Mahadol
1.0 Generic name
Aceclofenac & Paracetamol Tablets [100 mg + 325 mg]
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each film coated tablet contains :
Aceclofenac IP 100 mg
Paracetamol IP 325 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film-coated tablet, 100 mg of Aceclofenac and 325 mg of Paracetamol.
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
For acute painful conditions in adults only
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
The maximum recommended dose of Mahadol is two tablets daily, taken as one tablet in the morning and one in the evening.
Method of administration
Mahadol tablets are supplied for oral administration in adults and should be swallowed whole with sufficient amount of liquid. It should be taken preferably with or after food.
4.3 Contraindications
Mahadol is contraindicated in the following situations :
• Patients sensitive to Aceclofenac, Paracetamol or to any of the excipients of the product.
• Patients with active or history of recurrent peptic ulcer / haemorrhage (two or more distinct episodes of proven ulceration or bleeding).
• Patients who have previously shown hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. asthma, rhinitis, angioedema or urticaria) in response to Ibuprofen, Aspirin, or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
• Patients with severe heart failure, hypertension, hepatic or renal insufficiency should not be prescribed.
• During pregnancy, especially during the last trimester of pregnancy, unless there are compelling reasons for doing so. The lowest effective dosage should be used.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Undesirable effects may be minimized by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms. Concomitant use with NSAIDs including cyclooxygenase- 2 selective inhibitors should be avoided. It should not be combined with other analgesic medications that contain Paracetamol and should be given with care to patients with impaired kidney or liver function. The administration of an NSAID may cause a dose dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and precipitate renal failure. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, cardiac impairment, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and the elderly. Renal function should be monitored in these patients.
Respiratory disorders
Caution is required if administered to patients suffering from, or with a previous history of, bronchial asthma since NSAIDs have been reported to precipitate bronchospasm in such patients.
Hepatic toxicity
Paracetamol may cause liver damage if taken more than the recommended dose. Allergic reactions like swelling of the face, mouth and throat, difficulty in breathing, itching or rash may occur due to high doses of Paracetamol. Severe liver damage may occur if :
• Adult takes more than 4000 mg in 24 hours, which is the maximum daily amount.
• Child takes more than 5 doses in 24 hours.
• Taken with other drugs containing Paracetamol.
• Adult has 3 or more alcoholic drinks every day while using this product.
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects
Appropriate monitoring and advice are required for patients with a histor y of hypertension and/or mild to moderate congestive heart failure as fluid retention and oedema have been reported in association with NSAID therapy. Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that use of some NSAIDs (particularly at high doses and in long term treatment) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke). There are insufficient data to exclude such a risk for Aceclofenac. Patients with uncontrolled hypertension, congestive heart failure, established ischaemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and/or cerebrovascular disease should only be treated after careful consideration. Similar consideration should be made before initiating longer-term treatment of patients with risk factors for cardiovascular disease (e.g. hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking).
Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration and perforation
GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation, which can be fatal, has been reported with all NSAIDs at any time during treatment, with or without warning symptoms or a previous history of serious GI events. Close medical surveillance is imperative in patients with symptoms indicative of gastro-intestinal disorders, with a history suggestive of gastro-intestinal ulceration, with ulcerative colitis or with Crohn's disease, bleeding diathesis or haematological abnormalities.
The risk of GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation is higher with increasing NSAID doses, in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage or perforation, and in the elderly. These patients should commence treatment on the lowest dose available. Combination therapy with protective agents (e.g. misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) should be considered for these patients, and also for patients requiring concomitant low dose Aspirin, or other drugs likely to increase gastrointestinal risk.
Patients with a history of GI toxicity, particularly when elderly, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially GI bleeding) particularly in the initial stages of treatment. Caution should be advised in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors or antiplatelet agents such as Aspirin. When GI bleeding or ulceration occurs the treatment should be withdrawn. NSAIDs should be given with care to patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease) as these conditions may be exacerbated.
SLE and mixed connective tissue disease
In patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and mixed connective tissue disorders there may be an increased risk of aseptic meningitis.
Dermatological
Serious skin reactions, some of them fatal, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported very rarely in association with the use of NSAIDs. Patients appear to be at highest risk for these reactions early in the course of therapy : the onset of the reaction occurring in the majority of cases within the first month of treatment. Discontinuation should be done at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity. Doses higher than those recommended involve a risk of very severe liver damage. If liver damage is suspected, then liver function tests should be performed.
Hypersensitivity reactions
As with other NSAIDs, allergic reactions, including anaphylactic / anaphylactoid reactions, can also occur without earlier exposure to the drug.
Haematological
May cause reversibly inhibit platelet aggregation.
Long-term treatment
Individuals receiving long-term treatment should be regularly monitored for renal function tests, liver function tests and blood counts.
It is to be used with caution in hepatic porphyria, coagulation disorders, history of peptic ulcers, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, cerebrovascular bleeding, pregnancy and lactation. Caution should be exercised in patients with mild to moderate impairment of cardiac, hepatic or renal function and in elderly patients who are more likely to be suffering from these conditions. Caution is also required in patients on diuretic therapy or otherwise at risk of hypovolemia.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Other analgesics including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of two or more NSAIDs (including Aspirin) as this may increase the risk of adverse effects, including GI bleeding.
Anti-hypertensives
Reduced anti-hypertensive effect. The risk of acute renal insufficiency, which is usually reversible, may be increased in some patients with compromised renal function (e.g. dehydrated patients or elderly patients) when ACE- inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists are combined with NSAIDs. Therefore, the combination should be administered with caution, especially in the elderly. Patients should be adequately hydrated and consideration should be given to monitoring of renal function after initiation of concomitant therapy, and periodically thereafter
Diuretics
Reduced diuretic effect. Diuretics can increase the risk of nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs. Although it was not shown to affect blood pressure control when co-administered with Bendrofluazide, interactions with other diuretics cannot be ruled out. When concomitant administration with Potassium-sparing diuretics is employed, serum potassium should be monitored.
Cardiac glycosides like Digoxin
NSAIDs may exacerbate cardiac failure, reduce GFR (glomerular filtration rate) and increase plasma glycoside levels. The combination should be avoided unless frequent monitoring of glycoside levels can be performed.
Lithium
Several NSAIDs drugs inhibit the renal clearance of Lithium, resulting in increased serum concentration of Lithium. The combination should be avoided unless frequent monitoring of Lithium can be performed.
Methotrexate
The possible interaction between NSAIDs and Methotrexate should be born in mind also when low doses of Methotrexate are used, especially in patients with decreased renal function. When combination therapy has to be used, the renal function should be monitored. Caution should be exercised if NSAIDs and Methotrexate are administered within 24 hours of each other, since NSAIDs may increase plasma levels, resulting in increased toxicity.
Mifepristone
NSAIDs should not be used for 8 - 12 days after Mifepristone administration as NSAIDs can reduce the effect of Mifepristone
Corticosteroids
Increased risk of gastrointestinal ulceration or bleeding.
Anti-coagulants
NSAIDs may enhance the effects of anti-coagulants, such as Warfarin. Close monitoring of patients on combined anticoagulants and Aceclofenac 100 mg Film-coated Tablets therapy should be undertaken.
Quinolone antibiotics
Animal data indicate that NSAIDs can increase the risk of convulsions associated with Quinolone antibiotics. Patients taking NSAIDs and quinolones may have an increased risk of developing convulsions.
Anti-platelet agents and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Ciclosporin and Tacrolimus
Administration of NSAID drugs together with Cyclosporin or Tacrolimus is thought to increase the risk of nephrotoxicity due to decreased synthesis of prostacyclin in the kidney. During combination therapy it is therefore important to carefully monitor renal function.
Zidovudine
Increased risk of haematological toxicity when NSAIDs are given with Zidovudine. There is evidence of an increased risk of haemarthroses and haematoma in HIV(+) haemophiliacs receiving concurrent treatment with Zidovudine and Ibuprofen.
Antidiabetic agents
Clinical studies have shown that Diclofenac can be given together with oral antidiabetic agents without influencing their clinical effect. However, there have been isolated reports of hypoglycaemic and hyperglycaemic effects. Thus with Aceclofenac 100 mg Film-coated Tablets, consideration should be given to adjustment of the dosage of hypoglycaemic agents.
Other NSAIDs
Concomitant therapy with Aspirin or other NSAIDs may increase the frequency of adverse reactions, including the risk of GI bleeding.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Aceclofenac
Other analgesics including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of two or more NSAIDs (including Aspirin) as this may increase the risk of adverse effects.
Anti-hypertensives
Reduced anti-hypertensive effect.
Diuretics
Reduced diuretic effect. Diuretics can increase the risk of nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs. Although it was not shown to affect blood pressure control when co-administered with Bendrofluazide, interactions with other diuretics cannot be ruled out. When concomitant administration with Potassium-sparing diuretics is employed, serum potassium should be monitored.
Cardiac glycosides
NSAIDs may exacerbate cardiac failure, reduce GFR (glomerular filtration rate) and increase plasma glycoside levels.
Lithium
Decreased elimination of Lithium.
Methotrexate
Decreased elimination of Methotrexate. Caution should be exercised if NSAIDs and Methotrexate are administered within 24 hours of each other, since NSAIDs may increase plasma levels, resulting in increased toxicity.
Ciclosporin
Increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Mifepristone
NSAIDs should not be used for 8 - 12 days after Mifepristone administration as NSAIDs can reduce the effect of Mifepristone.
Corticosteroids
Increased risk of gastrointestinal ulceration or bleeding.
Anti-coagulants
NSAIDs may enhance the effects of anti-coagulants, such as Warfarin. Close monitoring of patients on combined anticoagulants and Aceclofenac therapy should be undertaken.
Quinolone antibiotics
Animal data indicate that NSAIDs can increase the risk of convulsions associated with Quinolone antibiotics. Patients taking NSAIDs and quinolones may have an increased risk of developing convulsions.
Anti-platelet agents and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Tacrolimus
Possible increased risk of nephrotoxicity when NSAIDs are given with Tacrolimus.
Zidovudine
Increased risk of haematological toxicity when NSAIDs are given with Zidovudine. There is evidence of an increased risk of haemarthroses and haematoma in HIV(+) haemophiliacs receiving concurrent treatment with Zidovudine and Ibuprofen.
Antidiabetic agents
Clinical studies have shown that diclofenac can be given together with oral antidiabetic agents without influencing their clinical effect. However, there have been isolated reports of hypoglycaemic and hyperglycaemic effects. Thus with Aceclofenac, consideration should be given to adjustment of the dosage of hypoglycaemic agents.
Other NSAIDs
Concomitant therapy with Aspirin or other NSAIDs may increase the frequency of adverse reactions, including the risk of GI bleeding.
Paracetamol
Drugs which induce hepatic microsomal enzymes such as alcohol, barbiturates and other anticonvulsants, may increase the hepatotoxicity of Paracetamol, particularly after over dosage. The anti-coagulant effect of Warfarin and other coumarins may be enhanced by prolonged regular use of Paracetamol with increased risk of bleeding. The effect appears to increase as the dose of Paracetamol is increased, but can occur with doses as low as 1.5 - 2 g Paracetamol per day for at least 5 - 7 days. Occasional doses have no significant effect. Probenicid inhibits the glucuronidation of Paracetamol which can affect the clearance of Paracetamol. This should be considered when these medicines are administered concomitantly. Paracetamol may affect the pharmacokinetics of chloramphenicol. This interaction should be considered when these medications are administered concomitantly, especially in malnourished patients. Enzyme-inducing medicines, such as some antiepileptic drugs (Phenytoin, Phenobarbital, Carbamazepine) have been shown in pharmacokinetic studies to reduce the plasma AUC of Paracetamol to approx. 60%. Other substances with enzyme inducing properties, e.g. Rifampicin and St. John's wort (hypericum) are also suspected of causing lowered concentrations of Paracetamol. In addition, the risk of liver damage during treatment with maximum recommended doses of Paracetamol will be higher in patients being treated with enzyme-inducing agents.
Renal impairment
It should be avoided in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment. The importance of prostaglandins in maintaining renal blood flow should be taken into account in patients with impaired cardiac or renal function, those being treated with diuretics or recovering from major surgery. Effects on renal function are usually reversible on withdrawal.
Hepatic impairment
In patients with hepatic impairment, dosage reductions are recommended. If abnormal liver function tests persist or worsen, clinical signs or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop or if other manifestations occur (eosinophilia, rash), it should be discontinued. Close medical surveillance is necessary in patients suffering from mild to moderate impairment of hepatic function. Hepatitis may occur without prodromal symptoms. Use in patients with hepatic porphyria may trigger an attack.
Pregnancy
Congenital abnormalities have been reported in association with NSAID administration in man; however, these are low in frequency and do not appear to follow any discernible pattern. In view of the known effects of NSAIDs on the foetal cardiovascular system (risk of closure of the ductus arteriosus) and on the possible risk of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the new born, use in the last trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated. The regular use of NSAIDs during the last trimester of pregnancy may decrease uterine tone and contraction. The onset of labour may be delayed and the duration increased with an increased bleeding tendency in both mother and child. NSAIDs should not be used during the first two trimesters of pregnancy or labour unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the potential risk to the foetus. The drug in not recommended in pregnant women.
Lactation
In limited studies so far available, NSAIDs can appear in breast milk in very low concentrations. NSAIDs should, if possible, be avoided when breastfeeding. The use of Aceclofenac should therefore be avoided in pregnancy and lactation unless the potential benefits to the other outweigh the possible risks to the foetus. The drug in not recommended in breast-feeding women.
Geriatric
As with other NSAIDs and combinations, caution is advised in elderly patients who are more likely to have concomitant renal, hepatic or cardiovascular impairment or receiving concurrent medication. The elderly has an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation which may be fatal.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
It may cause dizziness. Driving or operating machinery is to be avoided.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Renal
Nephrotoxicity in various forms, including interstitial nephritis, nephritic syndrome and renal failure.
Hepatic
Abnormal liver function, hepatitis and jaundice.
Neurological and special senses
Visual disturbances, optic neuritis, headaches, paraesthesia, reports of aseptic meningitis (especially in patients with existing auto-immune disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease), with symptoms such as stiff neck, headache, nausea, vomiting, fever or disorientation, depression, confusion, hallucinations, tinnitus, vertigo, dizziness, malaise, fatigue and drowsiness.
Haematological
Thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia and haemolytic anaemia.
Dermatological
Bullous reactions including Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (very rare), Photosensitivity. Fixed drug eruption (FDE) is associated with Paracetamol use. Within the system organ classes, undesirable effects are listed under headings of frequency, using the following categories : Very common (1/10); Common (1/100 to < 1/10); Uncommon (1/1,000 to < 1/100); Rare (1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); Very rare (< 1/10,000), Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness
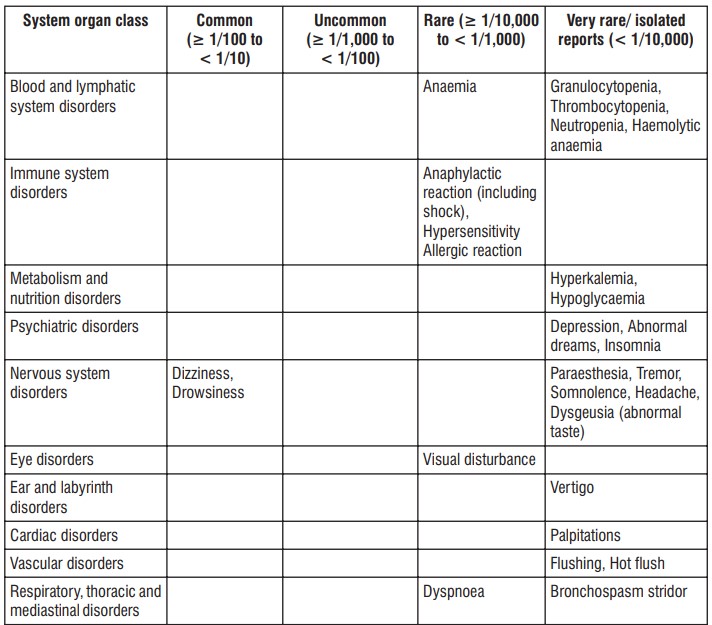
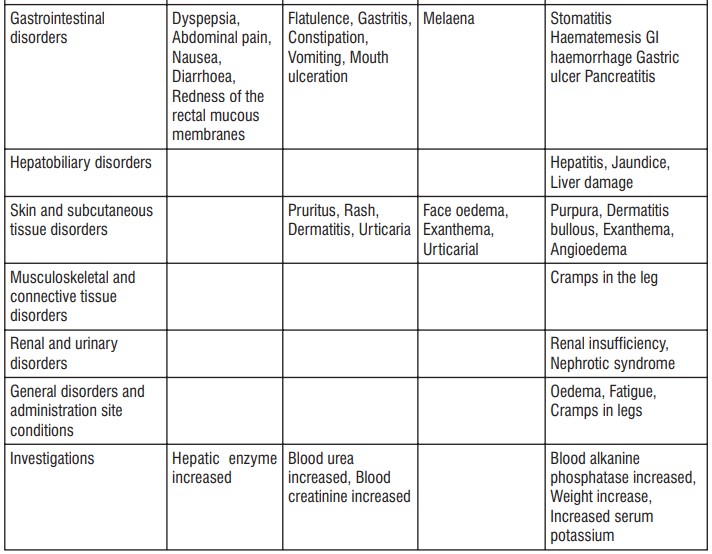
Most of the adverse events are minor and reversible with treatment discontinuation. As with other NSAIDs, severe mucocutaneous skin reactions may also occur
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Liver damage is possible in adults who have taken 10 g or more of Paracetamol. Ingestion of 5 g or more of Paracetamol may lead to liver damage if the patient has risk factors. Management of acute poisoning with NSAIDs essentially consists of supportive and symptomatic measures. Symptoms Symptoms include headache, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, gastrointestinal irritation, gastrointestinal bleeding, rarely diarrhoea, disorientation, excitation, coma, drowsiness, dizziness, tinnitus, hypotension, respirator y depression, fainting, occasionally convulsions. In cases of significant poisoning acute renal failure and liver damage are possible. Therapeutic measure Patients should be treated symptomatically as required. Within one hour of ingestion of a potentially toxic amount, activated charcoal should be considered. Alternatively, in adults, gastric lavage should be considered within one hour of ingestion of a potentially life-threatening overdose. Specific therapies such as dialysis or haemoperfusion are probable of no help in eliminating NSAIDs due to their high rate of protein binding and extensive metabolism. Good urine output should be ensured. Renal and liver function should be closely monitored. Patients should be observed for at least four hours after ingestion of potentially toxic amounts.
In case of frequent or prolonged convulsions, patients should be treated with intravenous diazepam. Other measures may be indicated by the patient's clinical condition. Management of acute poisoning with oral Aceclofenac essentially consists of supportive and symptomatic measures for complications such as hypotension, renal failure, convulsions, gastro-intestinal irritation, and respiratory depression.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Aceclofenac
Aceclofenac is a non-steroidal agent with marked anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. The mode of action of Aceclofenac is largely based on the inhibition to prostaglandin synthesis. Aceclofenac is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme cyclo-oxygenase, which is involved in the production of prostaglandins. Aceclofenac relieves pain and inflammation through a variety of mechanisms and in addition exerts stimulatory effects on cartilage matrix synthesis.
Anti-inflammatory activity
The anti-inflammatory effects of Aceclofenac have been shown in both acute and chronic inflammation. It inhibits various mediators of pain and inflammation including :
• PGE2 via cyclooxygenase inhibition (COX-1 and COX-2) after intracellular metabolism to 4-hydroxyaceclofenac and diclofenac in human rheumatoid synovial cells and other inflammatory cells.
• IL-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor in human osteoarthritic synovial cells and human articular chondrocytes.
• Reactive oxygen species (which plays a role in joint damage) has also been observed in patients with osteoarthritis of knee.
• Expression of cell adhesion molecules (which is implicated in cell migration and inflammation) has also been shown in human neutrophils.
Stimulatory effects on cartilage matrix synthesis
Aceclofenac stimulates glycosaminoglycan synthesis in human osteoarthritic cartilage by inhibition of IL-1 and suppresses cartilage degeneration by inhibiting IL-1 mediated promatrix metalloproteinase production and proteoglycan release.
Paracetamol
Paracetamol is an aniline derivative with analgesic and antipyretic actions similar to those of Aspirin but with no demonstrable anti-inflammatory activity. Paracetamol is less irritant to the stomach than Aspirin. It does not affect thrombocyte aggregation or bleeding time. Paracetamol is generally well tolerated by patients hypersensitive to Acetylsalicylic acid.
Analgesic action
The central analgesic action of Paracetamol resembles that of Aspirin. It produces analgesia by raising pain threshold
Antipyretic effect
The antipyretic effect of Paracetamol is attributed to its ability to inhibit COX in the brain where peroxide tone is low. Recent evidence suggests inhibition of COX-3 (believed to be splice variant product of the COX-1 gene) could represent a primary central mechanism by which Paracetamol decreases pain and possibly fever.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Aceclofenac
Absorption
After oral administration, Aceclofenac is rapidly and completely absorbed as unchanged drug. Peak plasma concentrations are reached approximately 1.25 to 3.00 hours following ingestion.
Distribution
Aceclofenac penetrates into the synovial fluid, where the concentrations reach approximately 57% of those in plasma. The volume of distribution is approximately 25 L. Aceclofenac is highly protein- bound (> 99%). Aceclofenac circulates mainly as unchanged drug.
Metabolism
4'hydroxyaceclofenac is the main metabolite detected in plasma.
Elimination
The mean plasma elimination half-life is around 4 hours. Approximately two-thirds of the administered dose is excreted via the urine, mainly as hydroxymetabolites.
Paracetamol
Absorption
Paracetamol is well absorbed by oral route. The plasma half-life is about 2 hours.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is negligible at usual therapeutic concentration but increases with increasing concentrations. Acetaminophen is relatively uniformly distributed throughout most body fluids. The plasma half-life is (t1/2) 2 - 3 hours and the effect after oral dose lasts for 3 - 5 hours.
Metabolism
Paracetamol is primarily metabolized in the liver by conjugation to glucuronide and sulphate. A small amount (about 3 - 10% of a therapeutic dose) is metabolized by oxidation and the reactive intermediate metabolite thus formed is bound preferentially to the liver glutathione and excreted as cysteine and mercapturic acid conjugates.
Elimination
Excretion occurs via the kidneys. 2 - 3% of a therapeutic dose is excreted unchanged; 80 - 90% as glucuronide and sulphate and a smaller amount as cystein and mercapturic acid derivatives.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
The results from preclinical studies conducted with Aceclofenac are consistent with those expected for NSAIDs. The principal target organ was the gastro-intestinal tract. No unexpected findings were recorded. Aceclofenac was not considered to have any mutagenic activity in three in vitro studies and an in vivo study in the mouse. Aceclofenac was not found to be carcinogenic in either the mouse or rat. Animal studies indicate that there was no evidence of teratogenesis in rats although the systemic exposure was low and in rabbits treatment with Aceclofenac (10 mg/kg/day) resulted in a series of morphological changes in some fetuses.
7.0 Description
Mahadol is a fixed dose combination of Aceclofenac 100 mg and Paracetamol 325 mg. This combination offers the advantage of peripheral effects of Aceclofenac and Central effect of Paracetamol for pain management. Aceclofenac is an orally administered Phenylacetic acid derivative with effects on a variety of inflammatory mediators. Through its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, Aceclofenac provides symptomatic relief in a variety of painful conditions. Due to its preferential COX-2 blockade, it has better safety than conventional NSAIDs with respect to adverse effects on gastrointestinal and cardiovascular system. Paracetamol acts predominantly by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in the central nervous system and to lesser extent, through a peripheral action by blocking pain impulse generation. Paracetamol is one of the effective mild analgesics, suitable for treating mild to moderate pain.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
• You have been prescribed this combination medicine for relieving pain and inflammation.
• Take Mahadol Tablet it with food to avoid getting an upset stomach.
• Do not take Mahadol Tablet with any other medicine containing Paracetamol (drugs for pain/fever or cough-andcold) without asking your doctor first.
• It may cause dizziness and sleepiness. Do not drive or do anything that requires mental focus until you know how it affects you.
• Avoid consuming alcohol when taking Mahadol Tablet as it may cause excessive drowsiness and increase the risk of liver damage.
• In case of muscle pain, your doctor might advise you to undergo physiotherapy to get relief along with taking Mahadol Tablet.
• Inform your doctor if you have a history of stomach ulcers before taking this medicine
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again. If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours. If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What MAHADOL® is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take MAHADOL®
3. How to take MAHADOL®
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store MAHADOL®
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What MAHADOL® is and what it is used for
MAHADOL® contains Aceclofenac and Paracetamol. Aceclofenac belongs to a group of medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have anti-inflammatory and painkiller properties causing a lowering of swelling, redness (inflammation) and pain. It works by blocking the production of hormone-like substances called prostaglandins. Prostaglandins have many functions in the body including an important role in both the way the body responds to inflammation and also the reabsorption of calcium in some diseases of the bone. Paracetamol belongs to a group of medicines called Analgesics and Antipyretic. It is used for the treatment of mild to moderate pain including headache, migraine, neuralgia (severe pain in nerves), toothache, period pains and the symptomatic relief of sprain, strain and rheumatic pains. They also reduce temperature and used for the symptomatic relief of feverishness, feverish colds and influenza. MAHADOL® is used to relieve pain and reduce redness and swelling (inflammation) in patients
suffering from:
Arthritis of the joints (osteoarthritis). This commonly occurs in patients over the age of 50 and causes the loss of the cartilage and bone tissue next to the joint.
Autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints (rheumatoid arthritis).
Arthritis of the spine which can lead to the fusion of the vertebrae (ankylosing spondylitis).
2. What you need to know before you take MAHADOL®
Do not take MAHADOL®, if
If you are allergic to aceclofenac, paracetamol, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine. If you are allergic to aspirin or any other NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, naproxen or diclofenac).
If you are taking any other medicines that contain Paracetamol.
If you have taken aspirin or any other NSAIDs and experienced one of the following:
Asthma attack causing tightness in the chest wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Runny nose, itching and/or sneezing (irritation of the nose).
Raised red circular patchy rash on the skin which may have felt itchy or like a sting or burn.
A severe allergic reaction known as anaphylactic shock. The symptoms may be life threatening and include difficulty breathing, wheezing, abdominal pain and vomiting.
If you have a history of, suffer from, or suspect that you have a stomach ulcer or have vomited blood or passed blood in your faeces (black tarry stools).
If you have severe kidney disease. If you have established heart disease and /or cerebrovascular disease e.g. if you have had a heart attack, stroke, mini-stroke (TIA) or blockages to blood vessels to the heart or brain or an operation to clear or bypass blockages.
If you have or have had problems with your blood circulation (peripheral arterial disease).
If you suffer from, or suspect that you have severe liver failure.
If you suffer from bleeding or any type of blood clotting disorders.
If you are pregnant (unless your doctor considers it essential for you to continue to take this medicine)
MAHADOL® is not recommended for use in children.
Warnings and precautions
Before you start taking MAHADOL®, tell your doctor:
If you suffer from any other form of kidney or liver disease.
If you have any of the following disorders, as they may worsen:
- Disorders of the stomach or gut/bowel
- Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis)
- Chronic inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease)
- Ulceration, bleeding or perforation of the stomach or bowel If you have, or have ever had problems with the circulation of the blood to your brain.
If you suffer from asthma or any other breathing problems.
If you suffer from a rare inherited disorder known as porphyria.
If you smoke If you have diabetes
If you have angina, blood clots, high blood pressure, raised cholesterol or other raised body fats such as triglycerides
If you suffer from an autoimmune condition known as systemic lupus erythematosus or other connective tissue disorders.
If you are infected with chicken pox, the use of this medicine should be avoided because a rare serious infection of the skin may develop.
If you are recovering from major surgery.
If you are elderly (your doctor will prescribe you the lowest effective dose over the shortest duration).
Hypersensitivity reactions can occur and very rarely, very serious allergic reactions are appearing. The risk is higher in the first month of treatment. MAHADOL® should be stopped immediately at the first onset of symptoms such as tightness of the chest, breathing difficulties, fever, skin rashes, soreness of the skin lining the mouth and other mucous membranes causing ulcers, or any signs of hypersensitivity. Medicines such as MAHADOL® may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack ("myocardial infarction”). Any risk is more likely with high doses and prolonged treatment.
Do not exceed the recommended dose or duration of treatment.
Other medicines and MAHADOL®
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. Please tell your doctor if you are taking:
Medicines used to treat mental health problems like depression (selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine and sertraline) or manic depression (lithium)
Medicines used to treat heart failure and irregular heartbeats (cardiac glycosides such as digoxin)
Medicines used to treat high blood pressure (antihypertensives: ACE inhibitors such as enalopril, lisinopril; angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan, candesartan; also hydralazine, methyldopa, clonidine, moxonidine, propranalol)
Medicines to treat infection (quinolone antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin moxifloxacin)
Drugs used to increase the rate of urine excretion (diuretics such as thiazides, furosemide, amiloride hydrochloride)
Medicines that stop blood clotting (anticoagulants) such as warfarin, heparin
Medicines to control nausea and vomiting e.g. Metoclopramide or domperidone
Medicines to control high lipid levels e.g. Colestyramine
Methotrexate which is used to treat cancer and autoimmune disorders such as arthritis and skin conditions
Chloramphenicol (an antibiotic): paracetamol may increase the levels of chloramphenicol in the blood.
Mifepristone
Any steroids for the treatment of swelling and inflammation (glucocorticoids such as hydrocortisone, prednisolone)
Medicines used to suppress the immune system after organ transplant (ciclosporin or tacrolimus)
Medicines used to treat HIV (zidovudine)
Medicines used to lower blood sugar levels in diabetes (antidiabetics such as glibenclamide, glicazide, tolbutamide)
Any other painkiller NSAID drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, COX-2 inhibitors such as celecoxib and etoricoxib)
Antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel.
MAHADOL® with food and drink
MAHADOL® must be taken preferably with or after food
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. You should inform your doctor if you have problems becoming pregnant. NSAIDs may make it more difficult to become pregnant.
Do not take MAHADOL® if you are pregnant or think you are pregnant. The safety of this medicine for use during pregnancy is not known. It is not recommended for use in pregnancy unless considered essential by your doctor. (it must not be used during the last three months of pregnancy).
MAHADOL® should not be used if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if this medicine passes into breast milk. It is not recommended for use during breast-feeding unless considered essential by your doctor.
Driving and using machines
If you are taking MAHADOL® and you experience dizziness, drowsiness, vertigo, tiredness or any difficulty with your eyesight, you must not drive or use machinery.
3. How to use MAHADOL®
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. You will be prescribed the lowest effective dose over the shortest duration to reduce side effects. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. The recommended dose in adults is 1 tablet twice a day. One tablet should be taken in the morning and one in the evening.
Children
MAHADOL® is not recommended for use in children under the age of 18. Elderly If you are elderly, you are more likely to experience serious side effects. If your doctor prescribes MAHADOL® for you, you will be given the medicine over the shortest duration of treatment.
Method and route of administration:
Tablets should be swallowed whole with a glass of water and should be taken with or after food.
Do not crush or chew the tablets.
Do not exceed the stated daily dose.
Continue to take your tablets for as long as your doctor recommends.
If you use more MAHADOL® than you should
If you accidentally take too many MAHADOL® Tablets, contact your doctor immediately or go to your nearest hospital casualty department. Please take this leaflet or the box the MAHADOL® Tablets came in, with you to the hospital so that they will know what you have taken.
If you forget to use MAHADOL®
If you miss a dose, do not worry, just take the next dose at the usual times. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using MAHADOL®
Do not stop having MAHADOL® until your doctor tells you to. If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Aceclofenac
Stop taking the medicine and seek medical advice IMMEDIATELY, if you experience any of the following side effects,
Severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock). Symptoms may develop quickly and can be life-threatening if not immediately treated and include fever, difficulty breathing, wheezing, abdominal pain, vomiting, swelling of the face and throat.
Severe skin rashes such as Stevens-Johnnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. These are potentially life-threatening and develop quickly forming large blisters and the skin to peel away. The rash can also appear in the mouth, throat or eyes. Fever, headache and aching of the joints usually occur at the same time.
Meningitis. The symptoms include high fever, headache, vomiting, blotchy red rashes, neck stiffness, sensitivity and intolerance to light.
Passing blood in your faeces (stools/motions).
Passing black tarry stools. Vomit any blood or dark particles that look like coffee grounds.
Kidney failure.
Stop taking the medicine and seek medical advice if you experience:
Indigestion or heartburn
Abdominal pain (pains in your stomach) or other abnormal stomach symptoms.
Blood disorders such as reduced production of blood cells, abnormal breakdown of red blood cells known as haemolytic anaemia, low content of iron in the blood, low level of white blood cells, low number of platelet cells, increased blood potassium levels which can irritate the blood vessels causing inflammation known as vasculitis. These disorders can cause you to feel extremely tired, breathless, aching of the joints and be prone to repeated infections and bruising.
If any of the below side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
Dizziness
Nausea (feeling sick)
Diarrhoea
Increased liver enzymes in the blood
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
Wind
Inflammation or irritation of the lining of the stomach
Constipation
Vomiting
Mouth ulcers
Itching
Rash
Inflammation of the skin
Raised circular red itchy, stinging or burning patches on the skin (hives)
Increase in blood urea levels
Increase in blood creatinine levels
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
Hypersensitivity (allergic reaction)
Problems with eyesight
Heart failure
High blood pressure shortness of breath
Bleeding from the stomach or bowel
Stomach or bowel ulceration
Very Rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
Depression
Strange dreams
Inability to sleep
Tingling, pricking or numbness of skin
Uncontrollable shaking
Drowsiness
Headaches
Abnormal taste in the mouth
Sensation of spinning when standing still
Ringing in the ears
Heart pounding or racing hot flushes
Difficulty breathing
High pitched noise when breathing
Inflammation of the mouth
Perforation of either the stomach, large intestine or bowel wall
Worsening of colitis and Crohn’s disease
Inflammation of the pancreas injury of the liver (including hepatitis)
Yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
Spontaneous bleeding into the skin (appears as a rash)
Nephrotic syndrome: a condition which indicates kidney damage and includes large amounts of protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood cholesterol levels and swelling of the legs, feet or ankles
Water retention and swelling
Tiredness
Leg cramps
Increased blood alkaline phosphatase levels
Weight gain
Other side effects that have been reported with this type of drug (NSAIDs) are
Hallucinations
Confusion
Blurred, partial or complete loss of vision
Painful movement of the eye
Worsening of asthma
Skin reaction to sunlight Inflammation of the kidneys
Generally feeling unwell
Serious skin infections may occur in association with chickenpox
Paracetamol
Severe allergic reactions include
Difficulty in breathing
Skin rash and itching
Swelling of the face and throat
Runny nose
Rare cases of serious skin reactions have been reported with symptoms like skin reddening, blisters or rash.
Other possible side effects
If any of the following side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effect not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist:
- Occasionally the blood does not clot well, which may result in easy bruising or bleeding.
- Rarely, a severe reduction in the number of white blood cells, which makes infections more likely.
- Nausea, sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, abdominal pain and swelling, dark colored urine or stools and yellowing of skin and eyes.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store MAHADOL®
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children
Do not store above 30°C.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
MAHADOL®
Each film coated tablet contains:
Aceclofenac IP 100mg
Paracetamol IP 325 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Di Oxide IP.