obstruction of the outflow tract of the left ventricle (e.g. high grade aortic stenosis)
Haemodynamically unstable heart failure after acute myocardial infarction The concomitant use of Eslo Tel with aliskiren-containing products is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus or renal impairment (GFR < 2 60 ml/min/1.73 m )
Posology and Method of Administration
Posology
The recommended dose of this medicinal product is one tablet per day.
The maximum recommended dose is one tablet 80 mg Telmisartan / 5 mg S (-) Amlodipine per day.
This medicinal product is indicated for long term treatment.
Add on therapy
Eslo Tel 40 mg/2.5 mg may be administered in patients whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled with S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg alone. Individual dose titration with the components (i.e. S (-) Amlodipine and Telmisartan) is recommended before changing to the fixed dose combination. When clinically appropriate, direct change from monotherapy to the fixed combination may be considered. Patients treated with 5 mg S (-) Amlodipine who experience any dose limiting adverse reactions, may be switched to Eslo-Tel 40 mg/2.5 mg once daily, reducing the dose of S (-) Amlodipine without reducing the overall expected antihypertensive response.
Replacement therapy
Patients receiving Telmisartan and S (-) Amlodipine from separate tablets can instead receive tablets of Eslo Tel containing the same component doses in one tablet once daily.
Elderly patients (> 65 years)
No dose adjustment is necessary for elderly patients.
Limited experience is available in patients with severe renal impairment or haemodialysis. Caution is advised when using Eslo Tel in such patients as S (-) Amlodipine and Telmisartan are not dialysable. No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. When Eslo Tel is used in patients with impaired renal function, a periodic monitoring of potassium and creatinine serum levels is recommended. There is no experience regarding the administration of Eslo Tel in patients with a recent kidney transplant. Telmisartan and S (-) Amlodipine are not dialysable.
Patients with renal impairment
In most patients, initiate S (-) Amlodipine therapy at 1.25 mg. Titrate slowly in patients with hepatic impairment. In patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, Eslo Tel should be administered with caution. For Telmisartan the dose should not exceed 40 mg once daily. Eslo Tel is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment
Paediatric population
No data are available.
Method of administration
Oral use. Eslo Tel can be taken with or without food. It is recommended to take Eslo Tel with some liquid.
Overdose
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of overdose are expected to be in line with exaggerated pharmacological effects of individual drugs. The most prominent manifestations of Telmisartan overdose are expected to be hypotension and tachycardia; bradycardia, dizziness, increase in serum creatinine, and acute renal failure have also been reported. Overdose with S (-) Amlodipine may result in excessive peripheral vasodilatation and possibly reflex tachycardia. Marked and probably prolonged systemic hypotension up to and including shock with fatal outcome have been reported.
Treatment
The patient should be closely monitored, and the treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Management depends on the time since ingestion and the severity of the symptoms. Suggested measures include induction of emesis and / or gastric lavage. Activated charcoal may be useful in the treatment of overdose of both Telmisartan and S (-) Amlodipine. Serum electrolytes and creatinine should be monitored frequently. If hypotension occurs, the patient should be placed in a supine position with elevation of extremities, with salt and volume replacement given quickly. Supportive treatment should be instituted. Intravenous calcium gluconate may be beneficial in reversing the effects of calcium channel blockade. Telmisartan and S (-) Amlodipine are not removed by haemodialysis.
Special Population
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Eslo Tel as soon as possible. Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus.
Breast-feeding
Because no information is available regarding the use of Telmisartan and/or Amlodipine during breastfeeding, Eslo Tel is not recommended and alternative treatments with better established safety profiles during breast-feeding are preferable, especially while breast-feeding a newborn or preterm infant.
Adverse Reactions
S (-) Amlodipine
Gingival Hypertrophy & Alopecia have been reported with S (-) Amlodipine use. No adverse drug reactions were observed in the Randomized Controlled Trials of S (-) Amlodipine. Post Marketing Surveillance studies of S (-) Amlodipine involving 4089 patients further confirmed the safety and tolerability of S (-) Amlodipine. On the basis of clinical data available, the following adverse events have been reported in less than 2% of patients : vertigo (0.05%), tachycardia (0.05%), cough (0.05%), headache (0.43%), difficulty in breathing (0.1%), and facial puffiness (0.05%).
Telmisartan
Telmisartan is usually well tolerated. The side effects have been mild and transient in nature and have only infrequently required discontinuation of therapy. The commonly observed side effects are back pain, diarrhea, pharyngitis, headache, dizziness, pain, fatigue and nausea. Uncommon adverse effects seen were anaemia, hyperkalaemia, dyspnoea, flatulence, hyperhidrosis, renal impairment including acute renal failure, and increased blood creatinine.
Drug Interactions
No interactions between the two components of this fixed dose combinations have been observed in clinical studies. No drug interaction studies have been performed for this combination.
To be taken into account with concomitant use :
Other antihypertensive medicinal products The blood pressure lowering effect of Eslo Tel can be increased by concomitant use of other antihypertensive medicinal products.
Medicinal products with blood pressure lowering potential
Based on their pharmacological properties it can be expected that the following medicinal products may potentiate the hypotensive effects of all antihypertensives including this medicinal product, e.g. baclofen, amifostine, neuroleptics or antidepressants. Furthermore, orthostatic hypotension may be aggravated by alcohol.
Corticosteroids
Reduction of the antihypertensive effect
| Drug | Interaction | Recommendation |
| Potassium sparing diuretics or Potassium supplements | Potassium sparing diuretics e.g. Spirinolactone, Eplerenone, Triamterene, or Amiloride, Potassium supplements, or Potassium-containing salt substitutes may lead to a significant increase in serum Potassium. | Concomitant use not recommended. If concomitant use is indicated, they should be used with caution and with frequent monitoring of serum Potassium. |
| Lithium | Reversible increases in serum Lithium concentrations and toxicity have been reported during concomitant administration of Lithium with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, and with angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including Telmisartan. | Concomitant use not recommended. If use of the combination proves necessary, careful monitoring of serum Lithium levels is recommended. |
| Dual blockade of RAAS (ACEI, ARB, Aliskiren) | ‹ risks of hypotension, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function. (including acute renal failure) | Dual blockade to be avoided. |
| NSAIDs | May reduce the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure, which is usually reversible. | Patients should be adequately hydrated and consideration should be given to monitoring of renal function after initiation of concomitant therapy and periodically thereafter |
| CYP3A4 inhibitors | Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (i.e. Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Ritonavir) may increase the plasma concentrations of S (-) Amlodipine. | S (-) Amlodipine should be used with caution together with CYP3A4 inhibitors. |
| CYP3A4 inducers | Lower plasma concentration. | The concomitant use of CYP3A4 inducers (i.e. Rifampicin, Hypericum perforatum) may lead to a lower plasma concentration of S (-) Amlodipine. |
| Tacrolimus | Risk of increased Tacrolimus blood levels. | Monitoring of Tacrolimus blood levels and dose adjustment of Tacrolimus when appropriate. |
| Cyclosporine | In renal transplant patients, where variable trough concentration increases (average 0% - 40%) of Cyclosporine were observed. | Monitoring Cyclosporine levels and Cyclosporine dose reductions should bemade as necessary. |
| Simvastatin | Co-administration of multiple doses of S (-) Amlodipine with Simvastatin 80 mg resulted in an increase in exposure to Simvastatin up to 77 % compared to Simvastatin alone. | Dose should be limited to 20 mg daily |
| Grapefruit and grapefruit juice | Bioavailability of S (-) Amlodipine may increase and may result in increased hypotensive effects. | The concomitant use of Amlodipine and grapefruit or grapefruit juice is still not recommended |
| Ramipril | Increase of up to 2.5 fold in the AUC and C of Ramipril and 0-24 max ramiprilat. | |
| Digoxin | Median increase in peak plasma concentration (49 %) and in trough concentration (20 %) were observed. | When initiating, adjusting, and discontinuing Telmisartan, monitor Digoxin levels in order to maintain levels within the therapeutic range. |
Warnings & Precautions
| Condition | Description |
| Renovascular hypertension | Increased risk of severe hypotension and renal insufficiency when patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the artery to a single functioning kidney are treated with medicinal products that affect the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). |
| Intravascular hypovolaemia |
Symptomatic hypotension, especially after the first dose, may occur in patients who are volume and/or sodium depleted by e.g. vigorous diuretic therapy, dietary salt restriction, and diarrhoea or vomiting. Such conditions should be corrected before the administration of Telmisartan. If hypotension occurs with Telmisartan/ S (-) Amlodipine, the patient should be placed in the supine position and, if necessary, given an intravenous infusion of normal saline. Treatment can be continued once blood pressure has been stabilised. |
| Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system (RAAS) | There is evidence that the concomitant use of ACE-inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers or aliskiren increases the risk of hypotension, hyperkalaemia and decreased renal function (including acute renal failure). Dual blockade of RAAS through the combined use of ACE-inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers or aliskiren is therefore not recommended. |
| Other conditions with stimulation of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system | In patients whose vascular tone and renal function depend predominantly on the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (e.g. patients with severe congestive heart failure or underlying renal disease, including renal artery stenosis), treatment with medicinal products that affect this system has been associated with acute hypotension, hyperazotaemia, oliguria, or rarely acute renal failure. |
| Primary aldosteronism | Patients with primary aldosteronism generally will not respond to antihypertensive medicinal products acting through inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system. Therefore, the use of Telmisartan is not recommended. |
| Aortic and mitral valve stenosis, obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | As with other vasodilators, special caution is indicated in patients suffering from aortic or mitral stenosis, or obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. |
| Unstable angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction | There are no data to support the use of Eslo Tel in unstable angina pectoris and during or within one month of a myocardial infarction. |
| Heart failure | S (-) Amlodipine was associated with increased reports of pulmonary oedema despite no significant difference in the incidence of worsening heart failure. |
| Diabetic patients treated with insulin or antidiabetics | In these patients hypoglycaemia may occur under Telmisartan treatment. Therefore, in these patients an appropriate blood glucose monitoring should be considered; a dose adjustment of insulin or antidiabetics may be required when indicated. |
| Hyperkalaemia |
The use of medicinal products that affect the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system may cause hyperkalaemia. Hyperkalaemia may be fatal in the elderly, in patients with renal insufficiency, in diabetic patients, in patients concomitantly treated with other medicinal products that may increase potassium levels, and/or in patients with intercurrent events Before considering the concomitant use of medicinal products that affect the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the benefit risk ratio should be evaluated. Serum potassium should be monitored closely in these patients. |
| Other | As with any antihypertensive medicinal product, excessive reduction of blood pressure in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy or ischaemic cardiovascular disease could result in a myocardial infarction or stroke. |
Storage
Store below 25°C. Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children. Moisture sensitive tablets, do not remove from blister strip until immediately before administration.
Shelf-life:
Refer on the pack.
Presentation
Eslo Tel 2.5 mg : Alu-Alu blister strip of 15 tablets.
Eslo Tel 5 mg : Alu-Alu blister strip of 15 tablets.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you:
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
- This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Eslo Tel® is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take Eslo Tel®
3. How to take Eslo Tel®
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Eslo Tel®
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Eslo Tel® is and what it is used for
Eslo Tel® tablets contain two substances called S(-)Amlodipine and Telmisartan. Both of these substances help to control high blood pressure.
− S(-)Amlodipine belongs to a group of substances called “calcium channel blockers”. S(-)Amlodipine stops calcium from moving into the blood vessel wall which stops the blood vessels from tightening.
− Telmisartan belongs to a group of substances called “angiotensin-II receptor antagonists”. Angiotensin II is produced by the body and makes the blood vessels tighten, thus increasing blood pressure. Telmisartan works by blocking the effect of angiotensin II.
This means that both substances help stop the blood vessel tightening. As a result, the blood vessels relax and blood pressure is lowered.
Eslo Tel® is used to treat high blood pressure in adults whose blood pressure is not controlled enough with either S(-)Amlodipine or Telmisartan on its own.
2. What you need to know before you take Eslo Tel®
Do not take Eslo Tel®:
- if you are allergic to S(-)Amlodipine, amlodipine, Telmisartan, any drug of a related class, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you think you may be allergic, talk to your doctor before taking Eslo Tel®.
- if you have severe liver problems or bile problems such as biliary cirrhosis or cholestasis.
- if you are more than 3 months pregnant. (It is also better to avoid Eslo Tel® in early pregnancy, see Pregnancy section).
- if you have severe low blood pressure (hypotension).
- if you have narrowing of the aortic valve (aortic stenosis) or cardiogenic shock (a condition where your heart is unable to supply enough blood to the body).
- if you suffer from heart failure after a heart attack.
- if you have diabetes or impaired kidney function and you are treated with a blood pressure lowering medicine containing aliskiren.
If any of the above applies to you, do not take Eslo Tel® and talk to your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before taking Eslo Tel® Tablets:
if you have been sick (vomiting or diarrhoea).
if you have liver or kidney problems.
if you have had a kidney transplant or if you had been told that you have a narrowing of your kidney arteries.
if you have a condition affecting the renal glands called “primary hyperaldosteronism”.
if you have had heart failure or have experienced a heart attack.
Follow your doctor’s instructions for the starting dose carefully. Your doctor may also check your kidney function.
if your doctor has told you that you have a narrowing of the valves in your heart (called “aortic or mitral stenosis”) or that the thickness of your heart muscle is abnormally increased (called “obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy”).
if you have experienced swelling, particularly of the face and throat while taking other medicines (including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors).
If you get these symptoms, stop taking Eslo Tel® and contact your doctor straight away. You should never take Eslo Tel® again.
if you are taking any of the following medicines used to treat high blood pressure:
- an ACE inhibitor (for example enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril), in particular if you have diabetes-related kidney problems.
- aliskiren.
Your doctor may check your kidney function, blood pressure, and the amount of electrolytes (e.g. potassium) in your blood at regular intervals.
See also information under the heading “Do not take Eslo Tel®”.
If any of these apply to you, tell your doctor before taking Eslo Tel®.
Children and adolescents
The use of Eslo Tel® in children and adolescents is not recommended (aged below 18 years old).
Other medicines and Eslo Tel® Tablets
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. Your doctor may need to change your dose and/or to take other precautions. In some cases, you may have to stop taking one of the medicines. This applies especially to the medicines listed below:
Eslo Tel® Tablets may affect or be affected by other medicines, such as:
ACE inhibitors or aliskiren (see also information under the headings “Do not take Eslo Tel ®” and “Warnings and precautions”);
diuretics (which increase the amount of urine you produce);
lithium (a medicine used to treat some types of depression);
potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, salt substitutes containing potassium and other substances that may increase potassium levels; certain types of painkillers called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines
(NSAIDs) or selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 inhibitors).
Your doctor may also check your kidney function;
anticonvulsant agents (e.g. carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, primidone).
St. John’s wort; nitroglycerin and other nitrates, or other substances called “vasodilators”;
medicines used for HIV/AIDS (e.g. ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir);
medicines used to treat fungal infections (e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole);
medicines used to treat bacterial infections (such as rifampicin, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin);
verapamil, diltiazem (heart medicines);
simvastatin (a medicine used to control high cholesterol levels);
dantrolene (infusion for severe body temperature abnormalities);
medicines used to protect against transplant rejection (ciclosporin).
Eslo Tel® Tablets with food and drink
Grapefruit juice and grapefruit should not be consumed by people who are taking Eslo Tel® Tablets. This is because grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood levels of the active ingredient S(-)Amlodipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase in the blood pressure-lowering effect of S(-)Amlodipine.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
Pregnancy
You must tell your doctor if you think you are (or might become) pregnant. Your doctor will normally advise you to stop taking Eslo Tel® before you become pregnant or as soon as you know you are pregnant and will advise you to take another medicine instead of Eslo Tel®. Eslo Tel® is not recommended in early pregnancy (first 3 months), and must not be taken when more than 3 months pregnant.
Breast-feeding
Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding or about to start breast-feeding. Eslo Tel® is not recommended for mothers who are breastfeeding, and your doctor may choose another treatment for you if you wish to breastfeed, especially if your baby is a newborn or was born prematurely. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
This medicine may make you feel dizzy. This can affect how well you can concentrate. So, if you are not sure how this medicine will affect you, do not drive, use machinery, or do other activities that you need to concentrate on.
3. How to take Eslo Tel® Tablets
Always take or give this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. This will help you get the best results and lower the risk of side effects.
The usual dose of Eslo Tel® is one tablet per day.
− It is preferable to take your medicine at the same time each day.
− Swallow the tablets with a glass of water.
− You can take Eslo Tel® with or without food. Do not take Eslo Tel® with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
Patients with kidney or liver problems
You should tell your doctor if you have kidney or liver problems as your doctor may need to alter the normal dose or medicine.
If you take more Eslo Tel® than you should
If you have taken too many tablets of Eslo Tel®, or if someone else has taken your tablets, consult a doctor immediately.
If you forget to take or give Eslo Tel®
If you forget to take this medicine, take it as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at its usual time. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten tablet.
If you stop taking Eslo Tel®
Stopping your treatment with Eslo Tel® may cause your disease to get worse. Do not stop taking your medicine unless your doctor tells you to.
4. Possible side effects
This medicine can cause side effects like all medicines, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious and need immediate medical attention: A few patients have experienced these serious side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people). If any of the following happens, tell your doctor straight away: Allergic reaction with symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling of face or lips or tongue, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure (feeling of faintness, light-headedness).
Other possible side effects of Eslo Tel®:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people): blocked nose, sore throat and discomfort when swallowing; headache; swelling of arms, hands, legs, ankles or feet; tiredness; asthenia (weakness); redness and warm feeling of the face and/or neck.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people): Dizziness; nausea and abdominal pain; dry mouth; drowsiness, tingling or numbness of the hands or feet; vertigo; fast heart beat including palpitations; dizziness on standing up; cough; diarrhoea; constipation; skin rash, redness of the skin; joint swelling, back pain; pain in joints.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people): Feeling anxious; ringing in the ears (tinnitus); fainting; passing more urine than normal or feeling more of an urge to pass urine; inability to get or maintain an erection; sensation of heaviness; low blood pressure with symptoms such as dizziness, light-headedness; excessive sweating; skin rash all over your body; itching; muscle spasm.
If any of these affect you severely, tell your doctor.
Side effects reported with S(-)amlodipine or Telmisartan alone and either not observed with Eslo Tel® or observed with a higher frequency than with Eslo Tel®:
S(-)Amlodipine
Consult a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following very rare, severe side effects
after taking this medicine:
- Sudden wheeziness, chest pain, shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing.
- Swelling of eyelids, face or lips.
- Swelling of the tongue and throat which causes great difficulty breathing.
- Severe skin reactions including intense skin rash, hives, reddening of the skin over your whole body, severe itching, blistering, peeling and swelling of the skin, inflammation of the mucous membranes (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) or other allergic reactions.
- Heart attack, abnormal heart beat.
- Inflamed pancreas, which may cause severe abdominal and back pain accompanied with feeling of being very unwell.
Telmisartan
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data): Decrease in red blood cells, fever, sore throat or mouth sores due to infections; spontaneous bleeding or bruising; high level of potassium in the blood; abnormal liver test results; decreased renal functions and severely decreased renal functions; swelling mainly of the face and the throat; muscle pain; rash, purplish-red spots; fever; itching; allergic reaction; blistering skin (sign of a condition called dermatitis bullous).
If you experience any of these, tell your doctor straight away.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Eslo Tel®
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and blister. Do not store above 30°C. Store in the original package in order to protect it from moisture. Do not use any Eslo Tel® pack that is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Eslo Tel® tablets contain
Eslo Tel® 2.5 mg/40 mg tablets
The active substances of Eslo Tel® are S(-)Amlodipine as s(-) Amlodipine besylate and Telmisartan. Each tablet contains 2.5 mg S(-)Amlodipine and 40 mg Telmisartan.
Eslo Tel® 5 mg/40 mg tablets
The active substances of Eslo Tel® are S(-)Amlodipine as s(-) Amlodipine besylate and Telmisartan. Each tablet contains 5 mg S(-)Amlodipine and 40 mg Telmisartan.
What Eslo Tel® looks like and contents of the pack
Eslo Tel® is available in packs of 10 tablets per strip.